[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
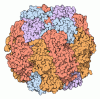
Yorodumi- PDB-7snv: H. neapolitanus carboxysomal rubisco/CsoSCA-peptide (1-50)complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7snv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | H. neapolitanus carboxysomal rubisco/CsoSCA-peptide (1-50)complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE / rubisco / TIM-barrel / complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcarboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / carbon fixation / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / monooxygenase activity / carbonic anhydrase / carbonate dehydratase activity / magnesium ion binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (bacteria) Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.07 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Blikstad, C. / Dugan, E. / Laughlin, T.G. / Liu, M. / Shoemaker, S. / Remis, J. / Savage, D.F. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: Identification of a carbonic anhydrase-Rubisco complex within the alpha-carboxysome. Authors: Cecilia Blikstad / Eli J Dugan / Thomas G Laughlin / Julia B Turnšek / Mira D Liu / Sophie R Shoemaker / Nikoleta Vogiatzi / Jonathan P Remis / David F Savage /   Abstract: Carboxysomes are proteinaceous organelles that encapsulate key enzymes of CO fixation-Rubisco and carbonic anhydrase-and are the centerpiece of the bacterial CO concentrating mechanism (CCM). In the ...Carboxysomes are proteinaceous organelles that encapsulate key enzymes of CO fixation-Rubisco and carbonic anhydrase-and are the centerpiece of the bacterial CO concentrating mechanism (CCM). In the CCM, actively accumulated cytosolic bicarbonate diffuses into the carboxysome and is converted to CO by carbonic anhydrase, producing a high CO concentration near Rubisco and ensuring efficient carboxylation. Self-assembly of the α-carboxysome is orchestrated by the intrinsically disordered scaffolding protein, CsoS2, which interacts with both Rubisco and carboxysomal shell proteins, but it is unknown how the carbonic anhydrase, CsoSCA, is incorporated into the α-carboxysome. Here, we present the structural basis of carbonic anhydrase encapsulation into α-carboxysomes from . We find that CsoSCA interacts directly with Rubisco via an intrinsically disordered N-terminal domain. A 1.98 Å single-particle cryoelectron microscopy structure of Rubisco in complex with this peptide reveals that CsoSCA binding is predominantly mediated by a network of hydrogen bonds. CsoSCA's binding site overlaps with that of CsoS2, but the two proteins utilize substantially different motifs and modes of binding, revealing a plasticity of the Rubisco binding site. Our results advance the understanding of carboxysome biogenesis and highlight the importance of Rubisco, not only as an enzyme but also as a central hub for mediating assembly through protein interactions. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7snv.cif.gz 7snv.cif.gz | 119 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7snv.ent.gz pdb7snv.ent.gz | 88.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7snv.json.gz 7snv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7snv_validation.pdf.gz 7snv_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7snv_full_validation.pdf.gz 7snv_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7snv_validation.xml.gz 7snv_validation.xml.gz | 35.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7snv_validation.cif.gz 7snv_validation.cif.gz | 51.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sn/7snv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sn/7snv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sn/7snv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sn/7snv | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25228MC  7smkC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 8
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 53831.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria) Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 23641 / c2 / Gene: cbbL, Hneap_0922 / Production host:  References: UniProt: O85040, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 12866.575 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria) Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 23641 / c2 / Gene: cbbS, rbcS, Hneap_0921 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P45686, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5690.505 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically Source: (synth.)  Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria) Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria)References: UniProt: O85042, carbonic anhydrase |
| #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.533 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria) Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (strain ATCC 23641 / c2) (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2665 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 0.5 uM of rubisco and 0.5 mM of peptide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: blot for 3 seconds |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 57000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 5742 / Details: 3 x 3 multishot image shift pattern. |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTF correction was performed during 3D reconstruction Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D4 (2x4 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.07 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 52375 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Map-model FSC and geometry |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj