+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Nucleosome-bound Ino80 ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | main map | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | chromatin remodeler / INO80 / Actin-related protein / DNA binding protein | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIno80 complex / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere ...Ino80 complex / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / gene expression / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / chromatin remodeling / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) / Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) /  Homo sapiens (human) / DNA molecule (others) Homo sapiens (human) / DNA molecule (others) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.45 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kunert F / Metzner FJ / Eustermann S / Jung J / Woike S / Schall K / Kostrewa D / Hopfner KP | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Germany, 5 items Germany, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022Title: Structural mechanism of extranucleosomal DNA readout by the INO80 complex. Authors: Franziska Kunert / Felix J Metzner / James Jung / Markus Höpfler / Stephan Woike / Kevin Schall / Dirk Kostrewa / Manuela Moldt / Jia-Xuan Chen / Susanne Bantele / Boris Pfander / Sebastian ...Authors: Franziska Kunert / Felix J Metzner / James Jung / Markus Höpfler / Stephan Woike / Kevin Schall / Dirk Kostrewa / Manuela Moldt / Jia-Xuan Chen / Susanne Bantele / Boris Pfander / Sebastian Eustermann / Karl-Peter Hopfner /  Abstract: The nucleosomal landscape of chromatin depends on the concerted action of chromatin remodelers. The INO80 remodeler specifically places nucleosomes at the boundary of gene regulatory elements, which ...The nucleosomal landscape of chromatin depends on the concerted action of chromatin remodelers. The INO80 remodeler specifically places nucleosomes at the boundary of gene regulatory elements, which is proposed to be the result of an ATP-dependent nucleosome sliding activity that is regulated by extranucleosomal DNA features. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy and functional assays to reveal how INO80 binds and is regulated by extranucleosomal DNA. Structures of the regulatory A-module bound to DNA clarify the mechanism of linker DNA binding. The A-module is connected to the motor unit via an HSA/post-HSA lever element to chemomechanically couple the motor and linker DNA sensing. Two notable sites of curved DNA recognition by coordinated action of the four actin/actin-related proteins and the motor suggest how sliding by INO80 can be regulated by extranucleosomal DNA features. Last, the structures clarify the recruitment of YY1/Ies4 subunits and reveal deep architectural similarities between the regulatory modules of INO80 and SWI/SNF complexes. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15647.map.gz emd_15647.map.gz | 6.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15647-v30.xml emd-15647-v30.xml emd-15647.xml emd-15647.xml | 25.4 KB 25.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_15647.png emd_15647.png | 58.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-15647.cif.gz emd-15647.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_15647_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15647_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15647_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15647_half_map_2.map.gz | 65.2 MB 65.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15647 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15647 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15647 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15647 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8atfMC  8a5aC  8a5dC  8a5oC  8a5pC  8a5qC  8av6C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15647.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15647.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | main map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.059 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
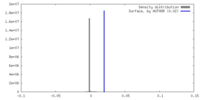
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half map B
| File | emd_15647_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map B | ||||||||||||
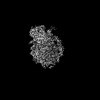
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
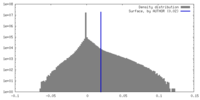
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map A
| File | emd_15647_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Chaetomium thermophilum INO80 A-Module (Arp4-Ies4-N-actin-Arp8-In...
+Supramolecule #1: Chaetomium thermophilum INO80 A-Module (Arp4-Ies4-N-actin-Arp8-In...
+Macromolecule #1: Ino80 ATPase
+Macromolecule #2: PAPA-1 domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #5: Histone H3.2
+Macromolecule #6: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #7: Histone H2A
+Macromolecule #8: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
+Macromolecule #3: DNA (227-MER)
+Macromolecule #4: DNA (226-MER)
+Macromolecule #9: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 44.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.1 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.45 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 137900 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



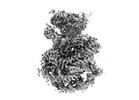





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






























 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)

