[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
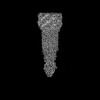
Yorodumi- EMDB-37590: Cryo-EM structure of the MS ring (C34) within the flagellar motor... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the MS ring (C34) within the flagellar motor-hook complex in the CW state | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Experimental map | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Flagellum / Flagellar motor / MS ring / MOTOR PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum basal body, MS ring / cytoskeletal motor activity / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
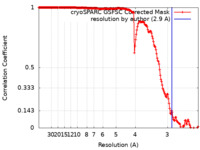
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tan JX / Zhang L / Zhou Y / Zhu YQ | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 3 items China, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis of the bacterial flagellar motor rotational switching. Authors: Jiaxing Tan / Ling Zhang / Xingtong Zhou / Siyu Han / Yan Zhou / Yongqun Zhu /  Abstract: The bacterial flagellar motor is a huge bidirectional rotary nanomachine that drives rotation of the flagellum for bacterial motility. The cytoplasmic C ring of the flagellar motor functions as the ...The bacterial flagellar motor is a huge bidirectional rotary nanomachine that drives rotation of the flagellum for bacterial motility. The cytoplasmic C ring of the flagellar motor functions as the switch complex for the rotational direction switching from counterclockwise to clockwise. However, the structural basis of the rotational switching and how the C ring is assembled have long remained elusive. Here, we present two high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of the C ring-containing flagellar basal body-hook complex from Salmonella Typhimurium, which are in the default counterclockwise state and in a constitutively active CheY mutant-induced clockwise state, respectively. In both complexes, the C ring consists of four subrings, but is in two different conformations. The CheY proteins are bound into an open groove between two adjacent protomers on the surface of the middle subring of the C ring and interact with the FliG and FliM subunits. The binding of the CheY protein induces a significant upward shift of the C ring towards the MS ring and inward movements of its protomers towards the motor center, which eventually remodels the structures of the FliG subunits and reverses the orientations and surface electrostatic potential of the α helices to trigger the counterclockwise-to-clockwise rotational switching. The conformational changes of the FliG subunits reveal that the stator units on the motor require a relocation process in the inner membrane during the rotational switching. This study provides unprecedented molecular insights into the rotational switching mechanism and a detailed overall structural view of the bacterial flagellar motors. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37590.map.gz emd_37590.map.gz | 483.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37590-v30.xml emd-37590-v30.xml emd-37590.xml emd-37590.xml | 20.2 KB 20.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_37590_fsc.xml emd_37590_fsc.xml | 17.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_37590.png emd_37590.png | 56.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37590.cif.gz emd-37590.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37590_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37590_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37590_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37590_half_map_2.map.gz | 474.1 MB 474.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37590 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37590 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37590 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37590 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8wjrMC  8whtC  8wiwC 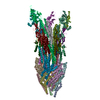 8wk3C  8wk4C  8wkiC  8wkkC  8wkqC  8wl2C  8wleC  8wlhC  8wliC  8wlnC  8wlpC  8wlqC  8wltC  8wo5C  8woeC  8xp0C  8xp1C  8yjtC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37590.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37590.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Experimental map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
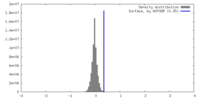
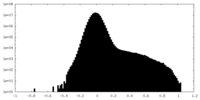
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_37590_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
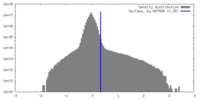
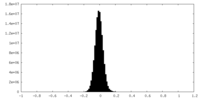
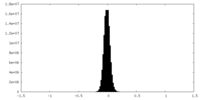
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_37590_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
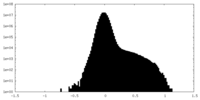
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : C ring-containing flagellar motor-hook complex in the CW state
| Entire | Name: C ring-containing flagellar motor-hook complex in the CW state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: C ring-containing flagellar motor-hook complex in the CW state
| Supramolecule | Name: C ring-containing flagellar motor-hook complex in the CW state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Flagellar M-ring protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Flagellar M-ring protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 34 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.295645 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSATASTATQ PKPLEWLNRL RANPRIPLIV AGSAAVAIVV AMVLWAKTPD YRTLFSNLSD QDGGAIVAQL TQMNIPYRFA NGSGAIEVP ADKVHELRLR LAQQGLPKGG AVGFELLDQE KFGISQFSEQ VNYQRALEGE LARTIETLGP VKSARVHLAM P KPSLFVRE ...String: MSATASTATQ PKPLEWLNRL RANPRIPLIV AGSAAVAIVV AMVLWAKTPD YRTLFSNLSD QDGGAIVAQL TQMNIPYRFA NGSGAIEVP ADKVHELRLR LAQQGLPKGG AVGFELLDQE KFGISQFSEQ VNYQRALEGE LARTIETLGP VKSARVHLAM P KPSLFVRE QKSPSASVTV TLEPGRALDE GQISAVVHLV SSAVAGLPPG NVTLVDQSGH LLTQSNTSGR DLNDAQLKFA ND VESRIQR RIEAILSPIV GNGNVHAQVT AQLDFANKEQ TEEHYSPNGD ASKATLRSRQ LNISEQVGAG YPGGVPGALS NQP APPNEA PIATPPTNQQ NAQNTPQTST STNSNSAGPR STQRNETSNY EVDRTIRHTK MNVGDIERLS VAVVVNYKTL ADGK PLPLT ADQMKQIEDL TREAMGFSDK RGDTLNVVNS PFSAVDNTGG ELPFWQQQSF IDQLLAAGRW LLVLVVAWIL WRKAV RPQL TRRVEEAKAA QEQAQVRQET EEAVEVRLSK DEQLQQRRAN QRLGAEVMSQ RIREMSDNDP RVVALVIRQW MSNDHE UniProtKB: Flagellar M-ring protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 180 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Blot time: 4 Blot force: 10 Wait time: 30 Blot total: 1 Drain time: 2. | |||||||||||||||
| Details | This sample was prepared by incubating the C ring-containing flagellar motor-hook complex with the constitutively active mutant of CheY (CheY**) |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: TFS Selectris / Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV |
| Software | Name: EPU |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Source name: Other / Chain - Initial model type: in silico model / Details: Model-Angelo |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  UCSF Chimera (ver. 1.17) UCSF Chimera (ver. 1.17) |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
| Output model |  PDB-8wjr: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)