[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0195: Multi-body refined map of the rabbit 80S stalled on globin mRNA a... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0195 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
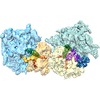
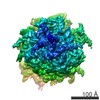
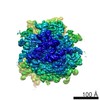
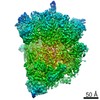
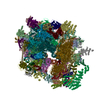
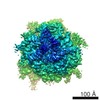
| Title | Multi-body refined map of the rabbit 80S stalled on globin mRNA at the stop codon | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Multi-body refined rabbit 80S ribosome stalled on globin mRNA at the stop codon | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Translation / Quality Control / Ribosome | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of macromolecule metabolic process / ribosomal subunit / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / gastrulation ...regulation of macromolecule metabolic process / ribosomal subunit / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / spindle / rRNA processing / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / rhythmic process / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / perikaryon / killing of cells of another organism / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cell differentiation / tRNA binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / rRNA binding / postsynaptic density / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / cell division / DNA repair / mRNA binding / apoptotic process / synapse / dendrite / centrosome / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
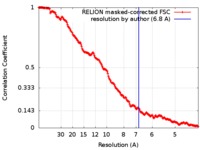
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Juszkiewicz S / Chandrasekaran V | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  France, 4 items France, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018Title: ZNF598 Is a Quality Control Sensor of Collided Ribosomes. Authors: Szymon Juszkiewicz / Viswanathan Chandrasekaran / Zhewang Lin / Sebastian Kraatz / V Ramakrishnan / Ramanujan S Hegde /  Abstract: Aberrantly slow translation elicits quality control pathways initiated by the ubiquitin ligase ZNF598. How ZNF598 discriminates physiologic from pathologic translation complexes and ubiquitinates ...Aberrantly slow translation elicits quality control pathways initiated by the ubiquitin ligase ZNF598. How ZNF598 discriminates physiologic from pathologic translation complexes and ubiquitinates stalled ribosomes selectively is unclear. Here, we find that the minimal unit engaged by ZNF598 is the collided di-ribosome, a molecular species that arises when a trailing ribosome encounters a slower leading ribosome. The collided di-ribosome structure reveals an extensive 40S-40S interface in which the ubiquitination targets of ZNF598 reside. The paucity of 60S interactions allows for different ribosome rotation states, explaining why ZNF598 recognition is indifferent to how the leading ribosome has stalled. The use of ribosome collisions as a proxy for stalling allows the degree of tolerable slowdown to be tuned by the initiation rate on that mRNA; hence, the threshold for triggering quality control is substrate specific. These findings illustrate how higher-order ribosome architecture can be exploited by cellular factors to monitor translation status. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0195.map.gz emd_0195.map.gz | 23.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0195-v30.xml emd-0195-v30.xml emd-0195.xml emd-0195.xml | 103.3 KB 103.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_0195_fsc.xml emd_0195_fsc.xml | 17.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_0195.png emd_0195.png | 157.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_0195_msk_1.map emd_0195_msk_1.map | 476.8 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0195.cif.gz emd-0195.cif.gz | 20.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_0195_half_map_1.map.gz emd_0195_half_map_1.map.gz emd_0195_half_map_2.map.gz emd_0195_half_map_2.map.gz | 345.1 MB 345.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0195 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0195 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_0195_validation.pdf.gz emd_0195_validation.pdf.gz | 407.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_0195_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_0195_full_validation.pdf.gz | 407 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_0195_validation.xml.gz emd_0195_validation.xml.gz | 22.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0195 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0195 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0195 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6hcmMC  0192C 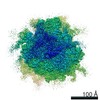 0194C  0197C  6hcfC  6hcjC  6hcqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0195.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0195.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Multi-body refined rabbit 80S ribosome stalled on globin mRNA at the stop codon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
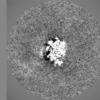
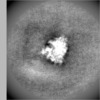
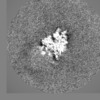
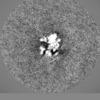
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.14 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
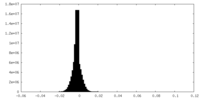
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_0195_msk_1.map emd_0195_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
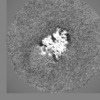
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
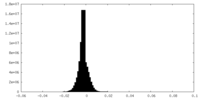
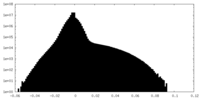
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Body1 half2 map
| File | emd_0195_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Body1 half2 map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
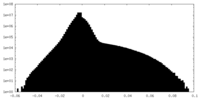
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Body1 half1 map
| File | emd_0195_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Body1 half1 map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Rabbit 80S stalled on globin mRNA at the stop codon
+Supramolecule #1: Rabbit 80S stalled on globin mRNA at the stop codon
+Macromolecule #1: 18S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #37: 28S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #38: 5S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #39: 5.8S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #80: P-site tRNA
+Macromolecule #81: mRNA
+Macromolecule #2: uS2
+Macromolecule #3: 40S ribosomal protein S3a
+Macromolecule #4: uS5
+Macromolecule #5: uS3
+Macromolecule #6: eS4
+Macromolecule #7: Ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #8: 40S ribosomal protein S6
+Macromolecule #9: 40S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #10: eS8
+Macromolecule #11: Ribosomal protein S9 (Predicted)
+Macromolecule #12: eS10
+Macromolecule #13: Ribosomal protein S11
+Macromolecule #14: 40S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #15: uS15
+Macromolecule #16: uS11
+Macromolecule #17: uS19
+Macromolecule #18: Ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #19: eS17
+Macromolecule #20: uS13
+Macromolecule #21: eS19
+Macromolecule #22: uS10
+Macromolecule #23: eS21
+Macromolecule #24: Ribosomal protein S15a
+Macromolecule #25: uS12
+Macromolecule #26: eS24
+Macromolecule #27: eS25
+Macromolecule #28: eS26
+Macromolecule #29: 40S ribosomal protein S27
+Macromolecule #30: Ribosomal protein S28
+Macromolecule #31: uS14
+Macromolecule #32: 40S ribosomal protein S30
+Macromolecule #33: Ribosomal protein S27a
+Macromolecule #34: RACK1
+Macromolecule #35: eRF1(AAQ)
+Macromolecule #36: ATP binding cassette subfamily E member 1
+Macromolecule #40: Ribosomal protein L8
+Macromolecule #41: uL3
+Macromolecule #42: uL4
+Macromolecule #43: 60S ribosomal protein L6
+Macromolecule #44: uL30
+Macromolecule #45: uL6
+Macromolecule #46: eL13
+Macromolecule #47: Ribosomal protein L14
+Macromolecule #48: Ribosomal protein L15
+Macromolecule #49: uL13
+Macromolecule #50: uL22
+Macromolecule #51: eL18
+Macromolecule #52: eL19
+Macromolecule #53: eL20
+Macromolecule #54: eL21
+Macromolecule #55: eL22
+Macromolecule #56: Ribosomal protein L23
+Macromolecule #57: eL24
+Macromolecule #58: uL23
+Macromolecule #59: Ribosomal protein L26
+Macromolecule #60: eL27
+Macromolecule #61: uL15
+Macromolecule #62: eL29
+Macromolecule #63: eL30
+Macromolecule #64: eL31
+Macromolecule #65: eL32
+Macromolecule #66: eL33
+Macromolecule #67: eL34
+Macromolecule #68: uL29
+Macromolecule #69: 60S ribosomal protein L36
+Macromolecule #70: Ribosomal protein L37
+Macromolecule #71: eL38
+Macromolecule #72: eL39
+Macromolecule #73: eL40
+Macromolecule #74: eL41
+Macromolecule #75: eL42
+Macromolecule #76: eL43
+Macromolecule #77: eL28
+Macromolecule #78: uL10
+Macromolecule #79: Ribosomal protein L12
+Macromolecule #82: Ribosomal protein L11
+Macromolecule #83: eL8
+Macromolecule #84: 60S ribosomal protein L5
+Macromolecule #85: 60S ribosomal protein L10
+Macromolecule #86: nascent chain
+Macromolecule #87: Ribosomal protein
+Macromolecule #88: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #89: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #90: IRON/SULFUR CLUSTER
+Macromolecule #91: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.79 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)