[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8bfb: Sarkosyl-extracted AppNL-G-F Abeta42 fibril structure (Methoxy-X0... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8bfb | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Sarkosyl-extracted AppNL-G-F Abeta42 fibril structure (Methoxy-X04-labelled mice) | |||||||||
 Components Components | Amyloid-beta precursor protein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / Amyloid / fibril / helical / cross-beta / beta amyloid / ex vivo / arctic mutant / alzheimers disease | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationamyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process ...amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / axon midline choice point recognition / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / regulation of synapse structure or activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / growth factor receptor binding / peptidase activator activity / Golgi-associated vesicle / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / astrocyte projection / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / dendrite development / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / signaling receptor activator activity / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / transition metal ion binding / main axon / The NLRP3 inflammasome / regulation of multicellular organism growth / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of T cell migration / neuronal dense core vesicle / response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / positive regulation of chemokine production / Notch signaling pathway / cellular response to manganese ion / swimming behavior / clathrin-coated pit / extracellular matrix organization / neuron projection maintenance / astrocyte activation / Mitochondrial protein degradation / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / axonogenesis / response to interleukin-1 / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / platelet alpha granule lumen / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of glycolytic process / central nervous system development / dendritic shaft / trans-Golgi network membrane / endosome lumen / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / adult locomotory behavior / learning / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / locomotory behavior / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / microglial cell activation / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / recycling endosome / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / synapse organization / visual learning / positive regulation of JNK cascade / response to lead ion / Golgi lumen / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / cellular response to amyloid-beta / endocytosis / neuron projection development / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / positive regulation of inflammatory response / calcium ion transport / Platelet degranulation / regulation of translation / heparin binding / regulation of gene expression Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wilkinson, M. / Leistner, C. / Burgess, A. / Goodfellow, S. / Deuchars, S. / Ranson, N.A. / Radford, S.E. / Frank, R.A.W. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: The in-tissue molecular architecture of β-amyloid pathology in the mammalian brain. Authors: Conny Leistner / Martin Wilkinson / Ailidh Burgess / Megan Lovatt / Stanley Goodbody / Yong Xu / Susan Deuchars / Sheena E Radford / Neil A Ranson / René A W Frank /  Abstract: Amyloid plaques composed of Aβ fibrils are a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the molecular architecture of amyloid plaques in the context of fresh mammalian brain tissue is unknown. ...Amyloid plaques composed of Aβ fibrils are a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the molecular architecture of amyloid plaques in the context of fresh mammalian brain tissue is unknown. Here, using cryogenic correlated light and electron tomography we report the in situ molecular architecture of Aβ fibrils in the App familial AD mouse model containing the Arctic mutation and an atomic model of ex vivo purified Arctic Aβ fibrils. We show that in-tissue Aβ fibrils are arranged in a lattice or parallel bundles, and are interdigitated by subcellular compartments, extracellular vesicles, extracellular droplets and extracellular multilamellar bodies. The Arctic Aβ fibril differs significantly from an earlier App fibril structure, indicating a striking effect of the Arctic mutation. These structural data also revealed an ensemble of additional fibrillar species, including thin protofilament-like rods and branched fibrils. Together, these results provide a structural model for the dense network architecture that characterises β-amyloid plaque pathology. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8bfb.cif.gz 8bfb.cif.gz | 70.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8bfb.ent.gz pdb8bfb.ent.gz | 53.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8bfb.json.gz 8bfb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/8bfb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/8bfb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/8bfb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/8bfb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16019MC  8bfaC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 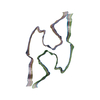
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4448.025 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Humanised Abeta42 from App^NL-G-F mice with arctic mutation (E22G) Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Sarkosyl-extracted AppNL-G-F Abeta42 fibril / Type: COMPLEX Details: Fibrils purified from mouse brain labelled with Methoxy-X04 Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 4.441 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Sarkosyl-insoluble fibrils from App^NL-G-F mouse brain labelled with Methoxy-X04 | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: 6s blot |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1400 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 6 sec. / Electron dose: 41 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4165 Details: 1442 raw EER frames were collected per image and combined into 40 fractions for processing |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: TFS Selectris / Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 179.355 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 2.414 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 136214 Details: Manually picked a subset of images to train a model for automatic fibril segment picking in crYOLO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 3640 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 52 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj