[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8frn: Acinetobacter baylyi LptB2FG bound to lipopolysaccharide and Zosu... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8frn | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Acinetobacter baylyi LptB2FG bound to lipopolysaccharide and Zosurabalpin | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID TRANSPORT / lipopolysaccharide / ABC / ATPase / antibiotic / macrocyclic peptide / gram-negative bacteria / ESKAPE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlipopolysaccharide transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / transmembrane transport / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pahil, K.S. / Gilman, M.S.A. / Kruse, A.C. / Kahne, D. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter. Authors: Karanbir S Pahil / Morgan S A Gilman / Vadim Baidin / Thomas Clairfeuille / Patrizio Mattei / Christoph Bieniossek / Fabian Dey / Dieter Muri / Remo Baettig / Michael Lobritz / Kenneth ...Authors: Karanbir S Pahil / Morgan S A Gilman / Vadim Baidin / Thomas Clairfeuille / Patrizio Mattei / Christoph Bieniossek / Fabian Dey / Dieter Muri / Remo Baettig / Michael Lobritz / Kenneth Bradley / Andrew C Kruse / Daniel Kahne /   Abstract: Gram-negative bacteria are extraordinarily difficult to kill because their cytoplasmic membrane is surrounded by an outer membrane that blocks the entry of most antibiotics. The impenetrable nature ...Gram-negative bacteria are extraordinarily difficult to kill because their cytoplasmic membrane is surrounded by an outer membrane that blocks the entry of most antibiotics. The impenetrable nature of the outer membrane is due to the presence of a large, amphipathic glycolipid called lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in its outer leaflet. Assembly of the outer membrane requires transport of LPS across a protein bridge that spans from the cytoplasmic membrane to the cell surface. Maintaining outer membrane integrity is essential for bacterial cell viability, and its disruption can increase susceptibility to other antibiotics. Thus, inhibitors of the seven lipopolysaccharide transport (Lpt) proteins that form this transenvelope transporter have long been sought. A new class of antibiotics that targets the LPS transport machine in Acinetobacter was recently identified. Here, using structural, biochemical and genetic approaches, we show that these antibiotics trap a substrate-bound conformation of the LPS transporter that stalls this machine. The inhibitors accomplish this by recognizing a composite binding site made up of both the Lpt transporter and its LPS substrate. Collectively, our findings identify an unusual mechanism of lipid transport inhibition, reveal a druggable conformation of the Lpt transporter and provide the foundation for extending this class of antibiotics to other Gram-negative pathogens. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8frn.cif.gz 8frn.cif.gz | 212.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8frn.ent.gz pdb8frn.ent.gz | 161.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8frn.json.gz 8frn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8frn_validation.pdf.gz 8frn_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8frn_full_validation.pdf.gz 8frn_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8frn_validation.xml.gz 8frn_validation.xml.gz | 46 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8frn_validation.cif.gz 8frn_validation.cif.gz | 67.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fr/8frn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fr/8frn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fr/8frn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fr/8frn | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29402MC  8frlC  8frmC 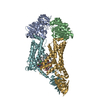 8froC  8frpC 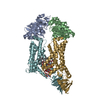 8ufgC  8ufhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Lipopolysaccharide export system ... , 2 types, 3 molecules ABF
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29032.344 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD1486 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host: Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD1486 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 41564.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD0254 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host: Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD0254 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host:  |
|---|
-Protein / Sugars , 2 types, 2 molecules G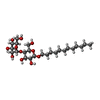

| #3: Protein | Mass: 40080.621 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD0255 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host: Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 (bacteria) / Gene: ACIAD0255 / Plasmid: pCDFDuet / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: Sugar | ChemComp-LMT / |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 
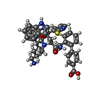

| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-JSG / ( |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj

 gel filtration
gel filtration