+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Type I beta-amyloid 42 Filaments from Down syndrome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Beta Amyloid filaments / Down Syndrome / NEUROPEPTIDE / Human Trisomy 21 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytosolic mRNA polyadenylation / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / microglia development / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction / signaling receptor activator activity / axon midline choice point recognition ...cytosolic mRNA polyadenylation / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / microglia development / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction / signaling receptor activator activity / axon midline choice point recognition / smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / ciliary rootlet / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / PTB domain binding / Golgi-associated vesicle / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / suckling behavior / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / dendrite development / presynaptic active zone / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / neuromuscular process controlling balance / The NLRP3 inflammasome / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / regulation of presynapse assembly / transition metal ion binding / regulation of multicellular organism growth / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / spindle midzone / positive regulation of T cell migration / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / clathrin-coated pit / positive regulation of chemokine production / forebrain development / Notch signaling pathway / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Mitochondrial protein degradation / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / cholesterol metabolic process / positive regulation of glycolytic process / extracellular matrix organization / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / response to interleukin-1 / axonogenesis / adult locomotory behavior / trans-Golgi network membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / dendritic shaft / learning / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / central nervous system development / endosome lumen / locomotory behavior / astrocyte activation / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of JNK cascade / microglial cell activation / synapse organization / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / visual learning / neuromuscular junction / recycling endosome / cognition / Golgi lumen / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / neuron cellular homeostasis / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / endocytosis / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / cellular response to amyloid-beta / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / neuron projection development / cell-cell junction / synaptic vesicle / Platelet degranulation / apical part of cell Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.17 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hoq MR / Bharath SR / Vago FS / Jiang W | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structures of amyloid-β and tau filaments in Down syndrome. Authors: Anllely Fernandez / Md Rejaul Hoq / Grace I Hallinan / Daoyi Li / Sakshibeedu R Bharath / Frank S Vago / Xiaoqi Zhang / Kadir A Ozcan / Kathy L Newell / Holly J Garringer / Wen Jiang / ...Authors: Anllely Fernandez / Md Rejaul Hoq / Grace I Hallinan / Daoyi Li / Sakshibeedu R Bharath / Frank S Vago / Xiaoqi Zhang / Kadir A Ozcan / Kathy L Newell / Holly J Garringer / Wen Jiang / Bernardino Ghetti / Ruben Vidal /  Abstract: Adult individuals with Down syndrome (DS) develop Alzheimer disease (AD). Whether there is a difference between AD in DS and AD regarding the structure of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau filaments is ...Adult individuals with Down syndrome (DS) develop Alzheimer disease (AD). Whether there is a difference between AD in DS and AD regarding the structure of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau filaments is unknown. Here we report the structure of Aβ and tau filaments from two DS brains. We found two Aβ filaments (types IIIa and IIIb) that differ from those previously reported in sporadic AD and two types of Aβ filaments (I and II) identical to those found in sporadic and familial AD. Tau filaments (paired helical filaments and straight filaments) were identical to those in AD, supporting the notion of a common mechanism through which amyloids trigger aggregation of tau. This knowledge is important for understanding AD in DS and assessing whether adults with DS could be included in AD clinical trials. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40416.map.gz emd_40416.map.gz | 186.6 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40416-v30.xml emd-40416-v30.xml emd-40416.xml emd-40416.xml | 13.8 KB 13.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_40416_fsc.xml emd_40416_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_40416.png emd_40416.png | 52.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40416.cif.gz emd-40416.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40416_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40416_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40416_half_map_2.map.gz emd_40416_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.7 MB 49.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40416 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40416 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40416 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40416 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_40416_validation.pdf.gz emd_40416_validation.pdf.gz | 830.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_40416_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40416_full_validation.pdf.gz | 829.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_40416_validation.xml.gz emd_40416_validation.xml.gz | 14.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_40416_validation.cif.gz emd_40416_validation.cif.gz | 18.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40416 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40416 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40416 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40416 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8sejMC  8sehC  8seiC  8sekC  8selC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40416.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 589.8 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40416.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 589.8 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
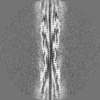
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.054 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
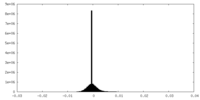
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_40416_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_40416_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Type I beta amyloid 42
| Entire | Name: Type I beta amyloid 42 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Type I beta amyloid 42
| Supramolecule | Name: Type I beta amyloid 42 / type: tissue / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Amyloid-beta protein 42
| Macromolecule | Name: Amyloid-beta protein 42 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Type I beta-amyloid 42 filaments from Down syndrome Case 2 Number of copies: 10 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.560128 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GYEVHHQKLV FFAEDVGSNK GAIIGLMVGG VVIA UniProtKB: Amyloid-beta precursor protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 1.103 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.46 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)