[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10760: Mammalian 48S late-stage initiation complex with beta-globin mRNA -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10760 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mammalian 48S late-stage initiation complex with beta-globin mRNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | initiation complex / 48S / eIF1A / eIF3 / ABCE1 / rabbit / TRANSLATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of macromolecule metabolic process / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 complex / eukaryotic 48S preinitiation complex / cellular response to chemical stress / laminin receptor activity / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / 90S preribosome / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / regulation of translational fidelity / phagocytic cup ...regulation of macromolecule metabolic process / eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 complex / eukaryotic 48S preinitiation complex / cellular response to chemical stress / laminin receptor activity / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / 90S preribosome / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / regulation of translational fidelity / phagocytic cup / laminin binding / rough endoplasmic reticulum / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / gastrulation / translation initiation factor activity / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / spindle / cytoplasmic stress granule / rRNA processing / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / rhythmic process / regulation of translation / ribosome binding / virus receptor activity / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / perikaryon / cytoplasmic translation / cell differentiation / tRNA binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / rRNA binding / postsynaptic density / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / cell division / DNA repair / mRNA binding / apoptotic process / synapse / dendrite / centrosome / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bochler A / Simonetti A | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  France, 2 items France, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2020Title: Structural Insights into the Mammalian Late-Stage Initiation Complexes. Authors: Angelita Simonetti / Ewelina Guca / Anthony Bochler / Lauriane Kuhn / Yaser Hashem /  Abstract: In higher eukaryotes, the mRNA sequence in the direct vicinity of the start codon, called the Kozak sequence (CRCCaugG, where R is a purine), is known to influence the rate of the initiation process. ...In higher eukaryotes, the mRNA sequence in the direct vicinity of the start codon, called the Kozak sequence (CRCCaugG, where R is a purine), is known to influence the rate of the initiation process. However, the molecular basis underlying its role remains poorly understood. Here, we present the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of mammalian late-stage 48S initiation complexes (LS48S ICs) in the presence of two different native mRNA sequences, β-globin and histone 4, at overall resolution of 3 and 3.5 Å, respectively. Our high-resolution structures unravel key interactions from the mRNA to eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs): 1A, 2, 3, 18S rRNA, and several 40S ribosomal proteins. In addition, we are able to study the structural role of ABCE1 in the formation of native 48S ICs. Our results reveal a comprehensive map of ribosome/eIF-mRNA and ribosome/eIF-tRNA interactions and suggest the impact of mRNA sequence on the structure of the LS48S IC. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10760.map.gz emd_10760.map.gz | 202.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10760-v30.xml emd-10760-v30.xml emd-10760.xml emd-10760.xml | 58.5 KB 58.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_10760.png emd_10760.png | 151.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10760.cif.gz emd-10760.cif.gz | 12.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10760 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10760 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10760 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10760 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6yalMC  6yamC  6yanC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10760.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10760.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
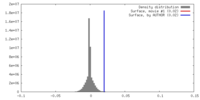
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : LS48S IC with beta-globin mRNA
+Supramolecule #1: LS48S IC with beta-globin mRNA
+Supramolecule #2: LS48S IC
+Supramolecule #3: beta-globin mRNA
+Macromolecule #1: initiator methionylated tRNA
+Macromolecule #34: 18S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #41: beta-globin mRNA
+Macromolecule #2: 60s ribosomal protein ul41
+Macromolecule #3: 40S ribosomal protein uS2
+Macromolecule #4: 40S ribosomal protein eS1
+Macromolecule #5: 40S ribosomal protein uS5
+Macromolecule #6: 40S Ribosomal protein uS3
+Macromolecule #7: 40S ribosomal protein eS4
+Macromolecule #8: 40S Ribosomal protein uS7
+Macromolecule #9: 40S ribosomal protein eS6
+Macromolecule #10: 40S ribosomal protein eS7
+Macromolecule #11: 40S ribosomal protein eS8
+Macromolecule #12: 40S ribosomal protein uS4
+Macromolecule #13: 40S ribosomal protein eS10
+Macromolecule #14: 40S ribosomal protein uS17
+Macromolecule #15: 40S ribosomal protein eS12
+Macromolecule #16: 40S ribosomal protein uS15
+Macromolecule #17: 40S ribosomal protein uS11
+Macromolecule #18: 40S ribosomal protein uS9
+Macromolecule #19: 40S ribosomal protein eS17
+Macromolecule #20: 40S ribosomal protein eS19
+Macromolecule #21: 40S ribosomal protein uS10
+Macromolecule #22: 40S ribosomal protein eS21
+Macromolecule #23: 40S ribosomal protein uS8
+Macromolecule #24: 40S ribosomal protein uS12
+Macromolecule #25: 40S ribosomal protein eS24
+Macromolecule #26: 40S ribosomal protein eS26
+Macromolecule #27: 40S ribosomal protein eS27
+Macromolecule #28: 40S ribosomal protein eS28
+Macromolecule #29: 40S ribosomal protein uS14
+Macromolecule #30: 40S ribosomal protein eS31
+Macromolecule #31: ribosomal protein RACK1
+Macromolecule #32: 40S ribosomal protein eS25
+Macromolecule #33: 40S ribosomal protein eS30
+Macromolecule #35: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #36: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit gamma
+Macromolecule #37: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A
+Macromolecule #38: ATP-binding cassette sub-family E member 1 (ABCE1)
+Macromolecule #39: 40S ribosomal protein uS13
+Macromolecule #40: 40S ribosomal protein uS19
+Macromolecule #42: IRON/SULFUR CLUSTER
+Macromolecule #43: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #44: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-GUANYLATE ESTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 26.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 252000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6yal: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









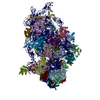
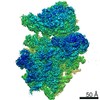

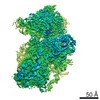


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)