[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7ru4: CC6.33 IgG in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein (RBD/Fv l... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ru4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
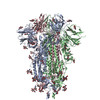
| Title | CC6.33 IgG in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein (RBD/Fv local refinement) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN/Immune System / COVID / SARS-CoV-2 / stabilizing mutations / neutralizing antibody / RBD / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-Immune System complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / Attachment and Entry / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / receptor ligand activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ozorowski, G. / Turner, H.L. / Ward, A.B. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: iScience / Year: 2022 Journal: iScience / Year: 2022Title: Engineering SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for increased potency and reduced viral escape pathways. Authors: Fangzhu Zhao / Celina Keating / Gabriel Ozorowski / Namir Shaabani / Irene M Francino-Urdaniz / Shawn Barman / Oliver Limbo / Alison Burns / Panpan Zhou / Michael J Ricciardi / Jordan Woehl ...Authors: Fangzhu Zhao / Celina Keating / Gabriel Ozorowski / Namir Shaabani / Irene M Francino-Urdaniz / Shawn Barman / Oliver Limbo / Alison Burns / Panpan Zhou / Michael J Ricciardi / Jordan Woehl / Quoc Tran / Hannah L Turner / Linghang Peng / Deli Huang / David Nemazee / Raiees Andrabi / Devin Sok / John R Teijaro / Timothy A Whitehead / Andrew B Ward / Dennis R Burton / Joseph G Jardine /  Abstract: The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants poses a constant threat of escape from monoclonal antibody and vaccine countermeasures. Mutations in the ACE2 receptor binding site on the surface S protein ...The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants poses a constant threat of escape from monoclonal antibody and vaccine countermeasures. Mutations in the ACE2 receptor binding site on the surface S protein have been shown to disrupt antibody binding and prevent viral neutralization. Here, we used a directed evolution-based approach to engineer three neutralizing antibodies for enhanced binding to S protein. The engineered antibodies showed increased functional activity in terms of neutralization potency and/or breadth of neutralization against viral variants. Deep mutational scanning revealed that higher binding affinity reduces the total number of viral escape mutations. Studies in the Syrian hamster model showed two examples where the affinity-matured antibody provided superior protection compared to the parental antibody. These data suggest that monoclonal antibodies for antiviral indications would benefit from affinity maturation to reduce viral escape pathways and appropriate affinity maturation in vaccine immunization could help resist viral variation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ru4.cif.gz 7ru4.cif.gz | 115.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ru4.ent.gz pdb7ru4.ent.gz | 72.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ru4.json.gz 7ru4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/7ru4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/7ru4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/7ru4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/7ru4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24696MC  7ru1C  7ru2C  7ru3C  7ru5C  7ru8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 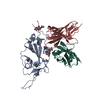
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Antibody | Mass: 12737.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 11727.018 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 141328.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Mutation: R682G, R683S, R685S, V705C, F817P, T883C, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Cell line (production host): HEK293F / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 |
| #4: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-[alpha-L-fucopyranose-(1-6)]2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-[alpha-L-fucopyranose-(1-6)]2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
| #5: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: Detergent added shortly before freezing | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.65 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: 3 s blot time |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 29000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 9.75 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 3465 |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 39 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 96012 Details: Particles were symmetry expanded and sorted on a single S protein RBD to classify only antibody-bound protomers using Relion 3.1. A mask was applied to the RBD and antibody Fv region, the ...Details: Particles were symmetry expanded and sorted on a single S protein RBD to classify only antibody-bound protomers using Relion 3.1. A mask was applied to the RBD and antibody Fv region, the remaining signal was subtracted, and the remaining signal was refined locally using cryoSPARC. Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6VXX Accession code: 6VXX / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj