+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ARP module of the human TIP60 complex | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | complex / chromatin regulator / GENE REGULATION | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpiccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / sperm DNA condensation / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex ...piccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / sperm DNA condensation / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / neural retina development / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / Swr1 complex / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / protein antigen binding / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Ino80 complex / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / blastocyst formation / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Adherens junctions interactions / RHOF GTPase cycle / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / apical junction complex / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / spinal cord development / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of chromosome organization / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / Recycling pathway of L1 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / regulation of DNA replication / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of embryonic development / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / spermatid development / kinesin binding / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of DNA repair / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / axonogenesis / telomere maintenance / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / replication fork / positive regulation of DNA repair / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / actin filament / adherens junction / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell differentiation / cell motility Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.29 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang Z / Mameri A / Florez Ariza AJ / Cote J / Nogales E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Canada, 5 items Canada, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Structural insights into the human NuA4/TIP60 acetyltransferase and chromatin remodeling complex. Authors: Zhenlin Yang / Amel Mameri / Claudia Cattoglio / Catherine Lachance / Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza / Jie Luo / Jonathan Humbert / Deepthi Sudarshan / Arul Banerjea / Maxime Galloy / Amélie ...Authors: Zhenlin Yang / Amel Mameri / Claudia Cattoglio / Catherine Lachance / Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza / Jie Luo / Jonathan Humbert / Deepthi Sudarshan / Arul Banerjea / Maxime Galloy / Amélie Fradet-Turcotte / Jean-Philippe Lambert / Jeff A Ranish / Jacques Côté / Eva Nogales /   Abstract: The human nucleosome acetyltransferase of histone H4 (NuA4)/Tat-interactive protein, 60 kilodalton (TIP60) coactivator complex, a fusion of the yeast switch/sucrose nonfermentable related 1 (SWR1) ...The human nucleosome acetyltransferase of histone H4 (NuA4)/Tat-interactive protein, 60 kilodalton (TIP60) coactivator complex, a fusion of the yeast switch/sucrose nonfermentable related 1 (SWR1) and NuA4 complexes, both incorporates the histone variant H2A.Z into nucleosomes and acetylates histones H4, H2A, and H2A.Z to regulate gene expression and maintain genome stability. Our cryo-electron microscopy studies show that, within the NuA4/TIP60 complex, the E1A binding protein P400 (EP400) subunit serves as a scaffold holding the different functional modules in specific positions, creating a distinct arrangement of the actin-related protein (ARP) module. EP400 interacts with the transformation/transcription domain-associated protein (TRRAP) subunit by using a footprint that overlaps with that of the Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase (SAGA) complex, preventing the formation of a hybrid complex. Loss of the TRRAP subunit leads to mislocalization of NuA4/TIP60, resulting in the redistribution of H2A.Z and its acetylation across the genome, emphasizing the dual functionality of NuA4/TIP60 as a single macromolecular assembly. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45252.map.gz emd_45252.map.gz | 483.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45252-v30.xml emd-45252-v30.xml emd-45252.xml emd-45252.xml | 23.3 KB 23.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_45252.png emd_45252.png | 81.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45252.cif.gz emd-45252.cif.gz | 9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45252_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45252_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45252_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45252_half_map_2.map.gz | 474.3 MB 474 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45252 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45252 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45252 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45252 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9c6nMC  9c47C  9c4bC  9c57C  9c62C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45252.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45252.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.19 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
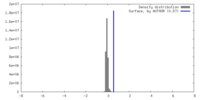
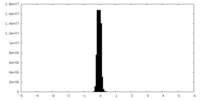
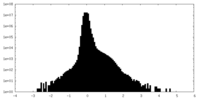
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_45252_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
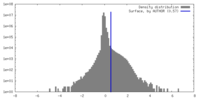
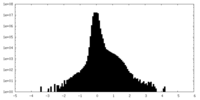
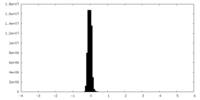
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_45252_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ARP module of the human TIP60 complex
| Entire | Name: ARP module of the human TIP60 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ARP module of the human TIP60 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ARP module of the human TIP60 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: E1A-binding protein p400
| Macromolecule | Name: E1A-binding protein p400 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 343.867312 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATGQ NVNITLQSVG PVVGGNQQI TLAPLPLPSP TSPGFQFSAQ PRRFEHGSPS YIQVTSPLSQ QVQTQSPTQP SPGPGQALQN VRAGAPGPGL G LCSSSPTG ...String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATGQ NVNITLQSVG PVVGGNQQI TLAPLPLPSP TSPGFQFSAQ PRRFEHGSPS YIQVTSPLSQ QVQTQSPTQP SPGPGQALQN VRAGAPGPGL G LCSSSPTG GFVDASVLVR QISLSPSSGG HFVFQDGSGL TQIAQGAQVQ LQHPGTPITV RERRPSQPHT QSGGTIHHLG PQ SPAAAGG AGLQPLASPS HITTANLPPQ ISSIIQGQLV QQQQVLQGPP LPRPLGFERT PGVLLPGAGG AAGFGMTSPP PPT SPSRTA VPPGLSSLPL TSVGNTGMKK VPKKLEEIPP ASPEMAQMRK QCLDYHYQEM QALKEVFKEY LIELFFLQHF QGNM MDFLA FKKKHYAPLQ AYLRQNDLDI EEEEEEEEEE EEKSEVINDE VKVVTGKDGQ TGTPVAIATQ LPPKVSAAFS SQQQP FQQA LAGSLVAGAG STVETDLFKR QQAMPSTGMA EQSKRPRLEV GHQGVVFQHP GADAGVPLQQ LMPTAQGGMP PTPQAA QLA GQRQSQQQYD PSTGPPVQNA ASLHTPLPQL PGRLPPAGVP TAALSSALQF AQQPQVVEAQ TQLQIPVKTQ QPNVPIP AP PSSQLPIPPS QPAQLALHVP TPGKVQVQAS QLSSLPQMVA STRLPVDPAP PCPRPLPTSS TSSLAPVSGS GPGPSPAR S SPVNRPSSAT NKALSPVTSR TPGVVASAPT KPQSPAQNAT SSQDSSQDTL TEQITLENQV HQRIAELRKA GLWSQRRLP KLQEAPRPKS HWDYLLEEMQ WMATDFAQER RWKVAAAKKL VRTVVRHHEE KQLREERGKK EEQSRLRRIA ASTAREIECF WSNIEQVVE IKLRVELEEK RKKALNLQKV SRRGKELRPK GFDALQESSL DSGMSGRKRK ASISLTDDEV DDEEETIEEE E ANEGVVDH QTELSNLAKE AELPLLDLMK LYEGAFLPSS QWPRPKPDGE DTSGEEDADD CPGDRESRKD LVLIDSLFIM DQ FKAAERM NIGKPNAKDI ADVTAVAEAI LPKGSARVTT SVKFNAPSLL YGALRDYQKI GLDWLAKLYR KNLNGILADE AGL GKTVQI IAFFAHLACN EGNWGPHLVV VRSCNILKWE LELKRWCPGL KILSYIGSHR ELKAKRQEWA EPNSFHVCIT SYTQ FFRGL TAFTRVRWKC LVIDEMQRVK GMTERHWEAV FTLQSQQRLL LIDSPLHNTF LELWTMVHFL VPGISRPYLS SPLRA PSEE SQDYYHKVVI RLHRVTQPFI LRRTKRDVEK QLTKKYEHVL KCRLSNRQKA LYEDVILQPG TQEALKSGHF VNVLSI LVR LQRICNHPGL VEPRHPGSSY VAGPLEYPSA SLILKALERD FWKEADLSMF DLIGLENKIT RHEAELLSKK KIPRKLM EE ISTSAAPAAR PAAAKLKASR LFQPVQYGQK PEGRTVAFPS THPPRTAAPT TASAAPQGPL RGRPPIATFS ANPEAKAA A APFQTSQASA SAPRHQPASA SSTAASPAHP AKLRAQTTAQ ASTPGQPPPQ PQAPSHAAGQ SALPQRLVLP SQAQARLPS GEVVKIAQLA SITGPQSRVA QPETPVTLQF QGSKFTLSHS QLRQLTAGQP LQLQGSVLQI VSAPGQPYLR APGPVVMQTV SQAGAVHGA LGSKPPAGGP SPAPLTPQVG VPGRVAVNAL AVGEPGTASK PASPIGGPTQ EEKTRLLKER LDQIYLVNER R CSQAPVYG RDLLRICALP SHGRVQWRGS LDGRRGKEAG PAHSYTSSSE SPSELMLTLC RCGESLQDVI DRVAFVIPPV VA APPSLRV PRPPPLYSHR MRILRQGLRE HAAPYFQQLR QTTAPRLLQF PELRLVQFDS GKLEALAILL QKLKSEGRRV LIL SQMILM LDILEMFLNF HYLTYVRIDE NASSEQRQEL MRSFNRDRRI FCAILSTHSR TTGINLVEAD TVVFYDNDLN PVMD AKAQE WCDRIGRCKD IHIYRLVSGN SIEEKLLKNG TKDLIREVAA QGNDYSMAFL TQRTIQELFE VYSPMDDAGF PVKAE EFVV LSQEPSVTET IAPKIARPFI EALKSIEYLE EDAQKSAQEG VLGPHTDALS SDSENMPCDE EPSQLEELAD FMEQLT PIE KYALNYLELF HTSIEQEKER NSEDAVMTAV RAWEFWNLKT LQEREARLRL EQEEAELLTY TREDAYSMEY VYEDVDG QT EVMPLWTPPT PPQDDSDIYL DSVMCLMYEA TPIPEAKLPP VYVRKERKRH KTDPSAAGRK KKQRHGEAVV PPRSLFDR A TPGLLKIRRE GKEQKKNILL KQQVPFAKPL PTFAKPTAEP GQDNPEWLIS EDWALLQAVK QLLELPLNLT IVSPAHTPN WDLVSDVVNS CSRIYRSSKQ CRNRYENVII PREEGKSKNN RPLRTSQIYA QDENATHTQL YTSHFDLMKM TAGKRSPPIK PLLGMNPFQ KNPKHASVLA ESGINYDKPL PPIQVASLRA ERIAKEKKAL ADQQKAQQPA VAQPPPPQPQ PPPPPQQPPP P LPQPQAAG SQPPAGPPAV QPQPQPQPQT QPQPVQAPAK AQPAITTGGS AAVLAGTIKT SVTGTSMPTG AVSGNVIVNT IA GVPAATF QSINKRLASP VAPGALTTPG GSAPAQVVHT QPPPRAVGSP ATATPDLVSM ATTQGVRAVT SVTASAVVTT NLT PVQTPA RSLVPQVSQA TGVQLPGKTI TPAHFQLLRQ QQQQQQQQQQ QQQQQQQQQQ QQQQQQQQTT TTSQVQVPQI QGQA QSPAQ IKAVGKLTPE HLIKMQKQKL QMPPQPPPPQ AQSAPPQPTA QVQVQTSQPP QQQSPQLTTV TAPRPGALLT GTTVA NLQV ARLTRVPTSQ LQAQGQMQTQ APQPAQVALA KPPVVSVPAA VVSSPGVTTL PMNVAGISVA IGQPQKAAGQ TVVAQP VHM QQLLKLKQQA VQQQKAIQPQ AAQGPAAVQQ KITAQQITTP GAQQKVAYAA QPALKTQFLT TPISQAQKLA GAQQVQT QI QVAKLPQVVQ QQTPVASIQQ VASASQQASP QTVALTQATA AGQQVQMIPA VTATAQVVQQ KLIQQQVVTT ASAPLQTP G APNPAQVPAS SDSPSQQPKL QMRVPAVRLK TPTKPPCQ UniProtKB: E1A-binding protein p400 |
-Macromolecule #2: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 93.589172 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESI YPGEFKMPKQ LIHIQPFSLD AEQPDYDLDS EDEVFVNKLK KKMDICPLQF EEMIDRLEKG SGQQPVSLQE A KLLLKEDD ...String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESI YPGEFKMPKQ LIHIQPFSLD AEQPDYDLDS EDEVFVNKLK KKMDICPLQF EEMIDRLEKG SGQQPVSLQE A KLLLKEDD ELIREVYEYW IKKRKNCRGP SLIPSVKQEK RDGSSTNDPY VAFRRRTEKM QTRKNRKNDE ASYEKMLKLR RD LSRAVTI LEMIKRREKS KRELLHLTLE IMEKRYNLGD YNGEIMSEVM AQRQPMKPTY AIPIIPITNS SQFKHQEAMD VKE FKVNKQ DKADLIRPKR KYEKKPKVLP SSAAATPQQT SPAALPVFNA KDLNQYDFPS SDEEPLSQVL SGSSEAEEDN DPDG PFAFR RKAGCQYYAP HLDQTGNWPW TSPKDGGLGD VRYRYCLTTL TVPQRCIGFA RRRVGRGGRV LLDRAHSDYD SVFHH LDLE MLSSPQHSPV NQFANTSETN TSDKSFSKDL SQILVNIKSC RWRHFRPRTP SLHDSDNDEL SCRKLYRSIN RTGTAQ PGT QTCSTSTQSK SSSGSAHFAF TAEQYQQHQQ QLALMQKQQL AQIQQQQANS NSSTNTSQNL ASNQQKSGFR LNIQGLE RT LQGFVSKTLD SASAQFAASA LVTSEQLMGF KMKDDVVLGI GVNGVLPASG VYKGLHLSST TPTALVHTSP STAGSALL Q PSNITQTSSS HSALSHQVTA ANSATTQVLI GNNIRLTVPS SVATVNSIAP INARHIPRTL SAVPSSALKL AAAANCQVS KVPSSSSVDS VPRENHESEK PALNNIADNT VAMEVT UniProtKB: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 53.090699 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGS KKVRPWKWMP FTNPARKDGA MFFHWRRAAE EGKDYPFARF NKTVQVPVYS EQEYQLYLHD DAWTKAETDH L FDLSRRFD ...String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGS KKVRPWKWMP FTNPARKDGA MFFHWRRAAE EGKDYPFARF NKTVQVPVYS EQEYQLYLHD DAWTKAETDH L FDLSRRFD LRFVVIHDRY DHQQFKKRSV EDLKERYYHI CAKLANVRAV PGTDLKIPVF DAGHERRRKE QLERLYNRTP EQ VAEEEYL LQELRKIEAR KKEREKRSQD LQKLITAADT TAEQRRTERK APKKKLPQKK EAEKPAVPET AGIKFPDFKS AGV TLRSQR MKLPSSVGQK KIKALEQMLL ELGVELSPTP TEELVHMFNE LRSDLVLLYE LKQACANCEY ELQMLRHRHE ALAR AGVLG GPATPASGPG PASAEPAVTE PGLGPDPKDT IIDVVGAPLT PNSRKRRESA SSSSSVKKAK KP UniProtKB: DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Actin, cytoplasmic 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.78266 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSGDGV T HTVPIYEG ...String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSGDGV T HTVPIYEG YALPHAILRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFTTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFEQEMA TAASSSSLEK SY ELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PEALFQPSFL GMESCGIHET TFNSIMKCDV DIRKDLYANT VLSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKEI TAL APSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ISKQEYDESG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Actin-like protein 6A
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin-like protein 6A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.509812 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLK NGMVEDWDSF QAILDHTYKM HVKSEASLHP VLMSEAPWNT RAKREKLTEL MFEHYNIPAF FLCKTAVLTA F ANGRSTGL ...String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLK NGMVEDWDSF QAILDHTYKM HVKSEASLHP VLMSEAPWNT RAKREKLTEL MFEHYNIPAF FLCKTAVLTA F ANGRSTGL ILDSGATHTT AIPVHDGYVL QQGIVKSPLA GDFITMQCRE LFQEMNIELV PPYMIASKEA VREGSPANWK RK EKLPQVT RSWHNYMCNC VIQDFQASVL QVSDSTYDEQ VAAQMPTVHY EFPNGYNCDF GAERLKIPEG LFDPSNVKGL SGN TMLGVS HVVTTSVGMC DIDIRPGLYG SVIVAGGNTL IQSFTDRLNR ELSQKTPPSM RLKLIANNTT VERRFSSWIG GSIL ASLGT FQQMWISKQE YEEGGKQCVE RKCP UniProtKB: Actin-like protein 6A |
-Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: 4D-STEM / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.29 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 214481 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)