+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Composite structure of dynein-dynactin-BICDR on microtubules | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite structure of the dynein-dynactin-BICDR1 complex | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dynein / dynactin / cargo transport / activating adaptor / cytoskeleton / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGolgi to secretory granule transport / : / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Adherens junctions interactions / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs ...Golgi to secretory granule transport / : / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Adherens junctions interactions / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / MAP2K and MAPK activation / UCH proteinases / Gap junction degradation / Formation of annular gap junctions / RHOF GTPase cycle / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / dynactin complex / centriolar subdistal appendage / positive regulation of neuromuscular junction development / centriole-centriole cohesion / visual behavior / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / transport along microtubule / F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / microtubule anchoring at centrosome / dynein light chain binding / ventral spinal cord development / dynein heavy chain binding / retromer complex / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / microtubule plus-end / Intraflagellar transport / nuclear membrane disassembly / cellular response to cytochalasin B / positive regulation of intracellular transport / positive regulation of microtubule nucleation / regulation of transepithelial transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of spindle assembly / barbed-end actin filament capping / melanosome transport / protein localization to adherens junction / establishment of spindle localization / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Neutrophil degranulation / coronary vasculature development / non-motile cilium assembly / regulation of cell morphogenesis / dynein complex / retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / P-body assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / microtubule motor activity / MHC class II antigen presentation / tight junction / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / microtubule associated complex / centrosome localization / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / ventricular septum development / aorta development / microtubule-based movement / nuclear migration / apical junction complex / neuromuscular process / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / neuromuscular junction development / ciliary tip / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / cortical cytoskeleton / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / cell leading edge / motor behavior / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / cleavage furrow / dynactin binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 20.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chaaban S / Carter AP | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, 3 items United Kingdom, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structure of dynein-dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding. Authors: Sami Chaaban / Andrew P Carter /  Abstract: Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule motor that is activated by its cofactor dynactin and a coiled-coil cargo adaptor. Up to two dynein dimers can be recruited per dynactin, and interactions between ...Cytoplasmic dynein is a microtubule motor that is activated by its cofactor dynactin and a coiled-coil cargo adaptor. Up to two dynein dimers can be recruited per dynactin, and interactions between them affect their combined motile behaviour. Different coiled-coil adaptors are linked to different cargos, and some share motifs known to contact sites on dynein and dynactin. There is limited structural information on how the resulting complex interacts with microtubules and how adaptors are recruited. Here we develop a cryo-electron microscopy processing pipeline to solve the high-resolution structure of dynein-dynactin and the adaptor BICDR1 bound to microtubules. This reveals the asymmetric interactions between neighbouring dynein motor domains and how they relate to motile behaviour. We found that two adaptors occupy the complex. Both adaptors make similar interactions with the dyneins but diverge in their contacts with each other and dynactin. Our structure has implications for the stability and stoichiometry of motor recruitment by cargos. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14549.map.gz emd_14549.map.gz | 201.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14549-v30.xml emd-14549-v30.xml emd-14549.xml emd-14549.xml | 44.7 KB 44.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_14549.png emd_14549.png | 61.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14549.cif.gz emd-14549.cif.gz | 14.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14549 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14549 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14549 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14549 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 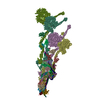 7z8fMC  7z8gC  7z8hC 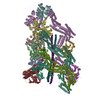 7z8iC  7z8jC  7z8kC  7z8lC  7z8mC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14549.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14549.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite structure of the dynein-dynactin-BICDR1 complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.489 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
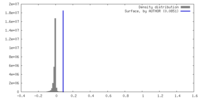
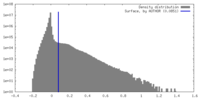
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Complex of dynein, dynactin, and BICDR1 bound to microtubules
+Supramolecule #1: Complex of dynein, dynactin, and BICDR1 bound to microtubules
+Supramolecule #2: Dynein, cytoplasmic 1
+Supramolecule #3: Dynactin
+Supramolecule #4: BICDR1
+Macromolecule #1: ARP1 actin related protein 1 homolog A
+Macromolecule #2: Actin, cytoplasmic 1
+Macromolecule #3: Arp11
+Macromolecule #4: Capping protein (Actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 1
+Macromolecule #5: F-actin capping protein beta subunit
+Macromolecule #6: Dynactin subunit 2
+Macromolecule #7: Dynactin subunit 3
+Macromolecule #8: Dynactin subunit 1
+Macromolecule #9: Dynactin 6
+Macromolecule #10: Dynactin subunit 5
+Macromolecule #11: BICD family-like cargo adapter 1
+Macromolecule #12: Dynactin subunit 4
+Macromolecule #13: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1
+Macromolecule #14: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2
+Macromolecule #15: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 light intermediate chain 2
+Macromolecule #16: Dynein light chain roadblock-type 1
+Macromolecule #17: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #18: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #19: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #20: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #21: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 20 second incubation. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 14 / Number real images: 88715 / Average exposure time: 3.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 53.0 e/Å2 Details: Images were collected in movie-mode and fractionated into 53 movie frames |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 20.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: RELION Details: This is a composite of multiple maps with resolutions ranging from 3.3-12.2 A, resampled on a grid of 2.5 A/pix Number images used: 628033 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7z8f: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)