+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7unf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
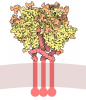
| Title | CryoEM structure of a mEAK7 bound human V-ATPase complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / mTOR signaling | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationBlockage of phagosome acidification / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / renal tubular secretion / Nef Mediated CD8 Down-regulation / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / Golgi lumen acidification ...Blockage of phagosome acidification / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy / intracellular pH reduction / renal tubular secretion / Nef Mediated CD8 Down-regulation / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / Golgi lumen acidification / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / vacuolar transport / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / regulation of pH / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / Nef Mediated CD4 Down-regulation / vacuolar acidification / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / regulation of cellular pH / dendritic spine membrane / azurophil granule membrane / proton transmembrane transporter activity / microvillus / ATPase activator activity / tertiary granule membrane / autophagosome membrane / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / cilium assembly / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / RHOA GTPase cycle / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / transporter activator activity / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / specific granule membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / enzyme regulator activity / ruffle / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / axon terminus / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / ossification / secretory granule / brush border membrane / sensory perception of sound / transmembrane transport / small GTPase binding / phagocytic vesicle membrane / endocytosis / apical part of cell / synaptic vesicle membrane / melanosome / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / basolateral plasma membrane / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / early endosome / endosome / endosome membrane / cilium / apical plasma membrane / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / focal adhesion / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.08 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, R. / Li, X. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Molecular basis of mEAK7-mediated human V-ATPase regulation. Authors: Rong Wang / Yu Qin / Xiao-Song Xie / Xiaochun Li /  Abstract: The activity of V-ATPase is well-known to be regulated by reversible dissociation of its V and V domains in response to growth factor stimulation, nutrient sensing, and cellular differentiation. The ...The activity of V-ATPase is well-known to be regulated by reversible dissociation of its V and V domains in response to growth factor stimulation, nutrient sensing, and cellular differentiation. The molecular basis of its regulation by an endogenous modulator without affecting V-ATPase assembly remains unclear. Here, we discover that a lysosome-anchored protein termed (mammalian Enhancer-of-Akt-1-7 (mEAK7)) binds to intact V-ATPase. We determine cryo-EM structure of human mEAK7 in complex with human V-ATPase in native lipid-containing nanodiscs. The structure reveals that the TLDc domain of mEAK7 engages with subunits A, B, and E, while its C-terminal domain binds to subunit D, presumably blocking V-V torque transmission. Our functional studies suggest that mEAK7, which may act as a V-ATPase inhibitor, does not affect the activity of V-ATPase in vitro. However, overexpression of mEAK7 in HCT116 cells that stably express subunit a4 of V-ATPase represses the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Thus, this finding suggests that mEAK7 potentially links mTOR signaling with V-ATPase activity. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7unf.cif.gz 7unf.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7unf.ent.gz pdb7unf.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7unf.json.gz 7unf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/un/7unf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/un/7unf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/un/7unf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/un/7unf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26623MC  7uneC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type proton ATPase ... , 14 types, 30 molecules aLMNOPQDbcdefgFCHkms8923456701
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98530.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP6V0A4, ATP6N1B, ATP6N2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP6V0A4, ATP6N1B, ATP6N2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9HBG4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9HBG4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 68379.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P38606, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #4: Protein | Mass: 56561.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21281 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21281#5: Protein | | Mass: 28311.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y5K8 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y5K8#6: Protein | Mass: 26183.346 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P36543 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P36543#7: Protein | Mass: 13781.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75348 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75348#8: Protein | | Mass: 13388.210 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16864 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16864#9: Protein | | Mass: 43999.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21283 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21283#10: Protein | | Mass: 55949.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UI12 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UI12#11: Protein | | Mass: 40369.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61421 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61421#12: Protein | | Mass: 9380.329 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15342 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15342#14: Protein | | Mass: 52067.480 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15904 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15904#16: Protein | Mass: 15743.655 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27449 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P27449#17: Protein | | Mass: 21418.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q99437 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q99437 |
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules Unr
| #2: Protein | Mass: 51096.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: D3DUL8 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: D3DUL8 |
|---|---|
| #13: Protein | Mass: 15435.220 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q6P5S7, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 38421.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: A0A1B0GVW0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: A0A1B0GVW0 |
-Sugars , 3 types, 8 molecules 
| #18: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 1397.245 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #19: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-alpha-D-mannopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
| #21: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 10 molecules 


| #20: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
|---|---|
| #22: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CryoEM structure of mEAK7 bound human V-ATPase complex Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#17 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.08 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 24984 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj