[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-17940: Structure of immature HTLV-1 CA-NTD from in vitro assembled MA126... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of immature HTLV-1 CA-NTD from in vitro assembled MA126-CANC tubes: axis angle 20 degrees | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, B-factor sharpened map | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Retrovirus / HTLV / immature capsid / CA / CA-NTD / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Human T-cell leukemia virus type I | |||||||||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Obr M / Percipalle M / Chernikova D / Yang H / Thader A / Pinke G / Porley D / Mansky LM / Dick RA / Schur FKM | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, Austria,  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Distinct stabilization of the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 immature Gag lattice. Authors: Martin Obr / Mathias Percipalle / Darya Chernikova / Huixin Yang / Andreas Thader / Gergely Pinke / Dario Porley / Louis M Mansky / Robert A Dick / Florian K M Schur /    Abstract: Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) immature particles differ in morphology from other retroviruses, suggesting a distinct way of assembly. Here we report the results of cryo-electron ...Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) immature particles differ in morphology from other retroviruses, suggesting a distinct way of assembly. Here we report the results of cryo-electron tomography studies of HTLV-1 virus-like particles assembled in vitro, as well as derived from cells. This work shows that HTLV-1 uses a distinct mechanism of Gag-Gag interactions to form the immature viral lattice. Analysis of high-resolution structural information from immature capsid (CA) tubular arrays reveals that the primary stabilizing component in HTLV-1 is the N-terminal domain of CA. Mutagenesis analysis supports this observation. This distinguishes HTLV-1 from other retroviruses, in which the stabilization is provided primarily by the C-terminal domain of CA. These results provide structural details of the quaternary arrangement of Gag for an immature deltaretrovirus and this helps explain why HTLV-1 particles are morphologically distinct. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17940.map.gz emd_17940.map.gz | 51.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17940-v30.xml emd-17940-v30.xml emd-17940.xml emd-17940.xml | 30.4 KB 30.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_17940.png emd_17940.png | 164.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-17940.cif.gz emd-17940.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17940_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17940_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17940_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17940_half_map_2.map.gz | 28.3 MB 28.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17940 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17940 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17940 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17940 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8pufMC  8pu6C  8pu7C  8pu8C  8pu9C  8puaC  8pubC  8pucC  8pudC  8pueC  8pugC  8puhC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17940.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 55.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17940.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 55.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, B-factor sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.327 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, halfmap 2
| File | emd_17940_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, halfmap 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
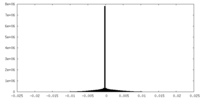
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, halfmap 1
| File | emd_17940_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | HTLV-1 MA126CANC tubes, axis angle 20, halfmap 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
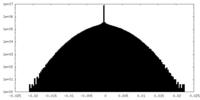
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human T-cell leukemia virus type I
| Entire | Name:  Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Human T-cell leukemia virus type I |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human T-cell leukemia virus type I
| Supramolecule | Name: Human T-cell leukemia virus type I / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 11908 / Sci species name: Human T-cell leukemia virus type I / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: Yes |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Gag protein (Fragment)
| Macromolecule | Name: Gag protein (Fragment) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Human T-cell leukemia virus type I |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.969809 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: PVMHPHGAPP NHRPWQMKDL QAIKQEVSQA APGSPQFMQT IRLAVQQFDP TAKDLQDLLQ YLCSSLVASL HHQQLDSLIS EAETRGITG YNPLAGPLRV QANNPQQQGL RREYQQLWLA AFAALP UniProtKB: Gag protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AMYLAMINE | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Details: Grids coated with 2nm continuous carbon layer. |
- Electron microscopy #1
Electron microscopy #1
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 1 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Average exposure time: 0.3675 sec. / Average electron dose: 3.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 80000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #1~
Electron microscopy #1~
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
|---|---|
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Image recording ID: 2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3708 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3838 pixel / Average exposure time: 1.05 sec. / Average electron dose: 3.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Residue range: 13-125 / Chain - Source name: Other / Chain - Initial model type: other Details: rigid body fit derived from refined model deposited in D_1292131146 |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-8puf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)