[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0323: Structural insights into the ability of nucleoplasmin to assemble... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0323 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
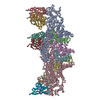
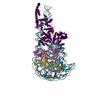
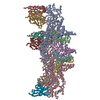
| Title | Structural insights into the ability of nucleoplasmin to assemble and chaperone histone octamers for DNA deposition | |||||||||
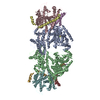
 Map data Map data | Complex between two nucleoplasmin molecules (each one a homopentamer) and an histone octamer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 14.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Valpuesta JM / Arranz R / Martin-Benito J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Spain, 1 items Spain, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Structural insights into the ability of nucleoplasmin to assemble and chaperone histone octamers for DNA deposition. Authors: Aitor Franco / Rocío Arranz / Noelia Fernández-Rivero / Adrián Velázquez-Campoy / Jaime Martín-Benito / Joan Segura / Adelina Prado / José M Valpuesta / Arturo Muga /   Abstract: Nucleoplasmin (NP) is a pentameric histone chaperone that regulates the condensation state of chromatin in different cellular processes. We focus here on the interaction of NP with the histone ...Nucleoplasmin (NP) is a pentameric histone chaperone that regulates the condensation state of chromatin in different cellular processes. We focus here on the interaction of NP with the histone octamer, showing that NP could bind sequentially the histone components to assemble an octamer-like particle, and crosslinked octamers with high affinity. The three-dimensional reconstruction of the NP/octamer complex generated by single-particle cryoelectron microscopy, revealed that several intrinsically disordered tail domains of two NP pentamers, facing each other through their distal face, encage the histone octamer in a nucleosome-like conformation and prevent its dissociation. Formation of this complex depended on post-translational modification and exposure of the acidic tract at the tail domain of NP. Finally, NP was capable of transferring the histone octamers to DNA in vitro, assembling nucleosomes. This activity may have biological relevance for processes in which the histone octamer must be rapidly removed from or deposited onto the DNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0323.map.gz emd_0323.map.gz | 365.8 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0323-v30.xml emd-0323-v30.xml emd-0323.xml emd-0323.xml | 15.9 KB 15.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_0323.png emd_0323.png | 39 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0323 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0323 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0323 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0323 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0323.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 549.8 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0323.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 549.8 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Complex between two nucleoplasmin molecules (each one a homopentamer) and an histone octamer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.35 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
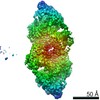
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Nucleoplasmin-histone octamer complex
| Entire | Name: Nucleoplasmin-histone octamer complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Nucleoplasmin-histone octamer complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Nucleoplasmin-histone octamer complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 320 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Nucleoplasmin
| Supramolecule | Name: Nucleoplasmin / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Histones
| Supramolecule | Name: Histones / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Nucleoplasmin
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleoplasmin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MASTVSNTSK LEKPVSLIW G CELNEQDK TF EFKVEDD EEK CEHQLA LRTV CLGDK AKDEF NIVE IVTQEE GAE KSVPIAT LK PSILPMAT M VGIELTPPV TFRLKAGSGP LYISGQHVA M EEDYSWAE EE DEGEAEG EEE EEEEED QESP PKAVK ...String: MASTVSNTSK LEKPVSLIW G CELNEQDK TF EFKVEDD EEK CEHQLA LRTV CLGDK AKDEF NIVE IVTQEE GAE KSVPIAT LK PSILPMAT M VGIELTPPV TFRLKAGSGP LYISGQHVA M EEDYSWAE EE DEGEAEG EEE EEEEED QESP PKAVK RPAAT KKAG QAKKKK LDK EDESSEE DS PTKKGKGA G RGRKPAAKK |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H2A
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK ARAKAKSRS S RAGLQFPV GR VHRLLRK GNY AERVGA GAPV YLAAV LEYLT AEIL ELAGNA ARD NKKTRII PR HLQLAIRN D EELNKLLGK |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2B
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAV T KTQKKGDK KR KKSRKES YSI YVYKVL KQVH PDTGI SSKAM GIMN SFVNDI FER IAGEASR LA HYNKRSTI T SREIQTAVR LLLPGELAKH AVSEGTKAV T KYTSSK |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H3
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK FTGGKAPRK Q LATKAARK SA PSTGGVK KPH RYRPGT VALR EIRRY QKSTE LLIR KLPFQR LVR EIAQDFK TD LRFQSAAI G ALQEASEAY LVGLFEDTNL CAIHAKRVT I MPKDIQLA RR IRGERA |
-Macromolecule #5: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRH R KVLRDNIQ GI TKPAIRR LAR RGGVKR ISGL IYEET RGVLK VFLE NVIRDA VTY TEHAKRK TV TAMDVVYA L KRQGRTLYG FGG |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 240 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 25 mM Hepes pH 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: LEICA EM CPC |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Number grids imaged: 5 / Number real images: 897 / Average electron dose: 2.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 80500 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)























