[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28999: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map of human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound mutant (dynein MT-B) | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dynein / motor domain / microtubule-bound / MOTOR PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationselenocysteine biosynthetic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic ...selenocysteine biosynthetic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / stress granule assembly / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / Separation of Sister Chromatids / azurophil granule lumen / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / cell cortex / microtubule / cell division / centrosome / Neutrophil degranulation / ATP hydrolysis activity / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
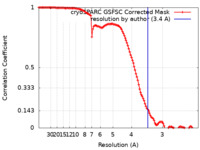
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ton W / Wang Y / Chai P | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Microtubule-binding-induced allostery triggers LIS1 dissociation from dynein prior to cargo transport. Authors: William D Ton / Yue Wang / Pengxin Chai / Cisloynny Beauchamp-Perez / Nicholas T Flint / Lindsay G Lammers / Hao Xiong / Kai Zhang / Steven M Markus /  Abstract: The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 ...The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 binding is required for dynein activity, its unbinding prior to initiation of cargo transport is equally important, since preventing dissociation leads to dynein dysfunction. To understand whether and how dynein-LIS1 binding is modulated, we engineered dynein mutants locked in a microtubule-bound (MT-B) or microtubule-unbound (MT-U) state. Whereas the MT-B mutant exhibits low LIS1 affinity, the MT-U mutant binds LIS1 with high affinity, and as a consequence remains almost irreversibly associated with microtubule plus-ends. We find that a monomeric motor domain is sufficient to exhibit these opposing LIS1 affinities, and that this is evolutionarily conserved between yeast and humans. Three cryo-EM structures of human dynein with and without LIS1 reveal microtubule-binding induced conformational changes responsible for this regulation. Our work reveals key biochemical and structural insight into LIS1-mediated dynein activation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28999.map.gz emd_28999.map.gz | 168 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28999-v30.xml emd-28999-v30.xml emd-28999.xml emd-28999.xml | 23.8 KB 23.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28999_fsc.xml emd_28999_fsc.xml | 11.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28999.png emd_28999.png | 60.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_28999_msk_1.map emd_28999_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28999.cif.gz emd-28999.cif.gz | 8.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28999_additional_1.map.gz emd_28999_additional_1.map.gz emd_28999_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28999_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28999_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28999_half_map_2.map.gz | 89.8 MB 165 MB 165 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28999 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28999 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_28999_validation.pdf.gz emd_28999_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_28999_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_28999_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_28999_validation.xml.gz emd_28999_validation.xml.gz | 20.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_28999_validation.cif.gz emd_28999_validation.cif.gz | 26.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28999 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-28999 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8fcyMC  8fd6C  8fdtC  8fduC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28999.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28999.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map of human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound mutant (dynein MT-B) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.149 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_28999_msk_1.map emd_28999_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Unsharpened map of human dynein motor domain in...
| File | emd_28999_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map of human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound mutant (dynein MT-B) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A of human dynein motor domain...
| File | emd_28999_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A of human dynein motor domain with microtubule-bound mutant (dynein MT-B) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B of human dynein motor domain...
| File | emd_28999_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B of human dynein motor domain with microtubule-bound mutant (dynein MT-B) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state
| Entire | Name: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state
| Supramolecule | Name: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-bound state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 350 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Serine--tRNA ligase
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Serine--tRNA ligase type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: residues 1458-3281 of dynein followed by residues 30-96 of serine-tRNA ligase, followed by residues 3412-4646 of dynein Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: serine-tRNA ligase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 357.931625 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSALEEFLKQ IREVWNTYEL DLVNYQNKCR LIRGWDDLFN KVKEHINSVS AMKLSPYYKV FEEDALSWED KLNRIMALFD VWIDVQRRW VYLEGIFTGS ADIKHLLPVE TQRFQSISTE FLALMKKVSK SPLVMDVLNI QGVQRSLERL ADLLGKIQKA L GEYLERER ...String: GSALEEFLKQ IREVWNTYEL DLVNYQNKCR LIRGWDDLFN KVKEHINSVS AMKLSPYYKV FEEDALSWED KLNRIMALFD VWIDVQRRW VYLEGIFTGS ADIKHLLPVE TQRFQSISTE FLALMKKVSK SPLVMDVLNI QGVQRSLERL ADLLGKIQKA L GEYLERER SSFPRFYFVG DEDLLEIIGN SKNVAKLQKH FKKMFAGVSS IILNEDNSVV LGISSREGEE VMFKTPVSIT EH PKINEWL TLVEKEMRVT LAKLLAESVT EVEIFGKATS IDPNTYITWI DKYQAQLVVL SAQIAWSENV ETALSSMGGG GDA APLHSV LSNVEVTLNV LADSVLMEQP PLRRRKLEHL ITELVHQRDV TRSLIKSKID NAKSFEWLSQ MRFYFDPKQT DVLQ QLSIQ MANAKFNYGF EYLGVQDKLV QTPLTDRCYL TMTQALEARL GGSPFGPAGT GKTESVKALG HQLGRFVLVF NCDET FDFQ AMGRIFVGLC QVGAWGCFDE FNRLEERMLS AVSQQVQCIQ EALREHSNPN YDKTSAPITC ELLNKQVKVS PDMAIF ITM NPGYAGRSNL PDNLKKLFRS LAMTKPDRQL IAQVMLYSQG FRTAEVLANK IVPFFKLCDE QLSSQSHYDF GLRALKS VL VSAGNVKRER IQKIKREKEE RGEAVDEGEI AENLPEQEIL IQSVCETMVP KLVAEDIPLL FSLLSDVFPG VQYHRGEM T ALREELKKVC QEMYLTYGDG EEVGGMWVEK VLQLYQITQI NHGLMMVGPS GSGKSMAWRV LLKALERLEG VEGVAHIID PKAISKDHLY GTLDPNTREW TDGLFTHVLR KIIDSVRGEL QKRQWIVFDG DVDPEWVENL NSVLDDNKLL TLPNGERLSL PPNVRIMFE VQDLKYATLA TVSRCGMVWF SEDVLSTDMI FNNFLARLRS IPLDEGEDEA QRRRKGKEDE GEEAASPMLQ I QRDAATIM QPYFTSNGLV TKALEHAFQL EHIMDLTRLR CLGSLFSMLH QACRNVAQYN ANHPDFPMQI EQLERYIQRY LV YAILWSL SGDSRLKMRA ELGEYIRRIT TVPLPTAPNI PIIDYEVSIS GEWSPWQAKV PQIEVETHKV AAPDVVVPTL DTV RHEALL YTWLAEHKPL VLCGPPGSGK TMTLFSALRA LPDMEVVGLN FSSATTPELL LKTFDHYCEY RRTPNGVVLA PVQL GKWLV LFCDEINLPD MDKYGTQRVI SFIRQMVEHG GFYRTSDQTW VKLERIQFVG ACNPPTDPGR KPLSHRFLRH VPVVY VDYP GPASLTQIYG TFNRAMLRLI PSLRTYAEPL TAAMVEFYTM SQERFTQDTQ PHYIYSPREM TRWVRGIFEA LRPLET LPV EGLIRIWAHE ALRLFQDRLV EDEERRWTDE NIDTVALKHF PNIDREKAMS RPILYSNWLS KDYIPVDQEE LRDYVKA RL KVFYEEELDV PLVLFNEVLD HVLRIDRIFR QPQGHLLLIG VSGAGKTTLS RFVAWMNGLS VYQIKVHRKY TGEDFDED L RTVLRRSGCK NEKIAFIMDE SNVLDSGFLE RMNTLLANGE VPGLFEGDEY ATLMTQCKEG AQKEGLMLDS HEELYKWFT SQVIRNLHVV FTMNPSSEGL KDRAATSPAL FNRCVLNWFG DWSTEALYQV GKEFTSKMDL EKPNYIVPDY MPVVYDKLPQ PPSHREAIV NSCVFVHQTL HQANARLAKR GGRTMAITPR HYLDFINHYA NLFHEKRSEL EEQQMHLNVG LRKIKETVDQ V EELRRDLR IKSQELEVKN AAANDKLKKM VKDQQEAEKK KVMSQEIQEQ LHKQQEVIAD KQMSVKEDLL ALDQEVQELK KR LQEVQTE RNQVAKRVPK APPEEKEALI ARGRALGEEA KRLEEALREK EAQLEALRNE LQKLEDDAKD NQQKANEVEQ MIR DLEASI ARYKEEYAVL ISEAQAIKAD LAAVEAKVNR STALLKSLSA ERERWEKTSE TFKNQMSTIA GDCLLSAAFI AYAG YFDQQ MRQNLFTTWS HHLQQANIQF RTDIARTEYL SNADERLRWQ ASSLPADDLC TENAIMLKRF NRYPLIIDPS GQATE FIMN EYKDRKITRT SFLDDAFRKN LESALRFGNP LLVQDVESYD PVLNPVLNRE VRRTGGRVLI TLGDQDIDLS PSFVIF LST RDPTVEFPPD LCSRVTFVNF TVTRSSLQSQ CLNEVLKAER PDVDEKRSDL LKLQGEFQLR LRQLEKSLLQ ALNEVKG RI LDDDTIITTL ENLKREAAEV TRKVEETDIV MQEVETVSQQ YLPLSTACSS IYFTMESLKQ IHFLYQYSLQ FFLDIYHN V LYENPNLKGV TDHTQRLSII TKDLFQVAFN RVARGMLHQD HITFAMLLAR IKLKGTVGEP TYDAEFQHFL RGNEIVLSA GSTPRIQGLT VEQAEAVVRL SCLPAFKDLI AKVQADEQFG IWLDSSSPEQ TVPYLWSEET PATPIGQAIH RLLLIQAFRP DRLLAMAHM FVSTNLGESF MSIMEQPLDL THIVGTEVKP NTPVLMCSVP GYDASGHVED LAAEQNTQIT SIAIGSAEGF N QADKAINT AVKSGRWVML KNVHLAPGWL MQLEKKLHSL QPHACFRLFL TMEINPKVPV NLLRAGRIFV FEPPPGVKAN ML RTFSSIP VSRICKSPNE RARLYFLLAW FHAIIQERLR YAPLGWSKKY EFGESDLRSA CDTVDTWLDD TAKGRQNISP DKI PWSALK TLMAQSIYGG RVDNEFDQRL LNTFLERLFT TRSFDSEFKL ACKVDGHKDI QMPDGIRREE FVQWVELLPD TQTP SWLGL PNNAERVLLT TQGVDMISKM LKMQMLEDED DLAYAETEKK TRTDSTSDGR PAWMRTLHTT ASNWLHLIPQ TLSHL KRTV ENIKDPLFRF FEREVKMGAK LLQDVRQDLA DVVQVCEGKK KQTNYLRTLI NELVKGILPR SWSHYTVPAG MTVIQW VSD FSERIKQLQN ISLAAASGGA KELKNIHVCL GGLFVPEAYI TATRQYVAQA NSWSLEELCL EVNVTTSQGA TLDACSF GV TGLKLQGATC NNNKLSLSNA ISTALPLTQL RWVKQTNTEK KASVVTLPVY LNFTRADLIF TVDFEIATKE DPRSFYER G VAVLCTEEF UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1, Serine--tRNA ligase, Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: 50 mM Tris pH 7.4, 150 mM potassium acetate, 2 mM magnesium acetate, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM Mg-ATP |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 7676 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 7420 pixel / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 3.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.2 µm / Calibrated magnification: 36000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 36000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8fcy: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)