[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-11340: Microtubule complexed with Kif15 motor domain. Symmetrised asymme... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11340 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
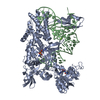
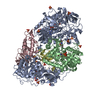
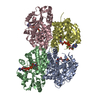
| Title | Microtubule complexed with Kif15 motor domain. Symmetrised asymmetric unit | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Kif15 motor domain (AMPPNP bound) complexed with microtubule (asymmetric unit). | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Kinesin / microtubules / kinesin binding protein / KBP / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end kinesin complex / centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic ...plus-end kinesin complex / centrosome separation / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Mitotic Prometaphase / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / kinesin complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / microtubule motor activity / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / microtubule-based movement / cytoskeletal motor activity / mitotic spindle assembly / MHC class II antigen presentation / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / spindle pole / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / GTPase activity / centrosome / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Atherton J / Hummel JJA | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Switzerland, Switzerland,  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: The mechanism of kinesin inhibition by kinesin-binding protein. Authors: Joseph Atherton / Jessica Ja Hummel / Natacha Olieric / Julia Locke / Alejandro Peña / Steven S Rosenfeld / Michel O Steinmetz / Casper C Hoogenraad / Carolyn A Moores /     Abstract: Subcellular compartmentalisation is necessary for eukaryotic cell function. Spatial and temporal regulation of kinesin activity is essential for building these local environments via control of ...Subcellular compartmentalisation is necessary for eukaryotic cell function. Spatial and temporal regulation of kinesin activity is essential for building these local environments via control of intracellular cargo distribution. Kinesin-binding protein (KBP) interacts with a subset of kinesins via their motor domains, inhibits their microtubule (MT) attachment, and blocks their cellular function. However, its mechanisms of inhibition and selectivity have been unclear. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the structure of KBP and of a KBP-kinesin motor domain complex. KBP is a tetratricopeptide repeat-containing, right-handed α-solenoid that sequesters the kinesin motor domain's tubulin-binding surface, structurally distorting the motor domain and sterically blocking its MT attachment. KBP uses its α-solenoid concave face and edge loops to bind the kinesin motor domain, and selected structure-guided mutations disrupt KBP inhibition of kinesin transport in cells. The KBP-interacting motor domain surface contains motifs exclusively conserved in KBP-interacting kinesins, suggesting a basis for kinesin selectivity. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11340.map.gz emd_11340.map.gz | 511.6 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11340-v30.xml emd-11340-v30.xml emd-11340.xml emd-11340.xml | 17 KB 17 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_11340.png emd_11340.png | 137.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11340.cif.gz emd-11340.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11340 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11340 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11340 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11340 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6zpiMC  6zpgC  6zphC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11340.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11340.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Kif15 motor domain (AMPPNP bound) complexed with microtubule (asymmetric unit). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
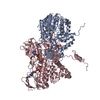
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.39 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Kif15 motor domain (AMPPNP bound) complexed with microtubule. Sym...
+Supramolecule #1: Kif15 motor domain (AMPPNP bound) complexed with microtubule. Sym...
+Supramolecule #2: Kif15 motor domain
+Supramolecule #3: Microtubule
+Macromolecule #1: Kinesin-like protein KIF15
+Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1B chain
+Macromolecule #3: Tubulin beta chain
+Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
+Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #6: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #7: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #8: TAXOL
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 / Details: Movies were dose weighted. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL / Details: Kinesin-1 decorated microtubule (synthetic model). |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Software - details: MiRP protocol / Number images used: 12674 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)