[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-13640: Structure of MCM2-7 DH complexed with Cdc7-Dbf4 in the presence o... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of MCM2-7 DH complexed with Cdc7-Dbf4 in the presence of ATPgS, state II (3D auto-refined map) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Helicase / Activation / Kinase / Phosphorylation / REPLICATION | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / positive regulation of DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of kinetochore assembly / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation / negative regulation of exit from mitosis / Dbf4-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / positive regulation of meiosis I / positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication ...positive regulation of spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / positive regulation of DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of kinetochore assembly / positive regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation / negative regulation of exit from mitosis / Dbf4-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / positive regulation of meiosis I / positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / regulation of cell cycle phase transition / MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / MCM complex binding / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / nuclear DNA replication / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / mitotic DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / CMG complex / nuclear pre-replicative complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / DNA replication preinitiation complex / protein-containing complex localization / MCM complex / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / nuclear replication fork / DNA replication origin binding / chromosome, centromeric region / DNA replication initiation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA helicase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / chromosome segregation / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / heterochromatin formation / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA helicase / chromosome, telomeric region / DNA replication / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / centrosome / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / chromatin / signal transduction / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
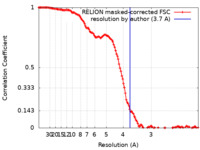
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Saleh A / Noguchi Y / Aramayo R / Ivanova ME / Speck C | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4 items United Kingdom, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: The structural basis of Cdc7-Dbf4 kinase dependent targeting and phosphorylation of the MCM2-7 double hexamer. Authors: Almutasem Saleh / Yasunori Noguchi / Ricardo Aramayo / Marina E Ivanova / Kathryn M Stevens / Alex Montoya / S Sunidhi / Nicolas Lopez Carranza / Marcin J Skwark / Christian Speck /  Abstract: The controlled assembly of replication forks is critical for genome stability. The Dbf4-dependent Cdc7 kinase (DDK) initiates replisome assembly by phosphorylating the MCM2-7 replicative helicase at ...The controlled assembly of replication forks is critical for genome stability. The Dbf4-dependent Cdc7 kinase (DDK) initiates replisome assembly by phosphorylating the MCM2-7 replicative helicase at the N-terminal tails of Mcm2, Mcm4 and Mcm6. At present, it remains poorly understood how DDK docks onto the helicase and how the kinase targets distal Mcm subunits for phosphorylation. Using cryo-electron microscopy and biochemical analysis we discovered that an interaction between the HBRCT domain of Dbf4 with Mcm2 serves as an anchoring point, which supports binding of DDK across the MCM2-7 double-hexamer interface and phosphorylation of Mcm4 on the opposite hexamer. Moreover, a rotation of DDK along its anchoring point allows phosphorylation of Mcm2 and Mcm6. In summary, our work provides fundamental insights into DDK structure, control and selective activation of the MCM2-7 helicase during DNA replication. Importantly, these insights can be exploited for development of novel DDK inhibitors. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13640.map.gz emd_13640.map.gz | 140.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13640-v30.xml emd-13640-v30.xml emd-13640.xml emd-13640.xml | 29.8 KB 29.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13640_fsc.xml emd_13640_fsc.xml | 12.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
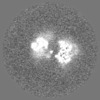
| Images |  emd_13640.png emd_13640.png | 53.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13640_msk_1.map emd_13640_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13640.cif.gz emd-13640.cif.gz | 9.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13640_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13640_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13640_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13640_half_map_2.map.gz | 140.7 MB 140.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13640 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13640 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13640 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13640 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13640_validation.pdf.gz emd_13640_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13640_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13640_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13640_validation.xml.gz emd_13640_validation.xml.gz | 20.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13640_validation.cif.gz emd_13640_validation.cif.gz | 26.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13640 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13640 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13640 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13640 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7pt6C  7pt7C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13640.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13640.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
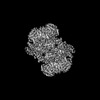
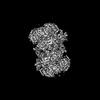
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
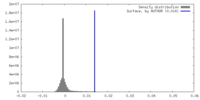
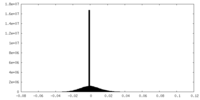
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13640_msk_1.map emd_13640_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
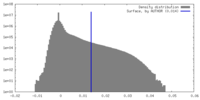
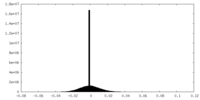
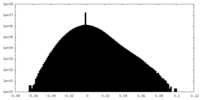
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 1 of C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II
| File | emd_13640_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 1 of C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 2 of C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II
| File | emd_13640_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 2 of C1 3D auto-refinement of MD-(ATPgS)state II | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : MCM2-7 double hexamer bound to one copy of Cdc7-Dbf4 and one copy...
| Entire | Name: MCM2-7 double hexamer bound to one copy of Cdc7-Dbf4 and one copy of the Dbf4 HBRCT domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: MCM2-7 double hexamer bound to one copy of Cdc7-Dbf4 and one copy...
| Supramolecule | Name: MCM2-7 double hexamer bound to one copy of Cdc7-Dbf4 and one copy of the Dbf4 HBRCT domain type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA replication licensing factor MCM2
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSDNRRRRRE EDDSDSENEL PPSSPQQHFR GGMNPVSSPI GSPDMINPEG DDNEVDDVPD IDEVEEQMNE VDLMDDNMYE DYAADHNRD RYDPDQVDDR EQQELSLSER RRIDAQLNER DRLLRNVAYI DDEDEEQEGA AQLDEMGLPV QRRRRRRQYE D LENSDDDL ...String: MSDNRRRRRE EDDSDSENEL PPSSPQQHFR GGMNPVSSPI GSPDMINPEG DDNEVDDVPD IDEVEEQMNE VDLMDDNMYE DYAADHNRD RYDPDQVDDR EQQELSLSER RRIDAQLNER DRLLRNVAYI DDEDEEQEGA AQLDEMGLPV QRRRRRRQYE D LENSDDDL LSDMDIDPLR EELTLESLSN VKANSYSEWI TQPNVSRTIA RELKSFLLEY TDETGRSVYG ARIRTLGEMN SE SLEVNYR HLAESKAILA LFLAKCPEEM LKIFDLVAME ATELHYPDYA RIHSEIHVRI SDFPTIYSLR ELRESNLSSL VRV TGVVTR RTGVFPQLKY VKFNCLKCGS ILGPFFQDSN EEIRISFCTN CKSKGPFRVN GEKTVYRNYQ RVTLQEAPGT VPPG RLPRH REVILLADLV DVSKPGEEVE VTGIYKNNYD GNLNAKNGFP VFATIIEANS IKRREGNTAN EGEEGLDVFS WTEEE EREF RKISRDRGII DKIISSMAPS IYGHRDIKTA VACSLFGGVP KNVNGKHSIR GDINVLLLGD PGTAKSQILK YVEKTA HRA VFATGQGASA VGLTASVRKD PITKEWTLEG GALVLADKGV CLIDEFDKMN DQDRTSIHEA MEQQSISISK AGIVTTL QA RCSIIAAANP NGGRYNSTLP LAQNVSLTEP ILSRFDILCV VRDLVDEEAD ERLATFVVDS HVRSHPENDE DREGEELK N NGESAIEQGE DEINEQLNAR QRRLQRQRKK EEEISPIPQE LLMKYIHYAR TKIYPKLHQM DMDKVSRVYA DLRRESIST GSFPITVRHL ESILRIAESF AKMRLSEFVS SYDLDRAIKV VVDSFVDAQK VSVRRQLRRS FAIYTLGH UniProtKB: DNA replication licensing factor MCM2 |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA replication licensing factor MCM3
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEGSTGFDGD ATTFFAPDAV FGDRVRRFQE FLDTFTSYRD SVRSIQVYNS NNAANYNDDQ DDADERDLLG DDDGDDLEKE KKAASSTSL NILPHRIIIS LDDLREFDRS FWSGILVEPA YFIPPAEKAL TDLADSMDDV PHPNASAVSS RHPWKLSFKG S FGAHALSP ...String: MEGSTGFDGD ATTFFAPDAV FGDRVRRFQE FLDTFTSYRD SVRSIQVYNS NNAANYNDDQ DDADERDLLG DDDGDDLEKE KKAASSTSL NILPHRIIIS LDDLREFDRS FWSGILVEPA YFIPPAEKAL TDLADSMDDV PHPNASAVSS RHPWKLSFKG S FGAHALSP RTLTAQHLNK LVSVEGIVTK TSLVRPKLIR SVHYAAKTGR FHYRDYTDAT TTLTTRIPTP AIYPTEDTEG NK LTTEYGY STFIDHQRIT VQEMPEMAPA GQLPRSIDVI LDDDLVDKTK PGDRVNVVGV FKSLGAGGMN QSNSNTLIGF KTL ILGNTV YPLHARSTGV AARQMLTDFD IRNINKLSKK KDIFDILSQS LAPSIYGHDH IKKAILLMLM GGVEKNLENG SHLR GDINI LMVGDPSTAK SQLLRFVLNT ASLAIATTGR GSSGVGLTAA VTTDRETGER RLEAGAMVLA DRGVVCIDEF DKMTD VDRV AIHEVMEQQT VTIAKAGIHT TLNARCSVIA AANPVFGQYD VNRDPHQNIA LPDSLLSRFD LLFVVTDDIN EIRDRS ISE HVLRTHRYLP PGYLEGEPVR ERLNLSLAVG EDADINPEEH SNSGAGVENE GEDDEDHVFE KFNPLLQAGA KLAKNKG NY NGTEIPKLVT IPFLRKYVQY AKERVIPQLT QEAINVIVKN YTDLRNDDNT KKSPITARTL ETLIRLATAH AKVRLSKT V NKVDAKVAAN LLRFALLGED IGNDIDEEES EYEEALSKRS PQKSPKKRQR VRQPASNSGS PIKSTPRRST ASSVNATPS SARRILRFQD DEQNAGEDDN DIMSPLPADE EAELQRRLQL GLRVSPRRRE HLHAPEEGSS GPLTEVGTPR LPNVSSAGQD DEQQQSVIS FDNVEPGTIS TGRLSLISGI IARLMQTEIF EEESYPVASL FERINEELPE EEKFSAQEYL AGLKIMSDRN N LMVADDKV WRV UniProtKB: DNA replication licensing factor MCM3 |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA replication licensing factor MCM4
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSQQSSSPTK EDNNSSSPVV PNPDSVPPQL SSPALFYSSS SSQGDIYGRN NSQNLSQGEG NIRAAIGSSP LNFPSSSQRQ NSDVFQSQG RQGRIRSSAS ASGRSRYHSD LRSDRALPTS SSSLGRNGQN RVHMRRNDIH TSDLSSPRRI VDFDTRSGVN T LDTSSSSA ...String: MSQQSSSPTK EDNNSSSPVV PNPDSVPPQL SSPALFYSSS SSQGDIYGRN NSQNLSQGEG NIRAAIGSSP LNFPSSSQRQ NSDVFQSQG RQGRIRSSAS ASGRSRYHSD LRSDRALPTS SSSLGRNGQN RVHMRRNDIH TSDLSSPRRI VDFDTRSGVN T LDTSSSSA PPSEASEPLR IIWGTNVSIQ ECTTNFRNFL MSFKYKFRKI LDEREEFINN TTDEELYYIK QLNEMRELGT SN LNLDARN LLAYKQTEDL YHQLLNYPQE VISIMDQTIK DCMVSLIVDN NLDYDLDEIE TKFYKVRPYN VGSCKGMREL NPN DIDKLI NLKGLVLRST PVIPDMKVAF FKCNVCDHTM AVEIDRGVIQ EPARCERIDC NEPNSMSLIH NRCSFADKQV IKLQ ETPDF VPDGQTPHSI SLCVYDELVD SCRAGDRIEV TGTFRSIPIR ANSRQRVLKS LYKTYVDVVH VKKVSDKRLD VDTST IEQE LMQNKVDHNE VEEVRQITDQ DLAKIREVAA REDLYSLLAR SIAPSIYELE DVKKGILLQL FGGTNKTFTK GGRYRG DIN ILLCGDPSTS KSQILQYVHK ITPRGVYTSG KGSSAVGLTA YITRDVDTKQ LVLESGALVL SDGGVCCIDE FDKMSDS TR SVLHEVMEQQ TISIAKAGII TTLNARSSIL ASANPIGSRY NPNLPVTENI DLPPPLLSRF DLVYLVLDKV DEKNDREL A KHLTNLYLED KPEHISQDDV LPVEFLTMYI SYAKEHIHPI ITEAAKTELV RAYVGMRKMG DDSRSDEKRI TATTRQLES MIRLAEAHAK MKLKNVVELE DVQEAVRLIR SAIKDYATDP KTGKIDMNLV QTGKSVIQRK LQEDLSREIM NVLKDQASDS MSFNELIKQ INEHSQDRVE SSDIQEALSR LQQEDKVIVL GEGVRRSVRL NNRV UniProtKB: DNA replication licensing factor MCM4 |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA replication licensing factor MCM5
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSFDRPEIYS APVLQGESPN DDDNTEIIKS FKNFILEFRL DSQFIYRDQL RNNILVKNYS LTVNMEHLIG YNEDIYKKLS DEPSDIIPL FETAITQVAK RISILSRAQS ANNNDKDPEN TSMDTDSLLL NSLPTFQLIL NSNANQIPLR DLDSEHVSKI V RLSGIIIS ...String: MSFDRPEIYS APVLQGESPN DDDNTEIIKS FKNFILEFRL DSQFIYRDQL RNNILVKNYS LTVNMEHLIG YNEDIYKKLS DEPSDIIPL FETAITQVAK RISILSRAQS ANNNDKDPEN TSMDTDSLLL NSLPTFQLIL NSNANQIPLR DLDSEHVSKI V RLSGIIIS TSVLSSRATY LSIMCRNCRH TTSITINNFN SITGNTVSLP RSCLSTIESE SSMANESNIG DESTKKNCGP DP YIIIHES SKFIDQQFLK LQEIPELVPV GEMPRNLTMT CDRYLTNKVI PGTRVTIVGI YSIYNSKNGA GSGRSGGGNG GSG VAIRTP YIKILGIQSD VETSSIWNSV TMFTEEEEEE FLQLSRNPKL YEILTNSIAP SIFGNEDIKK AIVCLLMGGS KKIL PDGMR LRGDINVLLL GDPGTAKSQL LKFVEKVSPI AVYTSGKGSS AAGLTASVQR DPMTREFYLE GGAMVLADGG VVCID EFDK MRDEDRVAIH EAMEQQTISI AKAGITTVLN SRTSVLAAAN PIYGRYDDLK SPGDNIDFQT TILSRFDMIF IVKDDH NEE RDISIANHVI NIHTGNANAM QNQQEENGSE ISIEKMKRYI TYCRLKCAPR LSPQAAEKLS SNFVTIRKQL LINELES TE RSSIPITIRQ LEAIIRITES LAKLELSPIA QERHVDEAIR LFQASTMDAA SQDPIGGLNQ ASGTSLSEIR RFEQELKR R LPIGWSTSYQ TLRREFVDTH RFSQLALDKA LYALEKHETI QLRHQGQNIY RSGV UniProtKB: Minichromosome maintenance protein 5 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA replication licensing factor MCM6
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSSPFPADTP SSNRPSNSSP PPSSIGAGFG SSSGLDSQIG SRLHFPSSSQ PHVSNSQTGP FVNDSTQFSS QRLQTDGSAT NDMEGNEPA RSFKSRALNH VKKVDDVTGE KVREAFEQFL EDFSVQSTDT GEVEKVYRAQ IEFMKIYDLN TIYIDYQHLS M RENGALAM ...String: MSSPFPADTP SSNRPSNSSP PPSSIGAGFG SSSGLDSQIG SRLHFPSSSQ PHVSNSQTGP FVNDSTQFSS QRLQTDGSAT NDMEGNEPA RSFKSRALNH VKKVDDVTGE KVREAFEQFL EDFSVQSTDT GEVEKVYRAQ IEFMKIYDLN TIYIDYQHLS M RENGALAM AISEQYYRFL PFLQKGLRRV VRKYAPELLN TSDSLKRSEG DEGQADEDEQ QDDDMNGSSL PRDSGSSAAP GN GTSAMAT RSITTSTSPE QTERVFQISF FNLPTVHRIR DIRSEKIGSL LSISGTVTRT SEVRPELYKA SFTCDMCRAI VDN VEQSFK YTEPTFCPNP SCENRAFWTL NVTRSRFLDW QKVRIQENAN EIPTGSMPRT LDVILRGDSV ERAKPGDRCK FTGV EIVVP DVTQLGLPGV KPSSTLDTRG ISKTTEGLNS GVTGLRSLGV RDLTYKISFL ACHVISIGSN IGASSPDANS NNRET ELQM AANLQANNVY QDNERDQEVF LNSLSSDEIN ELKEMVKDEH IYDKLVRSIA PAVFGHEAVK KGILLQMLGG VHKSTV EGI KLRGDINICV VGDPSTSKSQ FLKYVVGFAP RSVYTSGKAS SAAGLTAAVV RDEEGGDYTI EAGALMLADN GICCIDE FD KMDISDQVAI HEAMEQQTIS IAKAGIHATL NARTSILAAA NPVGGRYNRK LSLRGNLNMT APIMSRFDLF FVILDDCN E KIDTELASHI VDLHMKRDEA IEPPFSAEQL RRYIKYARTF KPILTKEARS YLVEKYKELR KDDAQGFSRS SYRITVRQL ESMIRLSEAI ARANCVDEIT PSFIAEAYDL LRQSIIRVDV DDVEMDEEFD NIESQSHAAS GNNDDNDDGT GSGVITSEPP ADIEEGQSE ATARPGTSEK KKTTVTYDKY VSMMNMIVRK IAEVDREGAE ELTAVDIVDW YLLQKENDLG SLAEYWEERR L AFKVIKRL VKDRILMEIH GTRHNLRDLE NEENENNKTV YVIHPNCEVL DQLEPQDSS UniProtKB: DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA replication licensing factor MCM7
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSAALPSIQL PVDYNNLFNE ITDFLVTFKQ DTLSSDATRN ENEDENLDAE NIEQHLLEKG PKYMAMLQKV ANRELNSVII DLDDILQYQ NEKFLQGTQA DDLVSAIQQN ANHFTELFCR AIDNNMPLPT KEIDYKDDVL DVILNQRRLR NERMLSDRTN E IRSENLMD ...String: MSAALPSIQL PVDYNNLFNE ITDFLVTFKQ DTLSSDATRN ENEDENLDAE NIEQHLLEKG PKYMAMLQKV ANRELNSVII DLDDILQYQ NEKFLQGTQA DDLVSAIQQN ANHFTELFCR AIDNNMPLPT KEIDYKDDVL DVILNQRRLR NERMLSDRTN E IRSENLMD TTMDPPSSMN DALREVVEDE TELFPPNLTR RYFLYFKPLS QNCARRYRKK AISSKPLSVR QIKGDFLGQL IT VRGIITR VSDVKPAVEV IAYTCDQCGY EVFQEVNSRT FTPLSECTSE ECSQNQTKGQ LFMSTRASKF SAFQECKIQE LSQ QVPVGH IPRSLNIHVN GTLVRSLSPG DIVDVTGIFL PAPYTGFKAL KAGLLTETYL EAQFVRQHKK KFASFSLTSD VEER VMELI TSGDVYNRLA KSIAPEIYGN LDVKKALLLL LVGGVDKRVG DGMKIRGDIN VCLMGDPGVA KSQLLKAICK ISPRG VYTT GKGSSGVGLT AAVMKDPVTD EMILEGGALV LADNGICCID EFDKMDESDR TAIHEVMEQQ TISISKAGIN TTLNAR TSI LAAANPLYGR YNPRLSPLDN INLPAALLSR FDILFLMLDI PSRDDDEKLA EHVTYVHMHN KQPDLDFTPV EPSKMRE YI AYAKTKRPVM SEAVNDYVVQ AYIRLRQDSK REMDSKFSFG QATPRTLLGI IRLSQALAKL RLADMVDIDD VEEALRLV R VSKESLYQET NKSKEDESPT TKIFTIIKKM LQETGKNTLS YENIVKTVRL RGFTMLQLSN CIQEYSYLNV WHLINEGNT LKFVDDGTMD TDQEDSLVST PKLAPQTTAS ANVSAQDSDI DLQDA UniProtKB: DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 |
-Macromolecule #7: Cell division control protein 7
| Macromolecule | Name: Cell division control protein 7 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MTSKTKNIDD IPPEIKEEMI QLYHDLPGIE NEYKLIDKIG EGTFSSVYKA KDITGKITKK FASHFWNYGS NYVALKKIYV TSSPQRIYN ELNLLYIMTG SSRVAPLCDA KRVRDQVIAV LPYYPHEEFR TFYRDLPIKG IKKYIWELLR ALKFVHSKGI I HRDIKPTN ...String: MTSKTKNIDD IPPEIKEEMI QLYHDLPGIE NEYKLIDKIG EGTFSSVYKA KDITGKITKK FASHFWNYGS NYVALKKIYV TSSPQRIYN ELNLLYIMTG SSRVAPLCDA KRVRDQVIAV LPYYPHEEFR TFYRDLPIKG IKKYIWELLR ALKFVHSKGI I HRDIKPTN FLFNLELGRG VLVDFGLAEA QMDYKSMISS QNDYDNYANT NHDGGYSMRN HEQFCPCIMR NQYSPNSHNQ TP PMVTIQN GKVVHLNNVN GVDLTKGYPK NETRRIKRAN RAGTRGFRAP EVLMKCGAQS TKIDIWSVGV ILLSLLGRRF PMF QSLDDA DSLLELCTIF GWKELRKCAA LHGLGFEASG LIWDKPNGYS NGLKEFVYDL LNKECTIGTF PEYSVAFETF GFLQ QELHD RMSIEPQLPD PKTNMDAVDA YELKKYQEEI WSDHYWCFQV LEQCFEMDPQ KRSSAEDLLK TPFFNELNEN TYLLD GEST DEDDVVSSSE ADLLDKDVLL ISE UniProtKB: Cell division control protein 7 |
-Macromolecule #8: DDK kinase regulatory subunit DBF4
| Macromolecule | Name: DDK kinase regulatory subunit DBF4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVSPTKMIIR SPLKETDTNL KHNNGIAAST TAAGHLNVFS NDNNCNNNNT TESFPKKRSL ERLELQQQQH LHEKKRARIE RARSIEGAV QVSKGTGLKN VEPRVTPKEL LEWQTNWKKI MKRDSRIYFD ITDDVEMNTY NKSKMDKRRD LLKRGFLTLG A QITQFFDT ...String: MVSPTKMIIR SPLKETDTNL KHNNGIAAST TAAGHLNVFS NDNNCNNNNT TESFPKKRSL ERLELQQQQH LHEKKRARIE RARSIEGAV QVSKGTGLKN VEPRVTPKEL LEWQTNWKKI MKRDSRIYFD ITDDVEMNTY NKSKMDKRRD LLKRGFLTLG A QITQFFDT TVTIVITRRS VENIYLLKDT DILSRAKKNY MKVWSYEKAA RFLKNLDVDL DHLSKTKSAS LAAPTLSNLL HN EKLYGPT DRDPRTKRDD IHYFKYPHVY LYDLWQTWAP IITLEWKPQE LTNLDELPYP ILKIGSFGRC PFIGDRNYDE SSY KRVVKR YSRDKANKKY ALQLRALFQY HADTLLNTSS VNDQTKNLIF IPHTCNDSTK SFKKWMQEKA KNFEKTELKK TDDS AVQDV RNEHADQTDE KNSILLNETE TKEPPLKEEK ENKQSIAEES NKYPQRKELA ATPKLNHPVL ATFARQETEE VPDDL CTLK TKSRQAFEIK ASGAHQSNDV ATSFGNGLGP TRASVMSKNM KSLSRLMVDR KLGVKQTNGN NKNYTATIAT TAETSK ENR HRLDFNALKK DEAPSKETGK DSAVHLETNR KPQNFPKVAT KSVSADSKVH NDIKITTTES PTASKKSTST NVTLHFN AQ TAQTAQPVKK ETVKNSGYCE NCRVKYESLE QHIVSEKHLS FAENDLNFEA IDSLIENLRF QI UniProtKB: DDK kinase regulatory subunit DBF4 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 2 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 25 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: 15 mA |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot for 1.5 seconds and blot force +2. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 9909 / Average electron dose: 45.9 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














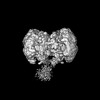
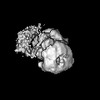

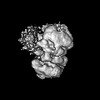
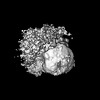
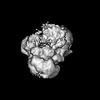
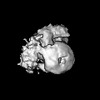
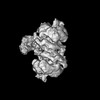






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)