+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
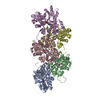
| Title | Dia1 in the Middle of F-actin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Actin / Filament / Elongation / Ends / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOC GTPase cycle / : / actin nucleation / neuron projection retraction / RHOB GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases Activate Formins ...negative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOC GTPase cycle / : / actin nucleation / neuron projection retraction / RHOB GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / RHOA GTPase cycle / profilin binding / axon midline choice point recognition / regulation of microtubule-based process / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / brush border / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / Neutrophil degranulation / actin filament polymerization / cytoskeleton organization / actin filament / filopodium / sensory perception of sound / brain development / small GTPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / spindle / ruffle membrane / neuron projection development / calcium-dependent protein binding / intracellular protein localization / regulation of cell shape / lamellipodium / presynapse / actin binding / actin cytoskeleton organization / cell body / gene expression / transmembrane transporter binding / neuron projection / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / centrosome / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
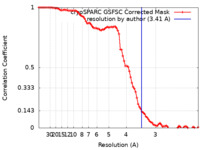
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.41 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Palmer NJ / Barrie KR / Dominguez R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms of actin filament severing and elongation by formins. Authors: Nicholas J Palmer / Kyle R Barrie / Roberto Dominguez /  Abstract: Humans express 15 formins that play crucial roles in actin-based processes, including cytokinesis, cell motility and mechanotransduction. However, the lack of structures bound to the actin filament ...Humans express 15 formins that play crucial roles in actin-based processes, including cytokinesis, cell motility and mechanotransduction. However, the lack of structures bound to the actin filament (F-actin) has been a major impediment to understanding formin function. Whereas formins are known for their ability to nucleate and elongate F-actin, some formins can additionally depolymerize, sever or bundle F-actin. Two mammalian formins, inverted formin 2 (INF2) and diaphanous 1 (DIA1, encoded by DIAPH1), exemplify this diversity. INF2 shows potent severing activity but elongates weakly whereas DIA1 has potent elongation activity but does not sever. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) we show five structural states of INF2 and two of DIA1 bound to the middle and barbed end of F-actin. INF2 and DIA1 bind differently to these sites, consistent with their distinct activities. The formin-homology 2 and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein-homology 2 (FH2 and WH2, respectively) domains of INF2 are positioned to sever F-actin, whereas DIA1 appears unsuited for severing. These structures also show how profilin-actin is delivered to the fast-growing barbed end, and how this is followed by a transition of the incoming monomer into the F-actin conformation and the release of profilin. Combined, the seven structures presented here provide step-by-step visualization of the mechanisms of F-actin severing and elongation by formins. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44135.map.gz emd_44135.map.gz | 32.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44135-v30.xml emd-44135-v30.xml emd-44135.xml emd-44135.xml | 20.8 KB 20.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44135_fsc.xml emd_44135_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44135.png emd_44135.png | 34.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_44135_msk_1.map emd_44135_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44135.cif.gz emd-44135.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44135_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44135_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44135_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44135_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44135 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44135 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44135 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44135 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9b3dMC  9az4C  9azpC  9azqC  9b03C  9b0kC  9b27C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44135.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44135.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
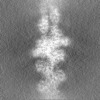
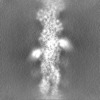
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_44135_msk_1.map emd_44135_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
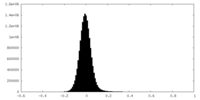
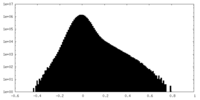
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44135_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44135_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments.
| Entire | Name: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments.
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 252 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: mDia1 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: mDia1 dimer / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Actin filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.387227 KDa |
| Sequence | String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP ...String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP HAIMRLDLAG RDLTDYLMKI LTERGYSFVT TAEREIVRDI KEKLCYVALD FENEMATAAS SSSLEKSY E LPDGQVITIG NERFRCPETL FQPSFIGMES AGIHETTYNS IMKCDIDIRK DLYANNVMSG GTTMYPGIAD RMQKEITAL APSTMKIKII APPERKYSVW IGGSILASLS TFQQMWITKQ EYDEAGPSIV HRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein diaphanous homolog 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein diaphanous homolog 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.313004 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: VLPFGLTPKK VYKPEVQLRR PNWSKFVAED LSQDCFWTKV KEDRFENNEL FAKLTLAFSA QTKTSKAKKD QEGGEEKKSV QKKKVKELK VLDSKTAQNL SIFLGSFRMP YQEIKNVILE VNEAVLTESM IQNLIKQMPE PEQLKMLSEL KEEYDDLAES E QFGVVMGT ...String: VLPFGLTPKK VYKPEVQLRR PNWSKFVAED LSQDCFWTKV KEDRFENNEL FAKLTLAFSA QTKTSKAKKD QEGGEEKKSV QKKKVKELK VLDSKTAQNL SIFLGSFRMP YQEIKNVILE VNEAVLTESM IQNLIKQMPE PEQLKMLSEL KEEYDDLAES E QFGVVMGT VPRLRPRLNA ILFKLQFSEQ VENIKPEIVS VTAACEELRK SENFSSLLEL TLLVGNYMNA GSRNAGAFGF NI SFLCKLR DTKSADQKMT LLHFLAELCE NDHPEVLKFP DELAHVEKAS RVSAENLQKS LDQMKKQIAD VERDVQNFPA ATD EKDKFV EKMTSFVKDA QEQYNKLRMM HSNMETLYKE LGDYFVFDPK KLSVEEFFMD LHNFRNMFLQ AVKENQKRRE TEE UniProtKB: Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.48 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: 20mM HEPES, 50mM NaCL, 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.05% Thesit | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 100 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 120 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||
| Details | Actin filaments were sonicated prior to addition of mDia1 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)