[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8ccy: Human heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1 in compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ccy | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1 in complex with calcium and 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CARBOHYDRATE / Deacetylase / Sulfotransferase / Heparan Sulfate / Glycosaminoglycan | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information[heparan sulfate]-glucosamine N-sulfotransferase / heparan sulfate N-sulfotransferase activity / heparan sulfate N-deacetylase activity / N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase activity / heparin proteoglycan biosynthetic process / embryonic neurocranium morphogenesis / embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis / HS-GAG biosynthesis / cardiac septum development / glycosaminoglycan metabolic process ...[heparan sulfate]-glucosamine N-sulfotransferase / heparan sulfate N-sulfotransferase activity / heparan sulfate N-deacetylase activity / N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase activity / heparin proteoglycan biosynthetic process / embryonic neurocranium morphogenesis / embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis / HS-GAG biosynthesis / cardiac septum development / glycosaminoglycan metabolic process / heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process / deacetylase activity / respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system / polysaccharide biosynthetic process / coronary vasculature development / positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / Hydrolases; Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds; In linear amides / aorta development / midbrain development / forebrain development / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / trans-Golgi network membrane / cell population proliferation / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / inflammatory response / Golgi membrane / Golgi apparatus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mycroft-West, C.J. / Wu, L. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 6items United Kingdom, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural and mechanistic characterization of bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1. Authors: Courtney J Mycroft-West / Sahar Abdelkarim / Helen M E Duyvesteyn / Neha S Gandhi / Mark A Skidmore / Raymond J Owens / Liang Wu /    Abstract: Heparan sulfate (HS) polysaccharides are major constituents of the extracellular matrix, which are involved in myriad structural and signaling processes. Mature HS polysaccharides contain complex, ...Heparan sulfate (HS) polysaccharides are major constituents of the extracellular matrix, which are involved in myriad structural and signaling processes. Mature HS polysaccharides contain complex, non-templated patterns of sulfation and epimerization, which mediate interactions with diverse protein partners. Complex HS modifications form around initial clusters of glucosamine-N-sulfate (GlcNS) on nascent polysaccharide chains, but the mechanistic basis underpinning incorporation of GlcNS itself into HS remains unclear. Here, we determine cryo-electron microscopy structures of human N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase (NDST)1, the bifunctional enzyme primarily responsible for initial GlcNS modification of HS. Our structures reveal the architecture of both NDST1 deacetylase and sulfotransferase catalytic domains, alongside a non-catalytic N-terminal domain. The two catalytic domains of NDST1 adopt a distinct back-to-back topology that limits direct cooperativity. Binding analyses, aided by activity-modulating nanobodies, suggest that anchoring of the substrate at the sulfotransferase domain initiates the NDST1 catalytic cycle, providing a plausible mechanism for cooperativity despite spatial domain separation. Our data shed light on key determinants of NDST1 activity, and describe tools to probe NDST1 function in vitro and in vivo. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ccy.cif.gz 8ccy.cif.gz | 207.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ccy.ent.gz pdb8ccy.ent.gz | 128.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ccy.json.gz 8ccy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/8ccy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/8ccy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/8ccy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/8ccy | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16564MC  8cd0C  8chsC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 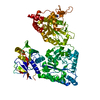
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 92407.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NDST1, HSST, HSST1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NDST1, HSST, HSST1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P52848, Hydrolases; Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds; In linear amides, [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine N-sulfotransferase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-A3P / | ||||||
| #3: Chemical | | #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Monodisperse sample from size exclusion |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: EPU / Category: image acquisition | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 371778 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 85.48 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj