[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8gtc: Cryo-EM model of the marine siphophage vB_DshS-R4C baseplate-tail... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8gtc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
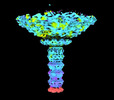
| Title | Cryo-EM model of the marine siphophage vB_DshS-R4C baseplate-tail complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Marine bacteriophage / Cryo-EM / Siphophage / Baseplate / Megatron protein / Tail fibre protein / Distal tail protein / Hub protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationProtein of unknown function DUF2793 / Protein of unknown function (DUF2793) / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84 / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84, C-terminal / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84, N-terminal / GTA TIM-barrel-like domain / Phage conserved hypothetical protein BR0599 / Uncharacterized conserved protein (DUF2163) / GTA TIM-barrel-like domain / Protein of unknown function DUF2460 ...Protein of unknown function DUF2793 / Protein of unknown function (DUF2793) / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84 / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84, C-terminal / Bacteriophage phiJL001, Gp84, N-terminal / GTA TIM-barrel-like domain / Phage conserved hypothetical protein BR0599 / Uncharacterized conserved protein (DUF2163) / GTA TIM-barrel-like domain / Protein of unknown function DUF2460 / Conserved hypothetical protein 2217 (DUF2460) / Tip attachment protein J / Putative phage tail protein / Glycoside hydrolase superfamily Similarity search - Domain/homology | ||||||
| Biological species |  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, Y. / Sun, H. / Wei, S. / Zheng, Q. / Li, S. / Zhang, R. / Xia, N. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structure and proposed DNA delivery mechanism of a marine roseophage. Authors: Yang Huang / Hui Sun / Shuzhen Wei / Lanlan Cai / Liqin Liu / Yanan Jiang / Jiabao Xin / Zhenqin Chen / Yuqiong Que / Zhibo Kong / Tingting Li / Hai Yu / Jun Zhang / Ying Gu / Qingbing Zheng ...Authors: Yang Huang / Hui Sun / Shuzhen Wei / Lanlan Cai / Liqin Liu / Yanan Jiang / Jiabao Xin / Zhenqin Chen / Yuqiong Que / Zhibo Kong / Tingting Li / Hai Yu / Jun Zhang / Ying Gu / Qingbing Zheng / Shaowei Li / Rui Zhang / Ningshao Xia /  Abstract: Tailed bacteriophages (order, Caudovirales) account for the majority of all phages. However, the long flexible tail of siphophages hinders comprehensive investigation of the mechanism of viral gene ...Tailed bacteriophages (order, Caudovirales) account for the majority of all phages. However, the long flexible tail of siphophages hinders comprehensive investigation of the mechanism of viral gene delivery. Here, we report the atomic capsid and in-situ structures of the tail machine of the marine siphophage, vB_DshS-R4C (R4C), which infects Roseobacter. The R4C virion, comprising 12 distinct structural protein components, has a unique five-fold vertex of the icosahedral capsid that allows genome delivery. The specific position and interaction pattern of the tail tube proteins determine the atypical long rigid tail of R4C, and further provide negative charge distribution within the tail tube. A ratchet mechanism assists in DNA transmission, which is initiated by an absorption device that structurally resembles the phage-like particle, RcGTA. Overall, these results provide in-depth knowledge into the intact structure and underlining DNA delivery mechanism for the ecologically important siphophages. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8gtc.cif.gz 8gtc.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8gtc.ent.gz pdb8gtc.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8gtc.json.gz 8gtc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8gtc_validation.pdf.gz 8gtc_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8gtc_full_validation.pdf.gz 8gtc_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8gtc_validation.xml.gz 8gtc_validation.xml.gz | 166.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8gtc_validation.cif.gz 8gtc_validation.cif.gz | 291.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/8gtc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/8gtc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/8gtc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gt/8gtc | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  34249MC  8gtaC  8gtbC  8gtdC  8gtfC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 13574.816 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6EGR9 Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6EGR9#2: Protein | Mass: 23378.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E7X5 Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E7X5#3: Protein | Mass: 154569.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E933 Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E933#4: Protein | Mass: 31055.357 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E762 Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E762#5: Protein | Mass: 22783.799 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E764 Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A4Y6E764 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) Dinoroseobacter phage vB_DshS-R4C (virus) |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Dinoroseobacter shibae DFL 12 = DSM 16493 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C3 (3 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 11598 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj