[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8fdt: Engineered human dynein motor domain in the microtubule-unbound s... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8fdt | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Engineered human dynein motor domain in the microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in the buffer containing ATP-Vi | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / Dynein / motor domain / microtubule-unbound / LIS1 | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / corpus callosum morphogenesis / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity ...microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / corpus callosum morphogenesis / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / acrosome assembly / central region of growth cone / cerebral cortex neuron differentiation / establishment of centrosome localization / microtubule sliding / positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of embryonic development / microtubule organizing center organization / interneuron migration / layer formation in cerebral cortex / auditory receptor cell development / astral microtubule / nuclear membrane disassembly / cortical microtubule organization / positive regulation of intracellular transport / positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / myeloid leukocyte migration / reelin-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / osteoclast development / stereocilium / microtubule plus-end binding / brain morphogenesis / vesicle transport along microtubule / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / kinesin complex / P-body assembly / negative regulation of JNK cascade / microtubule associated complex / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / neuromuscular process controlling balance / stem cell division / nuclear migration / cell leading edge / germ cell development / transmission of nerve impulse / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / dynactin binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / protein secretion / cochlea development / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of axon extension / microtubule-based process / lipid catabolic process / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / phospholipase binding / cytoplasmic microtubule / JNK cascade / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / axon cytoplasm / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / adult locomotory behavior / mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / hippocampus development / phosphoprotein binding / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / neuron migration / HCMV Early Events Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ton, W. / Wang, Y. / Chai, P. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Microtubule-binding-induced allostery triggers LIS1 dissociation from dynein prior to cargo transport. Authors: William D Ton / Yue Wang / Pengxin Chai / Cisloynny Beauchamp-Perez / Nicholas T Flint / Lindsay G Lammers / Hao Xiong / Kai Zhang / Steven M Markus /  Abstract: The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 ...The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 binding is required for dynein activity, its unbinding prior to initiation of cargo transport is equally important, since preventing dissociation leads to dynein dysfunction. To understand whether and how dynein-LIS1 binding is modulated, we engineered dynein mutants locked in a microtubule-bound (MT-B) or microtubule-unbound (MT-U) state. Whereas the MT-B mutant exhibits low LIS1 affinity, the MT-U mutant binds LIS1 with high affinity, and as a consequence remains almost irreversibly associated with microtubule plus-ends. We find that a monomeric motor domain is sufficient to exhibit these opposing LIS1 affinities, and that this is evolutionarily conserved between yeast and humans. Three cryo-EM structures of human dynein with and without LIS1 reveal microtubule-binding induced conformational changes responsible for this regulation. Our work reveals key biochemical and structural insight into LIS1-mediated dynein activation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8fdt.cif.gz 8fdt.cif.gz | 614 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8fdt.ent.gz pdb8fdt.ent.gz | 491.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8fdt.json.gz 8fdt.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8fdt_validation.pdf.gz 8fdt_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8fdt_full_validation.pdf.gz 8fdt_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8fdt_validation.xml.gz 8fdt_validation.xml.gz | 104.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8fdt_validation.cif.gz 8fdt_validation.cif.gz | 155.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/8fdt https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/8fdt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/8fdt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fd/8fdt | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29012MC  8fcyC  8fd6C  8fduC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 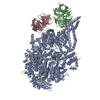
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 357459.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: residues 1458-3277 of dynein followed by residues 30-96 of serine-tRNA ligase, followed by residues 3412-4646 of dynein Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.) Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)Gene: DYNC1H1, DHC1, DNCH1, DNCL, DNECL, DYHC, KIAA0325, serS, TTHA0875 Strain: HB8 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q14204, UniProt: Q5SJX7, serine-tRNA ligase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 66423.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: SNAP tag present on C-terminus,SNAP tag present on C-terminus Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAFAH1B1, LIS1, MDCR, MDS, PAFAHA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAFAH1B1, LIS1, MDCR, MDS, PAFAHA / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / | #4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-VO4 / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in the buffer containing ATP-Vi Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.49 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 50 mM Tris pH 7.4, 150 mM potassium acetate, 2 mM magnesium acetate, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM Mg-ATP |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1200 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: UCSF ChimeraX / Version: 1.4/v9 / Classification: model building / URL: https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ / Os: macOS / Type: package | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 53572 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj