+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1559 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
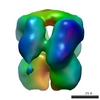
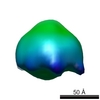
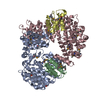
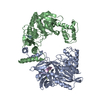
| Title | 3D structure of human endoglin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | structure of human endoglin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Endoglin / CD105 / TGF-beta / HHT disorder / zona pellucida / preeclampsia | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Zona pellucida domain / regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 25.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Llorca O / Trujillo A / Blanco FJ / Bernabeu C | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2007 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2007Title: Structural model of human endoglin, a transmembrane receptor responsible for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Authors: Oscar Llorca / Arturo Trujillo / Francisco J Blanco / Carmelo Bernabeu /  Abstract: Endoglin is a type I membrane protein expressed as a disulphide-linked homodimer on human vascular endothelial cells whose haploinsufficiency is responsible for the dominant vascular dysplasia known ...Endoglin is a type I membrane protein expressed as a disulphide-linked homodimer on human vascular endothelial cells whose haploinsufficiency is responsible for the dominant vascular dysplasia known as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Structurally, endoglin belongs to the zona pellucida (ZP) family of proteins that share a ZP domain of approximately 260 amino acid residues at their extracellular region. Endoglin is a component of the TGF-beta receptor complex, interacts with the TGF-beta signalling receptors types I and II, and modulates cellular responses to TGF-beta. Here, we have determined for the first time the three-dimensional structure of the approximately 140 kDa extracellular domain of endoglin at 25 A resolution, using single-particle electron microscopy (EM). This reconstruction provides the general architecture of endoglin, which arranges as a dome made of antiparallel oriented monomers enclosing a cavity at one end. A high-resolution structure of endoglin has also been modelled de novo and found to be consistent with the experimental reconstruction. Each subunit comprises three well-defined domains, two of them corresponding to ZP regions, organised into an open U-shaped monomer. This domain arrangement was found to closely resemble the overall structure derived experimentally and the three modelled de novo domains were tentatively assigned to the domains observed in the EM reconstruction. This molecular model was further tested by tagging endoglin's C terminus with an IgG Fc fragment visible after 3D reconstruction of the labelled protein. Combined, these data provide the structural framework to interpret endoglin's functional domains and mutations found in HHT patients. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1559.map.gz emd_1559.map.gz | 345.7 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1559-v30.xml emd-1559-v30.xml emd-1559.xml emd-1559.xml | 8.9 KB 8.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1559.gif 1559.gif | 55.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1559 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1559 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1559 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1559 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1559.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1559.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | structure of human endoglin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Extracellular region of human endoglin, from Glu26 to Leu587 residues.
| Entire | Name: Extracellular region of human endoglin, from Glu26 to Leu587 residues. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Extracellular region of human endoglin, from Glu26 to Leu587 residues.
| Supramolecule | Name: Extracellular region of human endoglin, from Glu26 to Leu587 residues. type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: One disulphide-linked homodimer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 130 KDa / Theoretical: 140 KDa / Method: SDS-PAGE |
-Macromolecule #1: Transmembrane receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Transmembrane receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Endoglin / Number of copies: 2 / Oligomeric state: Homodimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: Plasma membrane Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: Plasma membrane |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 130 KDa / Theoretical: 140 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Mouse myeloma cell line NS0 |
| Sequence | GO: regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway InterPro: Zona pellucida domain |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 / Details: 150mM NaCl, 50mM Na2HPO4, 10% glycerol |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: EndoEC was applied to carbon-coated grids and negatively stained with 1% w/v uranyl acetate. |
| Grid | Details: 40 mesh Copper/Palladium grid. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 1230 |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Correction with FFT and CCD camera |
| Details | Microscope used JEOL-1230 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 10.5 µm Details: Images scanned with a MINOLTA Dimage Scan Multi Pro scanner at 2400 dpi Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 100 kV / Electron source: TUNGSTEN HAIRPIN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.9 mm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 25.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: EMAN / Number images used: 2964 |
|---|---|
| Final two d classification | Number classes: 16 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















