+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of HECT E3 UBR5 forming K48 linked Ubiquitin chains | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | DeepEMhancer sharpened Focussed refinement map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | E3 ligase / UBR5 / Ubiquitination / UBQ / Ubiquitin / HECT / K48 / UBQ-chain / polyubiquitylation / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationheterochromatin boundary formation / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / protein branched polyubiquitination / HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / cytoplasm protein quality control / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / symbiont entry into host cell via disruption of host cell glycocalyx / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity ...heterochromatin boundary formation / protein K29-linked ubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / nuclear protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / protein branched polyubiquitination / HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / cytoplasm protein quality control / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / symbiont entry into host cell via disruption of host cell glycocalyx / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / symbiont entry into host cell via disruption of host cell envelope / virus tail / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / ubiquitin binding / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / protein polyubiquitination / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / DNA repair / DNA damage response / positive regulation of gene expression / chromatin / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein-containing complex / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
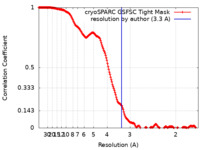
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hehl LA / Prabu JR / Schulman BA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024Title: Structural snapshots along K48-linked ubiquitin chain formation by the HECT E3 UBR5. Authors: Laura A Hehl / Daniel Horn-Ghetko / J Rajan Prabu / Ronnald Vollrath / D Tung Vu / David A Pérez Berrocal / Monique P C Mulder / Gerbrand J van der Heden van Noort / Brenda A Schulman /   Abstract: Ubiquitin (Ub) chain formation by homologous to E6AP C-terminus (HECT)-family E3 ligases regulates vast biology, yet the structural mechanisms remain unknown. We used chemistry and cryo-electron ...Ubiquitin (Ub) chain formation by homologous to E6AP C-terminus (HECT)-family E3 ligases regulates vast biology, yet the structural mechanisms remain unknown. We used chemistry and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to visualize stable mimics of the intermediates along K48-linked Ub chain formation by the human E3, UBR5. The structural data reveal a ≈ 620 kDa UBR5 dimer as the functional unit, comprising a scaffold with flexibly tethered Ub-associated (UBA) domains, and elaborately arranged HECT domains. Chains are forged by a UBA domain capturing an acceptor Ub, with its K48 lured into the active site by numerous interactions between the acceptor Ub, manifold UBR5 elements and the donor Ub. The cryo-EM reconstructions allow defining conserved HECT domain conformations catalyzing Ub transfer from E2 to E3 and from E3. Our data show how a full-length E3, ubiquitins to be adjoined, E2 and intermediary products guide a feed-forward HECT domain conformational cycle establishing a highly efficient, broadly targeting, K48-linked Ub chain forging machine. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16356.map.gz emd_16356.map.gz | 301.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16356-v30.xml emd-16356-v30.xml emd-16356.xml emd-16356.xml | 22.8 KB 22.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16356_fsc.xml emd_16356_fsc.xml | 16.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16356.png emd_16356.png | 58.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16356.cif.gz emd-16356.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16356_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16356_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16356_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16356_half_map_2.map.gz | 475.5 MB 475.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16356 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16356 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16356 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16356 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_16356_validation.pdf.gz emd_16356_validation.pdf.gz | 775.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_16356_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16356_full_validation.pdf.gz | 775.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_16356_validation.xml.gz emd_16356_validation.xml.gz | 26.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_16356_validation.cif.gz emd_16356_validation.cif.gz | 34.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16356 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16356 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16356 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16356 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8c07MC  8c06C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16356.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16356.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | DeepEMhancer sharpened Focussed refinement map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8512 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
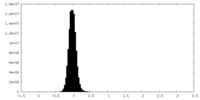
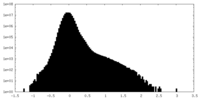
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Focused Local refinement half map
| File | emd_16356_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Focused Local refinement half map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
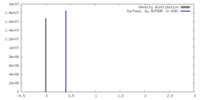
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Focused Local refinement half map
| File | emd_16356_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Focused Local refinement half map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
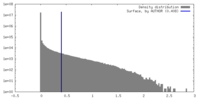
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : HECT E3 UBR5 forming K48 linked Ubiquitin chains
| Entire | Name: HECT E3 UBR5 forming K48 linked Ubiquitin chains |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: HECT E3 UBR5 forming K48 linked Ubiquitin chains
| Supramolecule | Name: HECT E3 UBR5 forming K48 linked Ubiquitin chains / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 620 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: 503 K is mutated to R. 710 L is mutated to D. / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 310.266188 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GSGSGAPMTS IHFVVHPLPG TEDQLNDRLR EVSEKLNKYN LNSHPPLNVL EQATIKQCVV GPNHAAFLLE DGRVCRIGFS VQPDRLELG KPDNNDGSKL NSNSGAGRTS RPGRTSDSPW FLSGSETLGR LAGNTLGSRW SSGVGGSGGG SSGRSSAGAR D SRRQTRVI ...String: GSGSGAPMTS IHFVVHPLPG TEDQLNDRLR EVSEKLNKYN LNSHPPLNVL EQATIKQCVV GPNHAAFLLE DGRVCRIGFS VQPDRLELG KPDNNDGSKL NSNSGAGRTS RPGRTSDSPW FLSGSETLGR LAGNTLGSRW SSGVGGSGGG SSGRSSAGAR D SRRQTRVI RTGRDRGSGL LGSQPQPVIP ASVIPEELIS QAQVVLQGKS RSVIIRELQR TNLDVNLAVN NLLSRDDEDG DD GDDTASE SYLPGEDLMS LLDADIHSAH PSVIIDADAM FSEDISYFGY PSFRRSSLSR LGSSRVLLLP LERDSELLRE RES VLRLRE RRWLDGASFD NERGSTSKEG EPNLDKKNTP VQSPVSLGED LQWWPDKDGT KFICIGALYS ELLAVSSKGE LYQW KWSES EPYRNAQNPS LHHPRATFLG LTNEKIVLLS ANSIRATVAT ENNKVATWVD ETLSSVASKL EHTAQTYSEL QGERI VSLH CCALYTCAQL ENSLYWWGVV PFSQRRKMLE KARAKNKKPK SSAGISSMPN ITVGTQVCLR NNPLYHAGAV AFSISA GIP KVGVLMESVW NMNDSCRFQL RSPESLKNME KASKTTEAKP ESKQEPVKTE MGPPPSPAST CSDASSIASS ASMPYKR RR STPAPKEEEK VNEEQWSLRE VVFVEDVKNV PVGKVLKVDG AYVAVKFPGT SSNTNCQNSS GPDADPSSLL QDCRDLRI D ELQVVKTGGT PKVPDCFQRT PKKLCIPEKT EILAVNVDSK GVHAVLKTGN WVRYCIFDLA TGKAEQENNF PTSSIAFLG QNERNVAIFT AGQESPIILR DGNGTIYPMA KDCMGGIRDP DWLDLPPISS LGMGVHSLIN LPANSTIKKK AAVIIMAVEK QTLMQHILR CDYEACRQYL MNLEQAVVLE QNLQMLQTFI SHRCDGNRNI LHACVSVCFP TSNKETKEEE EAERSERNTF A ERLSAVEA IANAISVVSS NGPGNRAGSS SSRSLRLREM MRRSLRAAGL GRHEAGASSS DHQDPVSPPI APPSWVPDPP AM DPDGDID FILAPAVGSL TTAATGTGQG PSTSTIPGPS TEPSVVESKD RKANAHFILK LLCDSVVLQP YLRELLSAKD ARG MTPFMS AVSGRAYPAA ITILETAQKI AKAEISSSEK EEDVFMGMVC PSGTNPDDSP LYVLCCNDTC SFTWTGAEHI NQDI FECRT CGLLESLCCC TECARVCHKG HDCKLKRTSP TAYCDCWEKC KCKTLIAGQK SARLDLLYRL LTATNLVTLP NSRGE HLLL FLVQTVARQT VEHCQYRPPR IREDRNRKTA SPEDSDMPDH DLEPPRFAQL ALERVLQDWN ALKSMIMFGS QENKDP LSA SSRIGHLLPE EQVYLNQQSG TIRLDCFTHC LIVKCTADIL LLDTLLGTLV KELQNKYTPG RREEAIAVTM RFLRSVA RV FVILSVEMAS SKKKNNFIPQ PIGKCKRVFQ ALLPYAVEEL CNVAESLIVP VRMGIARPTA PFTLASTSID AMQGSEEL F SVEPLPPRPS SDQSSSSSQS QSSYIIRNPQ QRRISQSQPV RGRDEEQDDI VSADVEEVEV VEGVAGEEDH HDEQEEHGE ENAEAEGQHD EHDEDGSDME LDLLAAAETE SDSESNHSNQ DNASGRRSVV TAATAGSEAG ASSVPAFFSE DDSQSNDSSD SDSSSSQSD DIEQETFMLD EPLERTTNSS HANGAAQAPR SMQWAVRNTQ HQRAASTAPS STSTPAASSA GLIYIDPSNL R RSGTISTS AAAAAAALEA SNASSYLTSA SSLARAYSIV IRQISDLMGL IPKYNHLVYS QIPAAVKLTY QDAVNLQNYV EE KLIPTWN WMVSIMDSTE AQLRYGSALA SAGDPGHPNH PLHASQNSAR RERMTAREEA SLRTLEGRRR ATLLSARQGM MSA RGDFLN YALSLMRSHN DEHSDVLPVL DVCSLKHVAY VFQALIYWIK AMNQQTTLDT PQLERKRTRE LLELGIDNED SEHE NDDDT NQSATLNDKD DDSLPAETGQ NHPFFRRSDS MTFLGCIPPN PFEVPLAEAI PLADQPHLLQ PNARKEDLFG RPSQG LYSS SASSGKCLME VTVDRNCLEV LPTKMSYAAN LKNVMNMQNR QKKEGEEQPV LPEETESSKP GPSAHDLAAQ LKSSLL AEI GLTESEGPPL TSFRPQCSFM GMVISHDMLL GRWRLSLELF GRVFMEDVGA EPGSILTELG GFEVKESKFR REMEKLR NQ QSRDLSLEVD RDRDLLIQQT MRQLNNHFGR RCATTPMAVH RVKVTFKDEP GEGSGVARSF YTAIAQAFLS NEKLPNLE C IQNANKGTHT SLMQRLRNRG ERDRERERER EMRRSSGLRA GSRRDRDRDF RRQLSIDTRP FRPASEGNPS DDPEPLPAH RQALGERLYP RVQAMQPAFA SKITGMLLEL SPAQLLLLLA SEDSLRARVD EAMELIIAHG RENGADSILD LGLVDSSEKV QQENRKRHG SSRSVVDMDL DDTDDGDDNA PLFYQPGKRG FYTPRPGKNT EARLNCFRNI GRILGLCLLQ NELCPITLNR H VIKVLLGR KVNWHDFAFF DPVMYESLRQ LILASQSSDA DAVFSAMDLA FAIDLCKEEG GGQVELIPNG VNIPVTPQNV YE YVRKYAE HRMLVVAEQP LHAMRKGLLD VLPKNSLEDL TAEDFRLLVN GCGEVNVQML ISFTSFNDES GENAEKLLQF KRW FWSIVE KMSMTERQDL VYFWTSSPSL PASEEGFQPM PSITIRPPDD QHLPTANTCI SRLYVPLYSS KQILKQKLLL AIKT KNFGF V UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 |
-Macromolecule #2: Polyubiquitin-B
| Macromolecule | Name: Polyubiquitin-B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: 48 LYS is mutated to CYS in the sequence / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.550794 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQIFVKTLTG KTITLEVEPS DTIENVKAKI QDKEGIPPDQ QRLIFAGCQL EDGRTLSDYN IQKESTLHLV LRLRGG UniProtKB: Tail fiber |
-Macromolecule #3: Polyubiquitin-B
| Macromolecule | Name: Polyubiquitin-B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.576831 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQIFVKTLTG KTITLEVEPS DTIENVKAKI QDKEGIPPDQ QRLIFAGKQL EDGRTLSDYN IQKESTLHLV LRLRGG UniProtKB: Tail fiber |
-Macromolecule #4: 5-azanylpentan-2-one
| Macromolecule | Name: 5-azanylpentan-2-one / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: SY8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 101.147 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-SY8: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 69.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)