+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
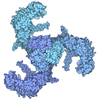
| Title | Human PIEZO1-A1988V-MDFIC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Human PIEZO1 / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmechanosensitive monoatomic cation channel activity / positive regulation of viral transcription / cuticular plate / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin / detection of mechanical stimulus / positive regulation of integrin activation / Tat protein binding / mechanosensitive monoatomic ion channel activity / stereocilium / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway ...mechanosensitive monoatomic cation channel activity / positive regulation of viral transcription / cuticular plate / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin / detection of mechanical stimulus / positive regulation of integrin activation / Tat protein binding / mechanosensitive monoatomic ion channel activity / stereocilium / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of JNK cascade / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / lamellipodium membrane / monoatomic cation transport / monoatomic cation channel activity / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / cyclin binding / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / regulation of membrane potential / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / nucleolus / endoplasmic reticulum / extracellular region / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang MF | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2025 Journal: Elife / Year: 2025Title: Structure of human PIEZO1 and its slow-inactivating channelopathy mutants. Authors: Yuanyue Shan / Xinyi Guo / Mengmeng Zhang / Meiyu Chen / Ying Li / Mingfeng Zhang / Duanqing Pei /  Abstract: PIEZO channels transmit mechanical force signals to cells, allowing them to make critical decisions during development and in pathophysiological conditions. Their fast/slow inactivation modes have ...PIEZO channels transmit mechanical force signals to cells, allowing them to make critical decisions during development and in pathophysiological conditions. Their fast/slow inactivation modes have been implicated in mechanopathologies but remain poorly understood. Here, we report several near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structures of fast-inactivating wild-type human PIEZO1 (hPIEZO1) and its slow-inactivating channelopathy mutants with or without its auxiliary subunit MDFIC. Our results suggest that hPIEZO1 has a more flattened and extended architecture than curved mouse PIEZO1 (mPIEZO1). The multi-lipidated MDFIC subunits insert laterally into the hPIEZO1 pore module like mPIEZO1, resulting in a more curved and extended state. Interestingly, the high-resolution structures suggest that the pore lipids, which directly seal the central hydrophobic pore, may be involved in the rapid inactivation of hPIEZO1. While the severe hereditary erythrocytosis mutant R2456H significantly slows down the inactivation of hPIEZO1, the hPIEZO1-R2456H-MDFIC complex shows a more curved and contracted structure with an inner helix twist due to the broken link between the pore lipid and R2456H. These results suggest that the pore lipids may be involved in the mechanopathological rapid inactivation mechanism of PIEZO channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_39219.map.gz emd_39219.map.gz | 1.8 GB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-39219-v30.xml emd-39219-v30.xml emd-39219.xml emd-39219.xml | 19.4 KB 19.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_39219.png emd_39219.png | 44.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-39219.cif.gz emd-39219.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_39219_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39219_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39219_half_map_2.map.gz emd_39219_half_map_2.map.gz | 1.8 GB 1.8 GB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39219 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39219 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_39219_validation.pdf.gz emd_39219_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_39219_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_39219_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_39219_validation.xml.gz emd_39219_validation.xml.gz | 26.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_39219_validation.cif.gz emd_39219_validation.cif.gz | 30.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39219 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39219 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8yfcMC  8yezC  8yfgC  8zu3C  8zu8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_39219.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_39219.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.57 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human PIEZO1-A1988V-MDFIC
| Entire | Name: Human PIEZO1-A1988V-MDFIC |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human PIEZO1-A1988V-MDFIC
| Supramolecule | Name: Human PIEZO1-A1988V-MDFIC / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 287.094062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MEPHVLGAVL YWLLLPCALL AACLLRFSGL SLVYLLFLLL LPWFPGPTRC GLQGHTGRLL RALLGLSLLF LVAHLALQIC LHIVPRLDQ LLGPSCSRWE TLSRHIGVTR LDLKDIPNAI RLVAPDLGIL VVSSVCLGIC GRLARNTRQS PHPRELDDDE R DVDASPTA ...String: MEPHVLGAVL YWLLLPCALL AACLLRFSGL SLVYLLFLLL LPWFPGPTRC GLQGHTGRLL RALLGLSLLF LVAHLALQIC LHIVPRLDQ LLGPSCSRWE TLSRHIGVTR LDLKDIPNAI RLVAPDLGIL VVSSVCLGIC GRLARNTRQS PHPRELDDDE R DVDASPTA GLQEAATLAP TRRSRLAARF RVTAHWLLVA AGRVLAVTLL ALAGIAHPSA LSSVYLLLFL ALCTWWACHF PI STRGFSR LCVAVGCFGA GHLICLYCYQ MPLAQALLPP AGIWARVLGL KDFVGPTNCS SPHALVLNTG LDWPVYASPG VLL LLCYAT ASLRKLRAYR PSGQRKEAAK GYEARELELA ELDQWPQERE SDQHVVPTAP DTEADNCIVH ELTGQSSVLR RPVR PKRAE PREASPLHSL GHLIMDQSYV CALIAMMVWS ITYHSWLTFV LLLWACLIWT VRSRHQLAML CSPCILLYGM TLCCL RYVW AMDLRPELPT TLGPVSLRQL GLEHTRYPCL DLGAMLLYTL TFWLLLRQFV KEKLLKWAES PAALTEVTVA DTEPTR TQT LLQSLGELVK GVYAKYWIYV CAGMFIVVSF AGRLVVYKIV YMFLFLLCLT LFQVYYSLWR KLLKAFWWLV VAYTMLV LI AVYTFQFQDF PAYWRNLTGF TDEQLGDLGL EQFSVSELFS SILVPGFFLL ACILQLHYFH RPFMQLTDME HVSLPGTR L PRWAHRQDAV SGTPLLREEQ QEHQQQQQEE EEEEEDSRDE GLGVATPHQA TQVPEGAAKW GLVAERLLEL AAGFSDVLS RVQVFLRRLL ELHVFKLVAL YTVWVALKEV SVMNLLLVVL WAFALPYPRF RPMASCLSTV WTCVIIVCKM LYQLKVVNPQ EYSSNCTEP FPNSTNLLPT EISQSLLYRG PVDPANWFGV RKGFPNLGYI QNHLQVLLLL VFEAIVYRRQ EHYRRQHQLA P LPAQAVFA SGTRQQLDQD LLGCLKYFIN FFFYKFGLEI CFLMAVNVIG QRMNFLVTLH GCWLVAILTR RHRQAIARLW PN YCLFLAL FLLYQYLLCL GMPPALCIDY PWRWSRAVPM NSALIKWLYL PDFFRAPNST NLISDFLLLL CASQQWQVFS AER TEEWQR MAGVNTDRLE PLRGEPNPVP NFIHCRSYLD MLKVAVFRYL FWLVLVVVFV TGATRISIFG LGYLLACFYL LLFG TALLQ RDTRARLVLW DCLILYNVTV IISKNMLSLL ACVFVEQMQT GFCWVIQLFS LVCTVKGYYD PKEMMDRDQD CLLPV EEAG IIWDSVCFFF LLLQRRVFLS HYYLHVRADL QATALLASRG FALYNAANLK SIDFHRRIEE KSLAQLKRQM ERIRAK QEK HRQGRVDRSR PQDTLGPKDP GLEPGPDSPG GSSPPRRQWW RPWLDHATVI HSGDYFLFES DSEEEEEAVP EDPRPSA QS AFQLAYQAWV TNAQAVLRRR QQEQEQARQE QAGQLPTGGG PSQEVEPAEG PEEAAAGRSH VVQRVLSTAQ FLWMLGQA L VDELTRWLQE FTRHHGTMSD VLRAERYLLT QELLQGGEVH RGVLDQLYTS QAEATLPGPT EAPNAPSTVS SGLGAEEPL SSMTDDMGSP LSTGYHTRSG SEEAVTDPGE REAGASLYQG LMRTASELLL DRRLRIPELE EAELFAEGQG RALRLLRAVY QCVAAHSEL LCYFIIILNH MVTASAGSLV LPVLVFLWAM LSIPRPSKRF WMTAIVFTEI AVVVKYLFQF GFFPWNSHVV L RRYENKPY FPPRILGLEK TDGYIKYDLV QLMALFFHRS QLLCYGLWDH EEDSPSKEHD KSGEEEQGAE EGPGVPAATT ED HIQVEAR VGPTDGTPEP QVELRPRDTR RISLRFRRRK KEGPARKGAA AIEAEDREEE EGEEEKEAPT GREKRPSRSG GRV RAAGRR LQGFCLSLAQ GTYRPLRRFF HDILHTKYRA ATDVYALMFL ADVVDFIIII FGFWAFGKHS AATDITSSLS DDQV PEAFL VMLLIQFSTM VVDRALYLRK TVLGKLAFQV ALVLAIHLWM FFILPAVTER MFNQNVVAQL WYFVKCIYFA LSAYQ IRCG YPTRILGNFL TKKYNHLNLF LFQGFRLVPF LVELRAVMDW VWTDTTLSLS SWMCVEDIYA NIFIIKCSRE TEKKYP QPK GQKKKKIVKY GMGGLIILFL IAIIWFPLLF MSLVRSVVGV VNQPIDVTVT LKLGGYEPLF TMSAQQPSII PFTAQAY EE LSRQFDPQPL AMQFISQYSP EDIVTAQIEG SSGALWRISP PSRAQMKREL YNGTADITLR FTWNFQRDLA KGGTVEYA N EKHMLALAPN STARRQLASL LEGTSDQSVV IPNLFPKYIR APNGPEANPV KQLQPNEEAD YLGVRIQLRR EQGAGATGF LEWWVIELQE CRTDCNLLPM VIFSDKVSPP SLGFLAGYGI MGLYVSIVLV IGKFVRGFFS EISHSIMFEE LPCVDRILKL CQDIFLVRE TRELELEEEL YAKLIFLYRS PETMIKWTRE KE UniProtKB: Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: MyoD family inhibitor domain-containing protein
| Macromolecule | Name: MyoD family inhibitor domain-containing protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.814113 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSGAGEALAP GPVGPQRVAE AGGGQLGSTA QGKCDKDNTE KDITQATNSH FTHGEMQDQS IWGNPSDGEL IRTQPQRLPQ LQTSAQVPS GEEIGKIKNG HTGLSNGNGI HHGAKHGSAD NRKLSAPVSQ KMHRKIQSSL SVNSDISKKS KVNAVFSQKT G SSPEDCCV ...String: MSGAGEALAP GPVGPQRVAE AGGGQLGSTA QGKCDKDNTE KDITQATNSH FTHGEMQDQS IWGNPSDGEL IRTQPQRLPQ LQTSAQVPS GEEIGKIKNG HTGLSNGNGI HHGAKHGSAD NRKLSAPVSQ KMHRKIQSSL SVNSDISKKS KVNAVFSQKT G SSPEDCCV HCILACLFCE FLTLCNIVLG QASCGICTSE ACCCCCGDEM GDDCNCPCDM DCGIMDACCE SSDCLEICME CC GICFPS UniProtKB: MyoD family inhibitor domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #3: DODECANE
| Macromolecule | Name: DODECANE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 15 / Formula: D12 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 170.335 Da |
| Chemical component information | 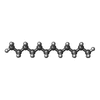 ChemComp-D12: |
-Macromolecule #4: (1S)-2-{[(S)-(2-aminoethoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(octadeca...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1S)-2-{[(S)-(2-aminoethoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(octadecanoyloxy)methyl]ethyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: L9Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 746.05 Da |
| Chemical component information | 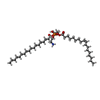 ChemComp-L9Q: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 10 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller