[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-35300: The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter bound with nitrate, ATP and PIP2 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter bound with nitrate, ATP and PIP2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Transporter / ATP / PIP2 / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnitrate:proton symporter activity / nitrate transmembrane transport / nitrate transmembrane transporter activity / response to nitrate / plant-type vacuole membrane / voltage-gated chloride channel activity / chloride transport / chloride channel complex Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.16 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang Z / Zhang X / Zhang P | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 2 items China, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Molecular mechanism underlying regulation of Arabidopsis CLCa transporter by nucleotides and phospholipids. Authors: Zhao Yang / Xue Zhang / Shiwei Ye / Jingtao Zheng / Xiaowei Huang / Fang Yu / Zhenguo Chen / Shiqing Cai / Peng Zhang /  Abstract: Chloride channels (CLCs) transport anion across membrane to regulate ion homeostasis and acidification of intracellular organelles, and are divided into anion channels and anion/proton antiporters. ...Chloride channels (CLCs) transport anion across membrane to regulate ion homeostasis and acidification of intracellular organelles, and are divided into anion channels and anion/proton antiporters. Arabidopsis thaliana CLCa (AtCLCa) transporter localizes to the tonoplast which imports NO and to a less extent Cl from cytoplasm. The activity of AtCLCa and many other CLCs is regulated by nucleotides and phospholipids, however, the molecular mechanism remains unclear. Here we determine the cryo-EM structures of AtCLCa bound with NO and Cl, respectively. Both structures are captured in ATP and PI(4,5)P bound conformation. Structural and electrophysiological analyses reveal a previously unidentified N-terminal β-hairpin that is stabilized by ATP binding to block the anion transport pathway, thereby inhibiting the AtCLCa activity. While AMP loses the inhibition capacity due to lack of the β/γ- phosphates required for β-hairpin stabilization. This well explains how AtCLCa senses the ATP/AMP status to regulate the physiological nitrogen-carbon balance. Our data further show that PI(4,5)P or PI(3,5)P binds to the AtCLCa dimer interface and occupies the proton-exit pathway, which may help to understand the inhibition of AtCLCa by phospholipids to facilitate guard cell vacuole acidification and stomatal closure. In a word, our work suggests the regulatory mechanism of AtCLCa by nucleotides and phospholipids under certain physiological scenarios and provides new insights for future study of CLCs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35300.map.gz emd_35300.map.gz | 97.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35300-v30.xml emd-35300-v30.xml emd-35300.xml emd-35300.xml | 17.4 KB 17.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_35300.png emd_35300.png | 112 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35300_additional_1.map.gz emd_35300_additional_1.map.gz emd_35300_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35300_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35300_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35300_half_map_2.map.gz | 51.6 MB 95.2 MB 95.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35300 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35300 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_35300_validation.pdf.gz emd_35300_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_35300_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_35300_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_35300_validation.xml.gz emd_35300_validation.xml.gz | 13.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_35300_validation.cif.gz emd_35300_validation.cif.gz | 15.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35300 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35300 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8iadMC  8iabC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35300.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35300.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unharden map
| File | emd_35300_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unharden map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
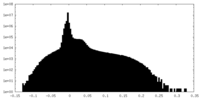
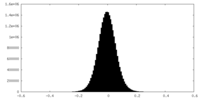
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35300_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
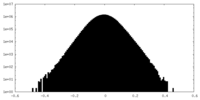
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35300_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter
| Entire | Name: The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter
| Supramolecule | Name: The Arabidopsis CLCa transporter / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Chloride channel protein CLC-a
| Macromolecule | Name: Chloride channel protein CLC-a / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 85.488906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) |
| Sequence | String: MDEDGNLQIS NSNYNGEEEG EDPENNTLNQ PLLKRHRTLS STPLALVGAK VSHIESLDYE INENDLFKHD WRSRSKAQVF QYIFLKWTL ACLVGLFTGL IATLINLAVE NIAGYKLLAV GYYIAQDRFW TGLMVFTGAN LGLTLVATVL VVYFAPTAAG P GIPEIKAY ...String: MDEDGNLQIS NSNYNGEEEG EDPENNTLNQ PLLKRHRTLS STPLALVGAK VSHIESLDYE INENDLFKHD WRSRSKAQVF QYIFLKWTL ACLVGLFTGL IATLINLAVE NIAGYKLLAV GYYIAQDRFW TGLMVFTGAN LGLTLVATVL VVYFAPTAAG P GIPEIKAY LNGIDTPNMF GFTTMMVKIV GSIGAVAAGL DLGKEGPLVH IGSCIASLLG QGGPDNHRIK WRWLRYFNND RD RRDLITC GSASGVCAAF RSPVGGVLFA LEEVATWWRS ALLWRTFFST AVVVVVLRAF IEICNSGKCG LFGSGGLIMF DVS HVEVRY HAADIIPVTL IGVFGGILGS LYNHLLHKVL RLYNLINQKG KIHKVLLSLG VSLFTSVCLF GLPFLAECKP CDPS IDEIC PTNGRSGNFK QFNCPNGYYN DLSTLLLTTN DDAVRNIFSS NTPNEFGMVS LWIFFGLYCI LGLITFGIAT PSGLF LPII LMGSAYGRML GTAMGSYTNI DQGLYAVLGA ASLMAGSMRM TVSLCVIFLE LTNNLLLLPI TMFVLLIAKT VGDSFN LSI YEIILHLKGL PFLEANPEPW MRNLTVGELN DAKPPVVTLN GVEKVANIVD VLRNTTHNAF PVLDGADQNT GTELHGL IL RAHLVKVLKK RWFLNEKRRT EEWEVREKFT PVELAEREDN FDDVAITSSE MQLYVDLHPL TNTTPYTVVQ SMSVAKAL V LFRSVGLRHL LVVPKIQASG MSPVIGILTR QDLRAYNILQ AFPHLDKHKS GKAR UniProtKB: Chloride channel protein CLC-a |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: NITRATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: NITRATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.005 Da |
| Chemical component information | 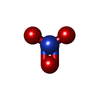 ChemComp-NO3: |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(o...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phosphoryl]oxy-propyl] octanoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PIO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 746.566 Da |
| Chemical component information | 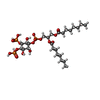 ChemComp-PIO: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.16 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 92708 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z
Z Y
Y X
X