+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12055 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ACAD9-ECSIT-CTD (ACAD9 core) | |||||||||
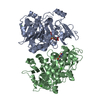
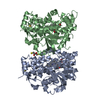
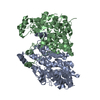
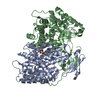
 Map data Map data | ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Giachin G / Jessop M / Soler-Lopez M / Gutsche I | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / Year: 2021 Journal: Angew Chem Int Ed Engl / Year: 2021Title: Assembly of The Mitochondrial Complex I Assembly Complex Suggests a Regulatory Role for Deflavination. Authors: Gabriele Giachin / Matthew Jessop / Romain Bouverot / Samira Acajjaoui / Melissa Saïdi / Anaïs Chretien / Maria Bacia-Verloop / Luca Signor / Philippe J Mas / Adrien Favier / Eve Borel ...Authors: Gabriele Giachin / Matthew Jessop / Romain Bouverot / Samira Acajjaoui / Melissa Saïdi / Anaïs Chretien / Maria Bacia-Verloop / Luca Signor / Philippe J Mas / Adrien Favier / Eve Borel Meneroud / Michael Hons / Darren J Hart / Eaazhisai Kandiah / Elisabetta Boeri Erba / Alain Buisson / Gordon Leonard / Irina Gutsche / Montserrat Soler-Lopez /  Abstract: Fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) are mitochondrial redox processes that generate ATP. The biogenesis of the respiratory Complex I, a 1 MDa multiprotein complex ...Fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) are mitochondrial redox processes that generate ATP. The biogenesis of the respiratory Complex I, a 1 MDa multiprotein complex that is responsible for initiating OXPHOS, is mediated by assembly factors including the mitochondrial complex I assembly (MCIA) complex. However, the organisation and the role of the MCIA complex are still unclear. Here we show that ECSIT functions as the bridging node of the MCIA core complex. Furthermore, cryo-electron microscopy together with biochemical and biophysical experiments reveal that the C-terminal domain of ECSIT directly binds to the vestigial dehydrogenase domain of the FAO enzyme ACAD9 and induces its deflavination, switching ACAD9 from its role in FAO to an MCIA factor. These findings provide the structural basis for the MCIA complex architecture and suggest a unique molecular mechanism for coordinating the regulation of the FAO and OXPHOS pathways to ensure an efficient energy production. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12055.map.gz emd_12055.map.gz | 14.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12055-v30.xml emd-12055-v30.xml emd-12055.xml emd-12055.xml | 14.7 KB 14.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_12055_fsc.xml emd_12055_fsc.xml | 5.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_12055.png emd_12055.png | 61.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_12055_msk_1.map emd_12055_msk_1.map | 15.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_12055_half_map_1.map.gz emd_12055_half_map_1.map.gz emd_12055_half_map_2.map.gz emd_12055_half_map_2.map.gz | 14.4 MB 14.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12055 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12055 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12055 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_12055.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_12055.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.067 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_12055_msk_1.map emd_12055_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) half map A
| File | emd_12055_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
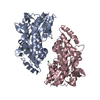
| Annotation | ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) half map B
| File | emd_12055_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | ACAD9-ECSIT-Cter (ACAD9 core) half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex between ACAD9 and a C-terminal construct of ECSIT
| Entire | Name: Complex between ACAD9 and a C-terminal construct of ECSIT |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex between ACAD9 and a C-terminal construct of ECSIT
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex between ACAD9 and a C-terminal construct of ECSIT type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Grids were pumped for 1 hour under vacuum prior to freezing.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 41.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)














































