+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vk9 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
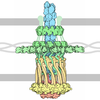
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of PilA-N/C from Geobacter sulfurreducens | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / Protein transport / Pili | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpilus assembly / protein secretion by the type II secretion system / type II protein secretion system complex / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gu, Y. / Srikanth, V. / Malvankar, N.S. / Samatey, F.A. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structure of Geobacter pili reveals secretory rather than nanowire behaviour. Authors: Yangqi Gu / Vishok Srikanth / Aldo I Salazar-Morales / Ruchi Jain / J Patrick O'Brien / Sophia M Yi / Rajesh Kumar Soni / Fadel A Samatey / Sibel Ebru Yalcin / Nikhil S Malvankar /  Abstract: Extracellular electron transfer by Geobacter species through surface appendages known as microbial nanowires is important in a range of globally important environmental phenomena, as well as for ...Extracellular electron transfer by Geobacter species through surface appendages known as microbial nanowires is important in a range of globally important environmental phenomena, as well as for applications in bio-remediation, bioenergy, biofuels and bioelectronics. Since 2005, these nanowires have been thought to be type 4 pili composed solely of the PilA-N protein. However, previous structural analyses have demonstrated that, during extracellular electron transfer, cells do not produce pili but rather nanowires made up of the cytochromes OmcS and OmcZ. Here we show that Geobacter sulfurreducens binds PilA-N to PilA-C to assemble heterodimeric pili, which remain periplasmic under nanowire-producing conditions that require extracellular electron transfer. Cryo-electron microscopy revealed that C-terminal residues of PilA-N stabilize its copolymerization with PilA-C (to form PilA-N-C) through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions that position PilA-C along the outer surface of the filament. PilA-N-C filaments lack π-stacking of aromatic side chains and show a conductivity that is 20,000-fold lower than that of OmcZ nanowires. In contrast with surface-displayed type 4 pili, PilA-N-C filaments show structure, function and localization akin to those of type 2 secretion pseudopili. The secretion of OmcS and OmcZ nanowires is lost when pilA-N is deleted and restored when PilA-N-C filaments are reconstituted. The substitution of pilA-N with the type 4 pili of other microorganisms also causes a loss of secretion of OmcZ nanowires. As all major phyla of prokaryotes use systems similar to type 4 pili, this nanowire translocation machinery may have a widespread effect in identifying the evolution and prevalence of diverse electron-transferring microorganisms and in determining nanowire assembly architecture for designing synthetic protein nanowires. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vk9.cif.gz 6vk9.cif.gz | 421.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vk9.ent.gz pdb6vk9.ent.gz | 355 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vk9.json.gz 6vk9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6vk9_validation.pdf.gz 6vk9_validation.pdf.gz | 888.3 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6vk9_full_validation.pdf.gz 6vk9_full_validation.pdf.gz | 910.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6vk9_validation.xml.gz 6vk9_validation.xml.gz | 60.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6vk9_validation.cif.gz 6vk9_validation.cif.gz | 98 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vk9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vk9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vk9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vk/6vk9 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21225MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10797 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of PilA-N/C from Geobacter sulfurreducens EMPIAR-10797 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of PilA-N/C from Geobacter sulfurreducensData size: 1.5 TB Data #1: Geobacter sulfurreducens PilA-N-C pili - raw unaligned/uncorrected super resolution images [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 16 / Rise per n subunits: 10.41 Å / Rotation per n subunits: 89.03 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 6576.502 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Fragment: UNP residues 30-90 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / Gene: pilA-N, GSU1496 / Production host: Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / Gene: pilA-N, GSU1496 / Production host:  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q74D23 Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q74D23#2: Protein | Mass: 10973.763 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Fragment: UNP residues 21-124 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / Gene: pilA-C, GSU1497 / Production host: Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / Gene: pilA-C, GSU1497 / Production host:  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q74D22 Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q74D22 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Polymerized hetero-dimers of PilA-N and PilA-C / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) Geobacter sulfurreducens (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 0.2 sec. / Electron dose: 2.308 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 7664 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 27 / Used frames/image: 2-10 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 89.01 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 10.41 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 83000 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 3 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.8 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj