[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-51244: Structure of Chd1 bound to a dinucleosome with a dyad-to-dyad dis... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
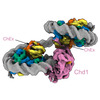
| Title | Structure of Chd1 bound to a dinucleosome with a dyad-to-dyad distance of 103 bp. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map of dinucleosome DN103 bound by Chd1 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | chromatin / remodeling / transcription / nucleosome / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / nucleolar chromatin / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / DNA double-strand break processing / nucleosome organization / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / SAGA complex ...regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / nucleolar chromatin / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / DNA double-strand break processing / nucleosome organization / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / SAGA complex / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / : / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / chromatin DNA binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of chromatin / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / site of double-strand break / histone binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Engeholm M / Roske JJ / Oberbeckmann E / Dienemann C / Lidschreiber M / Cramer P / Farnung L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 2 items Germany, European Union, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Resolution of transcription-induced hexasome-nucleosome complexes by Chd1 and FACT. Authors: Maik Engeholm / Johann J Roske / Elisa Oberbeckmann / Christian Dienemann / Michael Lidschreiber / Patrick Cramer / Lucas Farnung /    Abstract: To maintain the nucleosome organization of transcribed genes, ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers collaborate with histone chaperones. Here, we show that at the 5' ends of yeast genes, RNA polymerase ...To maintain the nucleosome organization of transcribed genes, ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers collaborate with histone chaperones. Here, we show that at the 5' ends of yeast genes, RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) generates hexasomes that occur directly adjacent to nucleosomes. The resulting hexasome-nucleosome complexes are then resolved by Chd1. We present two cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of Chd1 bound to a hexasome-nucleosome complex before and after restoration of the missing inner H2A/H2B dimer by FACT. Chd1 uniquely interacts with the complex, positioning its ATPase domain to shift the hexasome away from the nucleosome. In the absence of the inner H2A/H2B dimer, its DNA-binding domain (DBD) packs against the ATPase domain, suggesting an inhibited state. Restoration of the dimer by FACT triggers a rearrangement that displaces the DBD and stimulates Chd1 remodeling. Our results demonstrate how chromatin remodelers interact with a complex nucleosome assembly and suggest how Chd1 and FACT jointly support transcription by RNAPII. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_51244.map.gz emd_51244.map.gz | 223.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-51244-v30.xml emd-51244-v30.xml emd-51244.xml emd-51244.xml | 20.5 KB 20.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_51244.png emd_51244.png | 103.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-51244.cif.gz emd-51244.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51244 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51244 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51244 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51244 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9gd2MC  9gd0C  9gd1C  9gd3C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_51244.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_51244.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map of dinucleosome DN103 bound by Chd1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.834 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
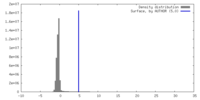
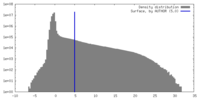
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Hexasome-nucleosome complex with a dyad-to-dyad distance of 103 bp.
+Supramolecule #1: Hexasome-nucleosome complex with a dyad-to-dyad distance of 103 bp.
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.2
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B 1.1
+Macromolecule #7: Chromo domain-containing protein 1
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (248-MER)
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (248-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #9: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
+Macromolecule #10: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 57.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 22337 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)














 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)

