[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-29014: Engineered human dynein motor domain in the microtubule-unbound s... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Engineered human dynein motor domain in the microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in the buffer containing ATP-Vi (local refined on AAA3-AAA5 and LIS1) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Unsharpened map of engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in buffer containing ATP-Vi (local refined on AAA3-AAA5 and LIS1 region) | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dynein / motor domain / microtubule-unbound / MOTOR PROTEIN / LIS1 | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / corpus callosum morphogenesis / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity ...microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / corpus callosum morphogenesis / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / acrosome assembly / central region of growth cone / cerebral cortex neuron differentiation / establishment of centrosome localization / microtubule sliding / positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of embryonic development / microtubule organizing center organization / interneuron migration / layer formation in cerebral cortex / auditory receptor cell development / astral microtubule / nuclear membrane disassembly / cortical microtubule organization / positive regulation of intracellular transport / positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / myeloid leukocyte migration / reelin-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / osteoclast development / stereocilium / microtubule plus-end binding / brain morphogenesis / vesicle transport along microtubule / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / kinesin complex / retrograde axonal transport / P-body assembly / negative regulation of JNK cascade / microtubule associated complex / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / neuromuscular process controlling balance / stem cell division / nuclear migration / germ cell development / cell leading edge / dynein intermediate chain binding / transmission of nerve impulse / dynein complex binding / dynactin binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / protein secretion / cochlea development / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of axon extension / microtubule-based process / lipid catabolic process / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / phospholipase binding / cytoplasmic microtubule / JNK cascade / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Mitotic Prometaphase / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / mitotic spindle organization / adult locomotory behavior / filopodium / hippocampus development / phosphoprotein binding / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / neuron migration / HCMV Early Events Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
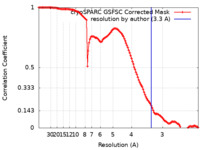
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ton W / Wang Y / Chai P | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Microtubule-binding-induced allostery triggers LIS1 dissociation from dynein prior to cargo transport. Authors: William D Ton / Yue Wang / Pengxin Chai / Cisloynny Beauchamp-Perez / Nicholas T Flint / Lindsay G Lammers / Hao Xiong / Kai Zhang / Steven M Markus /  Abstract: The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 ...The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 binding is required for dynein activity, its unbinding prior to initiation of cargo transport is equally important, since preventing dissociation leads to dynein dysfunction. To understand whether and how dynein-LIS1 binding is modulated, we engineered dynein mutants locked in a microtubule-bound (MT-B) or microtubule-unbound (MT-U) state. Whereas the MT-B mutant exhibits low LIS1 affinity, the MT-U mutant binds LIS1 with high affinity, and as a consequence remains almost irreversibly associated with microtubule plus-ends. We find that a monomeric motor domain is sufficient to exhibit these opposing LIS1 affinities, and that this is evolutionarily conserved between yeast and humans. Three cryo-EM structures of human dynein with and without LIS1 reveal microtubule-binding induced conformational changes responsible for this regulation. Our work reveals key biochemical and structural insight into LIS1-mediated dynein activation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29014.map.gz emd_29014.map.gz | 89.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29014-v30.xml emd-29014-v30.xml emd-29014.xml emd-29014.xml | 23.7 KB 23.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29014_fsc.xml emd_29014_fsc.xml | 11.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
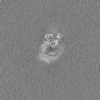
| Images |  emd_29014.png emd_29014.png | 73.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_29014_msk_1.map emd_29014_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29014.cif.gz emd-29014.cif.gz | 8.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29014_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29014_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29014_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29014_half_map_2.map.gz | 165 MB 165 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29014 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29014 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29014 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29014 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8fduMC  8fcyC  8fd6C  8fdtC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29014.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29014.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
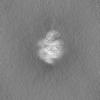
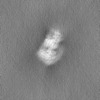
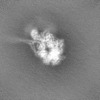
| Annotation | Unsharpened map of engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in buffer containing ATP-Vi (local refined on AAA3-AAA5 and LIS1 region) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
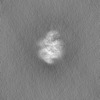
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.149 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
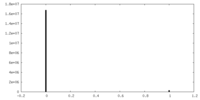
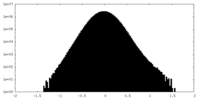
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_29014_msk_1.map emd_29014_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
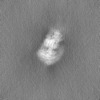
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
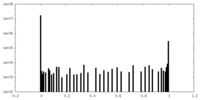
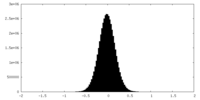
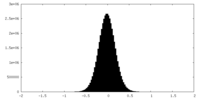
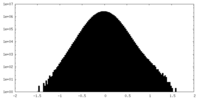
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A of engineered human dynein motor...
| File | emd_29014_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A of engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in buffer containing ATP-Vi (local refined on AAA3-AAA5 and LIS1 region) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B of engineered human dynein motor...
| File | emd_29014_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B of engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in buffer containing ATP-Vi (local refined on AAA3-AAA5 and LIS1 region) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state...
| Entire | Name: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in the buffer containing ATP-Vi |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state...
| Supramolecule | Name: Engineered human dynein motor domain in microtubule-unbound state with LIS1 complex in the buffer containing ATP-Vi type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 490 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Serine--tRNA ligase
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Serine--tRNA ligase type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: residues 1458-3277 of dynein followed by residues 30-96 of serine-tRNA ligase, followed by residues 3412-4646 of dynein Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: serine-tRNA ligase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 357.459125 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSALEEFLKQ IREVWNTYEL DLVNYQNKCR LIRGWDDLFN KVKEHINSVS AMKLSPYYKV FEEDALSWED KLNRIMALFD VWIDVQRRW VYLEGIFTGS ADIKHLLPVE TQRFQSISTE FLALMKKVSK SPLVMDVLNI QGVQRSLERL ADLLGKIQKA L GEYLERER ...String: GSALEEFLKQ IREVWNTYEL DLVNYQNKCR LIRGWDDLFN KVKEHINSVS AMKLSPYYKV FEEDALSWED KLNRIMALFD VWIDVQRRW VYLEGIFTGS ADIKHLLPVE TQRFQSISTE FLALMKKVSK SPLVMDVLNI QGVQRSLERL ADLLGKIQKA L GEYLERER SSFPRFYFVG DEDLLEIIGN SKNVAKLQKH FKKMFAGVSS IILNEDNSVV LGISSREGEE VMFKTPVSIT EH PKINEWL TLVEKEMRVT LAKLLAESVT EVEIFGKATS IDPNTYITWI DKYQAQLVVL SAQIAWSENV ETALSSMGGG GDA APLHSV LSNVEVTLNV LADSVLMEQP PLRRRKLEHL ITELVHQRDV TRSLIKSKID NAKSFEWLSQ MRFYFDPKQT DVLQ QLSIQ MANAKFNYGF EYLGVQDKLV QTPLTDRCYL TMTQALEARL GGSPFGPAGT GKTESVKALG HQLGRFVLVF NCDET FDFQ AMGRIFVGLC QVGAWGCFDE FNRLEERMLS AVSQQVQCIQ EALREHSNPN YDKTSAPITC ELLNKQVKVS PDMAIF ITM NPGYAGRSNL PDNLKKLFRS LAMTKPDRQL IAQVMLYSQG FRTAEVLANK IVPFFKLCDE QLSSQSHYDF GLRALKS VL VSAGNVKRER IQKIKREKEE RGEAVDEGEI AENLPEQEIL IQSVCETMVP KLVAEDIPLL FSLLSDVFPG VQYHRGEM T ALREELKKVC QEMYLTYGDG EEVGGMWVEK VLQLYQITQI NHGLMMVGPS GSGKSMAWRV LLKALERLEG VEGVAHIID PKAISKDHLY GTLDPNTREW TDGLFTHVLR KIIDSVRGEL QKRQWIVFDG DVDPEWVENL NSVLDDNKLL TLPNGERLSL PPNVRIMFE VQDLKYATLA TVSRCGMVWF SEDVLSTDMI FNNFLARLRS IPLDEGEDEA QRRRKGKEDE GEEAASPMLQ I QRDAATIM QPYFTSNGLV TKALEHAFQL EHIMDLTRLR CLGSLFSMLH QACRNVAQYN ANHPDFPMQI EQLERYIQRY LV YAILWSL SGDSRLKMRA ELGEYIRRIT TVPLPTAPNI PIIDYEVSIS GEWSPWQAKV PQIEVETHKV AAPDVVVPTL DTV RHEALL YTWLAEHKPL VLCGPPGSGK TMTLFSALRA LPDMEVVGLN FSSATTPELL LKTFDHYCEY RRTPNGVVLA PVQL GKWLV LFCDEINLPD MDKYGTQRVI SFIRQMVEHG GFYRTSDQTW VKLERIQFVG ACNPPTDPGR KPLSHRFLRH VPVVY VDYP GPASLTQIYG TFNRAMLRLI PSLRTYAEPL TAAMVEFYTM SQERFTQDTQ PHYIYSPREM TRWVRGIFEA LRPLET LPV EGLIRIWAHE ALRLFQDRLV EDEERRWTDE NIDTVALKHF PNIDREKAMS RPILYSNWLS KDYIPVDQEE LRDYVKA RL KVFYEEELDV PLVLFNEVLD HVLRIDRIFR QPQGHLLLIG VSGAGKTTLS RFVAWMNGLS VYQIKVHRKY TGEDFDED L RTVLRRSGCK NEKIAFIMDE SNVLDSGFLE RMNTLLANGE VPGLFEGDEY ATLMTQCKEG AQKEGLMLDS HEELYKWFT SQVIRNLHVV FTMNPSSEGL KDRAATSPAL FNRCVLNWFG DWSTEALYQV GKEFTSKMDL EKPNYIVPDY MPVVYDKLPQ PPSHREAIV NSCVFVHQTL HQANARLAKR GGRTMAITPR HYLDFINHYA NLFHEKRSEL EEQQMHLNVG LRKIKETVDQ V EELRRDLR IKSQELEVKN AAANDKLKKM VKDQQEAEKK KVMSQEIQEQ LHKQQEVIAD KQMSLLALDQ EVQELKKRLQ EV QTERNQV AKRVPKAPPE EKEALIARGR ALGEEAKRLE EALREKEAQL EALRNELQKL EDDAKDNQQK ANEVEQMIRD LEA SIARYK EEYAVLISEA QAIKADLAAV EAKVNRSTAL LKSLSAERER WEKTSETFKN QMSTIAGDCL LSAAFIAYAG YFDQ QMRQN LFTTWSHHLQ QANIQFRTDI ARTEYLSNAD ERLRWQASSL PADDLCTENA IMLKRFNRYP LIIDPSGQAT EFIMN EYKD RKITRTSFLD DAFRKNLESA LRFGNPLLVQ DVESYDPVLN PVLNREVRRT GGRVLITLGD QDIDLSPSFV IFLSTR DPT VEFPPDLCSR VTFVNFTVTR SSLQSQCLNE VLKAERPDVD EKRSDLLKLQ GEFQLRLRQL EKSLLQALNE VKGRILD DD TIITTLENLK REAAEVTRKV EETDIVMQEV ETVSQQYLPL STACSSIYFT MESLKQIHFL YQYSLQFFLD IYHNVLYE N PNLKGVTDHT QRLSIITKDL FQVAFNRVAR GMLHQDHITF AMLLARIKLK GTVGEPTYDA EFQHFLRGNE IVLSAGSTP RIQGLTVEQA EAVVRLSCLP AFKDLIAKVQ ADEQFGIWLD SSSPEQTVPY LWSEETPATP IGQAIHRLLL IQAFRPDRLL AMAHMFVST NLGESFMSIM EQPLDLTHIV GTEVKPNTPV LMCSVPGYDA SGHVEDLAAE QNTQITSIAI GSAEGFNQAD K AINTAVKS GRWVMLKNVH LAPGWLMQLE KKLHSLQPHA CFRLFLTMEI NPKVPVNLLR AGRIFVFEPP PGVKANMLRT FS SIPVSRI CKSPNERARL YFLLAWFHAI IQERLRYAPL GWSKKYEFGE SDLRSACDTV DTWLDDTAKG RQNISPDKIP WSA LKTLMA QSIYGGRVDN EFDQRLLNTF LERLFTTRSF DSEFKLACKV DGHKDIQMPD GIRREEFVQW VELLPDTQTP SWLG LPNNA ERVLLTTQGV DMISKMLKMQ MLEDEDDLAY AETEKKTRTD STSDGRPAWM RTLHTTASNW LHLIPQTLSH LKRTV ENIK DPLFRFFERE VKMGAKLLQD VRQDLADVVQ VCEGKKKQTN YLRTLINELV KGILPRSWSH YTVPAGMTVI QWVSDF SER IKQLQNISLA AASGGAKELK NIHVCLGGLF VPEAYITATR QYVAQANSWS LEELCLEVNV TTSQGATLDA CSFGVTG LK LQGATCNNNK LSLSNAISTA LPLTQLRWVK QTNTEKKASV VTLPVYLNFT RADLIFTVDF EIATKEDPRS FYERGVAV L CTEEF UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1, Serine--tRNA ligase, Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta,Platel...
| Macromolecule | Name: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta,Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta,human LIS1 protein with a SNAP tag type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: SNAP tag present on C-terminus,SNAP tag present on C-terminus Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 66.423547 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSVLSQRQRD ELNRAIADYL RSNGYEEAYS VFKKEAELDV NEELDKKYAG LLEKKWTSVI RLQKKVMELE SKLNEAKEEF TSGGPLGQK RDPKEWIPRP PEKYALSGHR SPVTRVIFHP VFSVMVSASE DATIKVWDYE TGDFERTLKG HTDSVQDISF D HSGKLLAS ...String: GSVLSQRQRD ELNRAIADYL RSNGYEEAYS VFKKEAELDV NEELDKKYAG LLEKKWTSVI RLQKKVMELE SKLNEAKEEF TSGGPLGQK RDPKEWIPRP PEKYALSGHR SPVTRVIFHP VFSVMVSASE DATIKVWDYE TGDFERTLKG HTDSVQDISF D HSGKLLAS CSADMTIKLW DFQGFECIRT MHGHDHNVSS VAIMPNGDHI VSASRDKTIK MWEVQTGYCV KTFTGHREWV RM VRPNQDG TLIASCSNDQ TVRVWVVATK ECKAELREHE HVVECISWAP ESSYSSISEA TGSETKKSGK PGPFLLSGSR DKT IKMWDV STGMCLMTLV GHDNWVRGVL FHSGGKFILS CADDKTLRVW DYKNKRCMKT LNAHEHFVTS LDFHKTAPYV VTGS VDQTV KVWECRGAGA GADKDCEMKR TTLDSPLGKL ELSGCEQGLH RIIFLGKGTS AADAVEVPAP AAVLGGPEPL MQATA WLNA YFHQPEAIEE FPVPALHHPV FQQESFTRQV LWKLLKVVKF GEVISYSHLA ALAGNPAATA AVKTALSGNP VPILIP CHR VVQGDLDVGG YEGGLAVKEW LLAHEGHRLG KPGLG UniProtKB: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: 50 mM Tris pH 7.4, 150 mM potassium acetate, 2 mM magnesium acetate, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM Mg-ATP |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 1 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 3.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.2 µm / Calibrated magnification: 105000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8fdu: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)