+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13428 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pfu sArlG (PF0333, N-d31-ArlG) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG Refinement Map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |   Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) | |||||||||
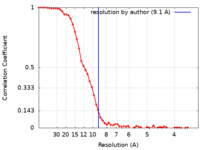
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Umrekar TR / Winterborn YB / Sivabalasarma S / Brantl J / Albers SV / Beeby M | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Front Microbiol / Year: 2021 Journal: Front Microbiol / Year: 2021Title: Evolution of Archaellum Rotation Involved Invention of a Stator Complex by Duplicating and Modifying a Core Component. Authors: Trishant R Umrekar / Yvonne B Winterborn / Shamphavi Sivabalasarma / Julian Brantl / Sonja-Verena Albers / Morgan Beeby /   Abstract: Novelty in biology can arise from opportunistic repurposing of nascent characteristics of existing features. Understanding how this process happens at the molecular scale, however, suffers from a ...Novelty in biology can arise from opportunistic repurposing of nascent characteristics of existing features. Understanding how this process happens at the molecular scale, however, suffers from a lack of case studies. The evolutionary emergence of rotary motors is a particularly clear example of evolution of a new function. The simplest of rotary motors is the archaellum, a molecular motor that spins a helical propeller for archaeal motility analogous to the bacterial flagellum. Curiously, emergence of archaellar rotation may have pivoted on the simple duplication and repurposing of a pre-existing component to produce a stator complex that anchors to the cell superstructure to enable productive rotation of the rotor component. This putative stator complex is composed of ArlF and ArlG, gene duplications of the filament component ArlB, providing an opportunity to study how gene duplication and neofunctionalization contributed to the radical innovation of rotary function. Toward understanding how this happened, we used electron cryomicroscopy to determine the structure of isolated ArlG filaments, the major component of the stator complex. Using a hybrid modeling approach incorporating structure prediction and validation, we show that ArlG filaments are open helices distinct to the closed helical filaments of ArlB. Curiously, further analysis reveals that ArlG retains a subset of the inter-protomer interactions of homologous ArlB, resulting in a superficially different assembly that nevertheless reflects the common ancestry of the two structures. This relatively simple mechanism to change quaternary structure was likely associated with the evolutionary neofunctionalization of the archaellar stator complex, and we speculate that the relative deformable elasticity of an open helix may facilitate elastic energy storage during the transmission of the discrete bursts of energy released by ATP hydrolysis to continuous archaellar rotation, allowing the inherent properties of a duplicated ArlB to be co-opted to fulfill a new role. Furthermore, agreement of diverse experimental evidence in our work supports recent claims to the power of new structure prediction techniques. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13428.map.gz emd_13428.map.gz | 6.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13428-v30.xml emd-13428-v30.xml emd-13428.xml emd-13428.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13428_fsc.xml emd_13428_fsc.xml | 7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13428.png emd_13428.png | 41.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13428_msk_1.map emd_13428_msk_1.map | 12.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_13428_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13428_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13428_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13428_half_map_2.map.gz | 12 MB 12 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13428 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13428 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13428 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13428 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13428.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 12.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13428.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 12.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG Refinement Map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13428_msk_1.map emd_13428_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
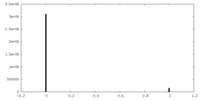
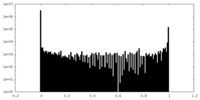
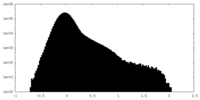
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG half map A
| File | emd_13428_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG half map B
| File | emd_13428_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homo-oligomeric helical filament of archaellum stator component P...
| Entire | Name: Homo-oligomeric helical filament of archaellum stator component Pfu sArlG |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homo-oligomeric helical filament of archaellum stator component P...
| Supramolecule | Name: Homo-oligomeric helical filament of archaellum stator component Pfu sArlG type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Recombinant plasmid: pSVA4014 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 142.4235 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG
| Macromolecule | Name: Pyrococcus furiosus sArlG / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) Pyrococcus furiosus (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: TDIANGMKDR GKLLANQLRV EFAIINDPQS VRVTGTGPYT YTFYIKNIGK ETIPFTSSSV QVFIDGNLIP PSNLTFKDVN GNQITSLKPY EVGVLEVTLG NPLDTTTTHR IVVVLENGKK RSLVFRVKS |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: Solutions were filtered and chilled before use in column chromatography. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 40.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 34.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 96000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
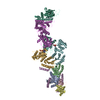
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





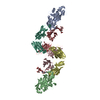


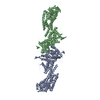

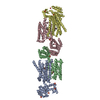
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)