[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j6p: Pseudo-atomic model of dynein microtubule binding domain-tubulin ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j6p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
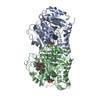
| Title | Pseudo-atomic model of dynein microtubule binding domain-tubulin complex based on a cryoEM map | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN/STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Motor Protein-Cytoskeleton Complex / MOTOR PROTEIN-STRUCTURAL PROTEIN complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationminus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / early phagosome membrane / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / phagolysosome membrane / CTPase activity / Neutrophil degranulation / phagosome maturation / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / cytoplasmic dynein complex ...minus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / early phagosome membrane / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / phagolysosome membrane / CTPase activity / Neutrophil degranulation / phagosome maturation / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / microtubule motor activity / dynein intermediate chain binding / ATPase complex / cytoplasmic microtubule / endocytic vesicle / mitotic spindle assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / tubulin binding / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / mitotic cell cycle / cell cortex / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / centrosome / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Uchimura, S. / Fujii, T. / Takazaki, H. / Ayukawa, R. / Nishikawa, Y. / Minoura, I. / Hachikubo, Y. / Kurisu, G. / Sutoh, K. / Kon, T. ...Uchimura, S. / Fujii, T. / Takazaki, H. / Ayukawa, R. / Nishikawa, Y. / Minoura, I. / Hachikubo, Y. / Kurisu, G. / Sutoh, K. / Kon, T. / Namba, K. / Muto, E. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2015 Journal: J Cell Biol / Year: 2015Title: A flipped ion pair at the dynein-microtubule interface is critical for dynein motility and ATPase activation. Authors: Seiichi Uchimura / Takashi Fujii / Hiroko Takazaki / Rie Ayukawa / Yosuke Nishikawa / Itsushi Minoura / You Hachikubo / Genji Kurisu / Kazuo Sutoh / Takahide Kon / Keiichi Namba / Etsuko Muto /  Abstract: Dynein is a motor protein that moves on microtubules (MTs) using the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis. To understand its motility mechanism, it is crucial to know how the signal of ...Dynein is a motor protein that moves on microtubules (MTs) using the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis. To understand its motility mechanism, it is crucial to know how the signal of MT binding is transmitted to the ATPase domain to enhance ATP hydrolysis. However, the molecular basis of signal transmission at the dynein-MT interface remains unclear. Scanning mutagenesis of tubulin identified two residues in α-tubulin, R403 and E416, that are critical for ATPase activation and directional movement of dynein. Electron cryomicroscopy and biochemical analyses revealed that these residues form salt bridges with the residues in the dynein MT-binding domain (MTBD) that work in concert to induce registry change in the stalk coiled coil and activate the ATPase. The R403-E3390 salt bridge functions as a switch for this mechanism because of its reversed charge relative to other residues at the interface. This study unveils the structural basis for coupling between MT binding and ATPase activation and implicates the MTBD in the control of directional movement. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j6p.cif.gz 3j6p.cif.gz | 203.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j6p.ent.gz pdb3j6p.ent.gz | 156.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j6p.json.gz 3j6p.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  3j6p_validation.pdf.gz 3j6p_validation.pdf.gz | 1003.4 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  3j6p_full_validation.pdf.gz 3j6p_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  3j6p_validation.xml.gz 3j6p_validation.xml.gz | 50 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  3j6p_validation.cif.gz 3j6p_validation.cif.gz | 71 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6p https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j6/3j6p | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 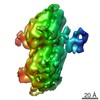 5931MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules DAB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 12327.559 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 50107.238 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 49907.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 4 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-TA1 / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dictyostelium dynein microtubule binding domain bound to a 15-protofilament microtubule Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Method: Blot for 3.5 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL 3200FSC / Date: Nov 5, 2012 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 60000 X / Calibrated magnification: 109489 X / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 1.6 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 50 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F415 (4k x 4k) |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND3 Each particle | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Projection Matching / Resolution: 8.2 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.37 Å / Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient Details: METHOD--Flexible fitting REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--Flexible fitting | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj