+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ilb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
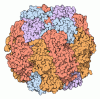
| Title | The complexes of RbcL, AtRaf1 and AtBSD2 (LFB) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE/CHAPERONE / RUBISCO ASSEMBL INTERMIDATES / COMPLEX / CHAPERONE / LYASE-CHAPERONE complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribulose bisphosphate carboxylase complex assembly / photorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / protein folding chaperone complex / chloroplast stroma / : / protein folding chaperone ...ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase complex assembly / photorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / protein folding chaperone complex / chloroplast stroma / : / protein folding chaperone / chloroplast / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding / zinc ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, R. / Song, H. / Zhang, W. / Wang, N. / Zhang, S. / Shao, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Plant / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Plant / Year: 2023Title: Structural insights into the functions of Raf1 and Bsd2 in hexadecameric Rubisco assembly. Authors: Ran Wang / Hui Song / Wenjuan Zhang / Ning Wang / Shijia Zhang / Ruiqi Shao / Cuimin Liu /  Abstract: Hexadecameric form I Rubisco, which consisting consists of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits, is the most abundant enzyme on earth. Extensive efforts to engineer an improved Rubisco ...Hexadecameric form I Rubisco, which consisting consists of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits, is the most abundant enzyme on earth. Extensive efforts to engineer an improved Rubisco to speed up its catalytic efficiency and ultimately increase agricultural productivity. However, difficulties with correct folding and assembly in foreign hosts or in vitro have hampered the genetic manipulation of hexadecameric Rubisco. In this study, we reconstituted Synechococcus sp. PCC6301 Rubisco in vitro using the chaperonin system and assembly factors from cyanobacteria and Arabidopsis thaliana (At). Rubisco holoenzyme was produced in the presence of cyanobacterial Rubisco accumulation factor 1 (Raf1) alone or both AtRaf1 and bundle-sheath defective-2 (AtBsd2) from Arabidopsis. RbcL released from GroEL is assembly capable in the presence of ATP, and AtBsd2 functions downstream of AtRaf1. Cryo-EM structures of RbcL-AtRaf1, RbcL-AtRaf1-AtBsd2, and RbcL revealed that the interactions between RbcL and AtRaf1 are looser than those between prokaryotic RbcL and Raf1, with AtRaf1 tilting 7° farther away from RbcL. AtBsd2 stabilizes the flexible regions of RbcL, including the N and C termini, the 60s loop, and loop 6. Using these data, combined with previous findings, we propose the possible biogenesis pathways of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Rubisco. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ilb.cif.gz 8ilb.cif.gz | 776.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ilb.ent.gz pdb8ilb.ent.gz | 650 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ilb.json.gz 8ilb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/il/8ilb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/il/8ilb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/il/8ilb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/il/8ilb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  35532MC  8ilmC  8io2C  8iojC  8iolC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52516.605 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 (bacteria)Gene: cbbL, rbcA, rbcL, syc0130_c / Production host:  References: UniProt: P00880, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #2: Protein | Mass: 43732.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | Mass: 8355.468 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rubisco assembly intermidate complex with Syn6301RbcL, AtRaf1 and AtBsd2 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 233489 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj