[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5iv7: Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the star-shaped, hubless po... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5iv7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the star-shaped, hubless post-attachment T4 baseplate | ||||||
 Components Components | (Baseplate wedge protein ...) x 8 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / T4 / baseplate / post-attachment / bacteriophage / bacterial virus / star-shaped / hubless / membrane-piercing / cell attachment / infection | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvirus tail, baseplate / viral tail assembly / viral release from host cell / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.77 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Taylor, N.M.I. / Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C. / Goldie, K.N. / Stahlberg, H. / Leiman, P.G. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction. Authors: Nicholas M I Taylor / Nikolai S Prokhorov / Ricardo C Guerrero-Ferreira / Mikhail M Shneider / Christopher Browning / Kenneth N Goldie / Henning Stahlberg / Petr G Leiman /   Abstract: Several systems, including contractile tail bacteriophages, the type VI secretion system and R-type pyocins, use a multiprotein tubular apparatus to attach to and penetrate host cell membranes. This ...Several systems, including contractile tail bacteriophages, the type VI secretion system and R-type pyocins, use a multiprotein tubular apparatus to attach to and penetrate host cell membranes. This macromolecular machine resembles a stretched, coiled spring (or sheath) wound around a rigid tube with a spike-shaped protein at its tip. A baseplate structure, which is arguably the most complex part of this assembly, relays the contraction signal to the sheath. Here we present the atomic structure of the approximately 6-megadalton bacteriophage T4 baseplate in its pre- and post-host attachment states and explain the events that lead to sheath contraction in atomic detail. We establish the identity and function of a minimal set of components that is conserved in all contractile injection systems and show that the triggering mechanism is universally conserved. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5iv7.cif.gz 5iv7.cif.gz | 6.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5iv7.ent.gz pdb5iv7.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5iv7.json.gz 5iv7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/5iv7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/5iv7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/5iv7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/iv/5iv7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3396MC  3374C  3392C 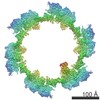 3393C  3394C  3395C  3397C  5iv5C  5iw9C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Baseplate wedge protein ... , 8 types, 96 molecules ABQRghwxBFBGEAEBCSiyCAECDETUjkzAACBCCEDEE...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 74492.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / References: UniProt: P19060 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / References: UniProt: P19060#2: Protein | Mass: 119336.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P19061 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P19061#3: Protein | Mass: 38041.668 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P19062 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P19062#4: Protein | Mass: 31024.725 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10927 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10927#5: Protein | Mass: 66281.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10928 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10928#6: Protein | Mass: 23725.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10929 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P10929#7: Protein | Mass: 15111.101 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P09425 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P09425#8: Protein | Mass: 22990.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P16011 Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Plasmid details: am18/am23 mutant / References: UniProt: P16011 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Star-shaped, hubless post-attachment T4 baseplate-tail tube complex Type: COMPLEX Details: The short tail fibers (gp12 trimers) appear more flexible, and no special effort was made to reconstruct them. They were partly masked out by the circular mask.The total mass of the ...Details: The short tail fibers (gp12 trimers) appear more flexible, and no special effort was made to reconstruct them. They were partly masked out by the circular mask.The total mass of the reconstructed volume was approximately 4.5 MDa (excluding short tail fibers). The short-tail fibers were not included in the PDB file. Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 5.5 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Strain: am18/am23 mutant Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Strain: am18/am23 mutant | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: In addition to hexagonal pre-attachment baseplate-tail tube complexes, the sample also contained some star-shaped, hubless post-attachment baseplates. The current model is that star-shaped, ...Details: In addition to hexagonal pre-attachment baseplate-tail tube complexes, the sample also contained some star-shaped, hubless post-attachment baseplates. The current model is that star-shaped, hubless post-attachment baseplate. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % Details: Applied 3.5 ul of sample and blotting 3 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 37700 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: HELIUM / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 80 K / Temperature (min): 80 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter upper: 20 eV / Energyfilter lower: 0 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 3-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 47516 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C6 (6 fold cyclic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.77 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 5176 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5IV5 Accession code: 5IV5 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj