+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tl6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of DDB1deltaB-DDA1-DCAF5 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / E3 ligase / protein degradation / cryo-EM / WD40 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / UV-damage excision repair / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / WD40-repeat domain binding / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex ...negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / UV-damage excision repair / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / WD40-repeat domain binding / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / viral release from host cell / cullin family protein binding / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / positive regulation of viral genome replication / proteasomal protein catabolic process / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / nucleotide-excision repair / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / regulation of circadian rhythm / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Wnt signaling pathway / protein polyubiquitination / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / cellular response to UV / rhythmic process / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / site of double-strand break / Neddylation / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / protein ubiquitination / DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.63 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Yue, H. / Hunkeler, M. / Roy Burman, S.S. / Fischer, E.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Targeting DCAF5 suppresses SMARCB1-mutant cancer by stabilizing SWI/SNF. Authors: Sandi Radko-Juettner / Hong Yue / Jacquelyn A Myers / Raymond D Carter / Alexis N Robertson / Priya Mittal / Zhexin Zhu / Baranda S Hansen / Katherine A Donovan / Moritz Hunkeler / Wojciech ...Authors: Sandi Radko-Juettner / Hong Yue / Jacquelyn A Myers / Raymond D Carter / Alexis N Robertson / Priya Mittal / Zhexin Zhu / Baranda S Hansen / Katherine A Donovan / Moritz Hunkeler / Wojciech Rosikiewicz / Zhiping Wu / Meghan G McReynolds / Shourya S Roy Burman / Anna M Schmoker / Nada Mageed / Scott A Brown / Robert J Mobley / Janet F Partridge / Elizabeth A Stewart / Shondra M Pruett-Miller / Behnam Nabet / Junmin Peng / Nathanael S Gray / Eric S Fischer / Charles W M Roberts /  Abstract: Whereas oncogenes can potentially be inhibited with small molecules, the loss of tumour suppressors is more common and is problematic because the tumour-suppressor proteins are no longer present to ...Whereas oncogenes can potentially be inhibited with small molecules, the loss of tumour suppressors is more common and is problematic because the tumour-suppressor proteins are no longer present to be targeted. Notable examples include SMARCB1-mutant cancers, which are highly lethal malignancies driven by the inactivation of a subunit of SWI/SNF (also known as BAF) chromatin-remodelling complexes. Here, to generate mechanistic insights into the consequences of SMARCB1 mutation and to identify vulnerabilities, we contributed 14 SMARCB1-mutant cell lines to a near genome-wide CRISPR screen as part of the Cancer Dependency Map Project. We report that the little-studied gene DDB1-CUL4-associated factor 5 (DCAF5) is required for the survival of SMARCB1-mutant cancers. We show that DCAF5 has a quality-control function for SWI/SNF complexes and promotes the degradation of incompletely assembled SWI/SNF complexes in the absence of SMARCB1. After depletion of DCAF5, SMARCB1-deficient SWI/SNF complexes reaccumulate, bind to target loci and restore SWI/SNF-mediated gene expression to levels that are sufficient to reverse the cancer state, including in vivo. Consequently, cancer results not from the loss of SMARCB1 function per se, but rather from DCAF5-mediated degradation of SWI/SNF complexes. These data indicate that therapeutic targeting of ubiquitin-mediated quality-control factors may effectively reverse the malignant state of some cancers driven by disruption of tumour suppressor complexes. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tl6.cif.gz 8tl6.cif.gz | 418.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tl6.ent.gz pdb8tl6.ent.gz | 324.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tl6.json.gz 8tl6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tl6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tl6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tl6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tl/8tl6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41363MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 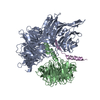
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 96425.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 108948.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DCAF5, BCRG2, KIAA1824, WDR22 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DCAF5, BCRG2, KIAA1824, WDR22 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96JK2 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96JK2 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 14542.154 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDA1, C19orf58, PCIA1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDA1, C19orf58, PCIA1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BW61 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BW61 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of DDB1deltaB-DDA1-DCAF5 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.22 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 / Details: 25mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 200mM NaCl, 4mM TCEP | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.9 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: NITROGEN / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4.494 sec. / Electron dose: 53.349 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1072 / Details: 50 frames per movie |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: implemented in cryoSPARCv3.2 / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1404938 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.63 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 547805 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 97 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 41.71 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj



