[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24697: CC6.30 fragment antigen binding in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
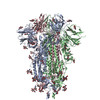
| Title | CC6.30 fragment antigen binding in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein (non-uniform refinement) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | COVID / SARS-CoV-2 / stabilizing mutations / neutralizing antibody / RBD / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-Immune System complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / receptor ligand activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
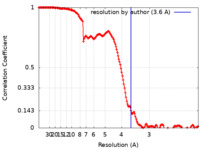
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ozorowski G / Turner HL / Ward AB | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: iScience / Year: 2022 Journal: iScience / Year: 2022Title: Engineering SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for increased potency and reduced viral escape pathways. Authors: Fangzhu Zhao / Celina Keating / Gabriel Ozorowski / Namir Shaabani / Irene M Francino-Urdaniz / Shawn Barman / Oliver Limbo / Alison Burns / Panpan Zhou / Michael J Ricciardi / Jordan Woehl ...Authors: Fangzhu Zhao / Celina Keating / Gabriel Ozorowski / Namir Shaabani / Irene M Francino-Urdaniz / Shawn Barman / Oliver Limbo / Alison Burns / Panpan Zhou / Michael J Ricciardi / Jordan Woehl / Quoc Tran / Hannah L Turner / Linghang Peng / Deli Huang / David Nemazee / Raiees Andrabi / Devin Sok / John R Teijaro / Timothy A Whitehead / Andrew B Ward / Dennis R Burton / Joseph G Jardine /  Abstract: The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants poses a constant threat of escape from monoclonal antibody and vaccine countermeasures. Mutations in the ACE2 receptor binding site on the surface S protein ...The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants poses a constant threat of escape from monoclonal antibody and vaccine countermeasures. Mutations in the ACE2 receptor binding site on the surface S protein have been shown to disrupt antibody binding and prevent viral neutralization. Here, we used a directed evolution-based approach to engineer three neutralizing antibodies for enhanced binding to S protein. The engineered antibodies showed increased functional activity in terms of neutralization potency and/or breadth of neutralization against viral variants. Deep mutational scanning revealed that higher binding affinity reduces the total number of viral escape mutations. Studies in the Syrian hamster model showed two examples where the affinity-matured antibody provided superior protection compared to the parental antibody. These data suggest that monoclonal antibodies for antiviral indications would benefit from affinity maturation to reduce viral escape pathways and appropriate affinity maturation in vaccine immunization could help resist viral variation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24697.map.gz emd_24697.map.gz | 324.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24697-v30.xml emd-24697-v30.xml emd-24697.xml emd-24697.xml | 28.6 KB 28.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24697_fsc.xml emd_24697_fsc.xml | 15.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24697.png emd_24697.png | 86.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_24697_msk_1.map emd_24697_msk_1.map | 343 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24697.cif.gz emd-24697.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24697_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24697_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24697_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24697_half_map_2.map.gz | 318.5 MB 318.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24697 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24697 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24697 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24697 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ru5MC  7ru1C  7ru2C  7ru3C  7ru4C  7ru8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24697.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24697.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
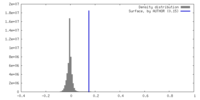
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_24697_msk_1.map emd_24697_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
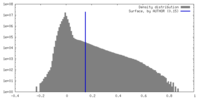
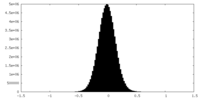
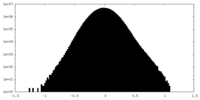
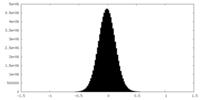
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_24697_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
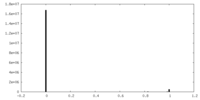
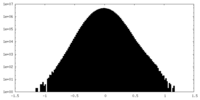
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_24697_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
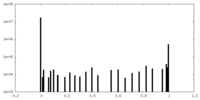
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : CC6.30 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein
| Entire | Name: CC6.30 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: CC6.30 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein
| Supramolecule | Name: CC6.30 Fab in complex with SARS-CoV-2-6P-Mut7 S protein type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 Details: Incubated Fab at 9:2 ratio with Spike trimer for about 15 minutes at room temperature |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Spike glycoprotein
| Supramolecule | Name: Spike glycoprotein / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: CC6.30 Fab
| Supramolecule | Name: CC6.30 Fab / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Spike glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Spike glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 141.328359 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MFVFLVLLPL VSSQCVNLTT RTQLPPAYTN SFTRGVYYPD KVFRSSVLHS TQDLFLPFFS NVTWFHAIHV SGTNGTKRFD NPVLPFNDG VYFASTEKSN IIRGWIFGTT LDSKTQSLLI VNNATNVVIK VCEFQFCNDP FLGVYYHKNN KSWMESEFRV Y SSANNCTF ...String: MFVFLVLLPL VSSQCVNLTT RTQLPPAYTN SFTRGVYYPD KVFRSSVLHS TQDLFLPFFS NVTWFHAIHV SGTNGTKRFD NPVLPFNDG VYFASTEKSN IIRGWIFGTT LDSKTQSLLI VNNATNVVIK VCEFQFCNDP FLGVYYHKNN KSWMESEFRV Y SSANNCTF EYVSQPFLMD LEGKQGNFKN LREFVFKNID GYFKIYSKHT PINLVRDLPQ GFSALEPLVD LPIGINITRF QT LLALHRS YLTPGDSSSG WTAGAAAYYV GYLQPRTFLL KYNENGTITD AVDCALDPLS ETKCTLKSFT VEKGIYQTSN FRV QPTESI VRFPNITNLC PFGEVFNATR FASVYAWNRK RISNCVADYS VLYNSASFST FKCYGVSPTK LNDLCFTNVY ADSF VIRGD EVRQIAPGQT GKIADYNYKL PDDFTGCVIA WNSNNLDSKV GGNYNYLYRL FRKSNLKPFE RDISTEIYQA GSTPC NGVE GFNCYFPLQS YGFQPTNGVG YQPYRVVVLS FELLHAPATV CGPKKSTNLV KNKCVNFNFN GLTGTGVLTE SNKKFL PFQ QFGRDIADTT DAVRDPQTLE ILDITPCSFG GVSVITPGTN TSNQVAVLYQ DVNCTEVPVA IHADQLTPTW RVYSTGS NV FQTRAGCLIG AEHVNNSYEC DIPIGAGICA SYQTQTNSPG SASSVASQSI IAYTMSLGAE NSCAYSNNSI AIPTNFTI S VTTEILPVSM TKTSVDCTMY ICGDSTECSN LLLQYGSFCT QLNRALTGIA VEQDKNTQEV FAQVKQIYKT PPIKDFGGF NFSQILPDPS KPSKRSPIED LLFNKVTLAD AGFIKQYGDC LGDIAARDLI CAQKFNGLTV LPPLLTDEMI AQYTSALLAG TICSGWTFG AGPALQIPFP MQMAYRFNGI GVTQNVLYEN QKLIANQFNS AIGKIQDSLS STPSALGKLQ DVVNQNAQAL N TLVKQLSS NFGAISSVLN DILSRLDPPE AEVQIDRLIT GRLQSLQTYV TQQLIRAAEI RASANLAATK MSECVLGQSK RV DFCGKGY HLMSFPQSAP HGVVFLHVTY VPAQEKNFTT APAICHDGKA HFPREGVFVS NGTHWFVTQR NFYEPQIITT DNT FVSGNC DVVIGIVNNT VYDPLQPELD SFKEELDKYF KNHTSPDVDL GDISGINASV VNIQKEIDRL NEVAKNLNES LIDL QELGK YEQGSGYIPE APRDGQAYVR KDGEWVLLST FLGRSLEVLF QGPGSAWSHP QFEKGGGSGG GGSGGSAWSH PQFEK UniProtKB: Spike glycoprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: CC6.30 Fab heavy chain Fv
| Macromolecule | Name: CC6.30 Fab heavy chain Fv / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.701453 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QVQLVQSGAE VKKPGSSVKV SCKASGGTFS IYAITWVRQA PGQGLEWMGG IIPIIGTANY AQKFQGRVTI TADKSTSTAY MELSSLRSE DTAVYYCARD FRYCSSTRCY FWFDPWGQGT LVTVSS |
-Macromolecule #3: CC6.30 Fab kappa chain Fv
| Macromolecule | Name: CC6.30 Fab kappa chain Fv / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.57072 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDRVT ITCRASQNIS SYLNWYQQEA GKAPKLLIYA ASSLQSGVPS RFSGSGSGTD FTLTISSLQP EDFATYYCQ QSYSTPRTFG QGTKVDIK |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 20 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.76 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: Detergent added shortly before freezing | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 3 s blot time. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3710 pixel / Number real images: 3348 / Average exposure time: 9.75 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)