+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
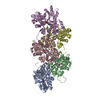
| Title | Dia1 at the Barbed End of F-Actin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Actin / Filament / Elongation / Ends / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOC GTPase cycle / : / actin nucleation / neuron projection retraction / RHOB GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases Activate Formins ...negative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOC GTPase cycle / : / actin nucleation / neuron projection retraction / RHOB GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / RHOA GTPase cycle / profilin binding / axon midline choice point recognition / regulation of microtubule-based process / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / brush border / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / Neutrophil degranulation / actin filament polymerization / cytoskeleton organization / actin filament / filopodium / sensory perception of sound / brain development / small GTPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / spindle / ruffle membrane / neuron projection development / calcium-dependent protein binding / intracellular protein localization / regulation of cell shape / lamellipodium / presynapse / actin binding / cell body / actin cytoskeleton organization / gene expression / transmembrane transporter binding / neuron projection / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / centrosome / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
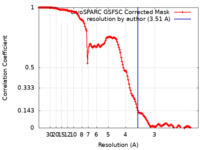
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.51 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Palmer NJ / Barrie KR / Dominguez R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Mechanisms of actin filament severing and elongation by formins. Authors: Nicholas J Palmer / Kyle R Barrie / Roberto Dominguez /  Abstract: Humans express 15 formins that play crucial roles in actin-based processes, including cytokinesis, cell motility and mechanotransduction. However, the lack of structures bound to the actin filament ...Humans express 15 formins that play crucial roles in actin-based processes, including cytokinesis, cell motility and mechanotransduction. However, the lack of structures bound to the actin filament (F-actin) has been a major impediment to understanding formin function. Whereas formins are known for their ability to nucleate and elongate F-actin, some formins can additionally depolymerize, sever or bundle F-actin. Two mammalian formins, inverted formin 2 (INF2) and diaphanous 1 (DIA1, encoded by DIAPH1), exemplify this diversity. INF2 shows potent severing activity but elongates weakly whereas DIA1 has potent elongation activity but does not sever. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) we show five structural states of INF2 and two of DIA1 bound to the middle and barbed end of F-actin. INF2 and DIA1 bind differently to these sites, consistent with their distinct activities. The formin-homology 2 and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein-homology 2 (FH2 and WH2, respectively) domains of INF2 are positioned to sever F-actin, whereas DIA1 appears unsuited for severing. These structures also show how profilin-actin is delivered to the fast-growing barbed end, and how this is followed by a transition of the incoming monomer into the F-actin conformation and the release of profilin. Combined, the seven structures presented here provide step-by-step visualization of the mechanisms of F-actin severing and elongation by formins. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44099.map.gz emd_44099.map.gz | 133.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44099-v30.xml emd-44099-v30.xml emd-44099.xml emd-44099.xml | 20 KB 20 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44099_fsc.xml emd_44099_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44099.png emd_44099.png | 23.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_44099_msk_1.map emd_44099_msk_1.map | 266.8 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44099.cif.gz emd-44099.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44099_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44099_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44099_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44099_half_map_2.map.gz | 247.8 MB 247.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44099 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44099 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44099 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44099 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9b27MC  9az4C  9azpC  9azqC  9b03C  9b0kC  9b3dC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44099.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 266.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44099.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 266.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
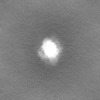
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_44099_msk_1.map emd_44099_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
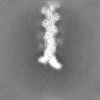
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
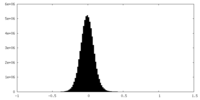
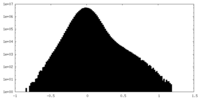
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44099_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
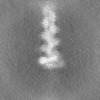
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44099_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments.
| Entire | Name: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments.
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of mDia1 dimer bound at the barbed end of actin filaments. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 252 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: mDia1 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: mDia1 dimer / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Actin filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.387227 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP ...String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP HAIMRLDLAG RDLTDYLMKI LTERGYSFVT TAEREIVRDI KEKLCYVALD FENEMATAAS SSSLEKSY E LPDGQVITIG NERFRCPETL FQPSFIGMES AGIHETTYNS IMKCDIDIRK DLYANNVMSG GTTMYPGIAD RMQKEITAL APSTMKIKII APPERKYSVW IGGSILASLS TFQQMWITKQ EYDEAGPSIV HRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein diaphanous homolog 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein diaphanous homolog 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.189508 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: VLPFGLTPKK VYKPEVQLRR PNWSKFVAED LSQDCFWTKV KEDRFENNEL FAKLTLAFSA QTKTSKAKKD QEGGEEKKSV QKKKVKELK VLDSKTAQNL SIFLGSFRMP YQEIKNVILE VNEAVLTESM IQNLIKQMPE PEQLKMLSEL KEEYDDLAES E QFGVVMGT ...String: VLPFGLTPKK VYKPEVQLRR PNWSKFVAED LSQDCFWTKV KEDRFENNEL FAKLTLAFSA QTKTSKAKKD QEGGEEKKSV QKKKVKELK VLDSKTAQNL SIFLGSFRMP YQEIKNVILE VNEAVLTESM IQNLIKQMPE PEQLKMLSEL KEEYDDLAES E QFGVVMGT VPRLRPRLNA ILFKLQFSEQ VENIKPEIVS VTAACEELRK SENFSSLLEL TLLVGNYMNA GSRNAGAFGF NI SFLCKLR DTKSADQKMT LLHFLAELCE NDHPEVLKFP DELAHVEKAS RVSAENLQKS LDQMKKQIAD VERDVQNFPA ATD EKDKFV EKMTSFVKDA QEQYNKLRMM HSNMETLYKE LGDYFVFDPK KLSVEEFFMD LHNFRNMFLQ AVKENQKRRE TEEK MRRAK LAKEKAEKER LEKQQKR UniProtKB: Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.48 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 100 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 120 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)