[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24059: Single particle cryo-EM structure of the Chaetomium thermophilum ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
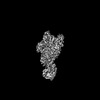
| Title | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the Chaetomium thermophilum Nup188-Nic96-Nup145N complex (Nup188 residues 1-1858; Nic96 residues 240-301; Nup145N residues 640-732) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Unsharpened map generated with cryoSPARC NU refine | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nuclear pore complex / nucleocytoplasmic transport / alpha-helical solenoid / nuclear pore / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnuclear pore inner ring / telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear localization sequence binding / structural constituent of nuclear pore / RNA export from nucleus / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / mRNA transport ...nuclear pore inner ring / telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear localization sequence binding / structural constituent of nuclear pore / RNA export from nucleus / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / protein import into nucleus / nuclear membrane / hydrolase activity / RNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) / Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) /  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus) | |||||||||||||||
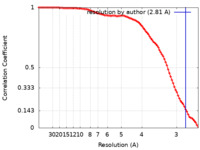
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.81 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Petrovic S / Samanta D / Perriches T / Bley CJ / Thierbach K / Brown B / Nie S / Mobbs GW / Stevens TA / Liu X ...Petrovic S / Samanta D / Perriches T / Bley CJ / Thierbach K / Brown B / Nie S / Mobbs GW / Stevens TA / Liu X / Tomaleri GP / Schaus L / Hoelz A | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Architecture of the linker-scaffold in the nuclear pore. Authors: Stefan Petrovic / Dipanjan Samanta / Thibaud Perriches / Christopher J Bley / Karsten Thierbach / Bonnie Brown / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Taylor A Stevens / Xiaoyu Liu / Giovani Pinton ...Authors: Stefan Petrovic / Dipanjan Samanta / Thibaud Perriches / Christopher J Bley / Karsten Thierbach / Bonnie Brown / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Taylor A Stevens / Xiaoyu Liu / Giovani Pinton Tomaleri / Lucas Schaus / André Hoelz /  Abstract: INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, the selective bidirectional transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm occurs through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Embedded in nuclear envelope ...INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, the selective bidirectional transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm occurs through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Embedded in nuclear envelope pores, the ~110-MDa human NPC is an ~1200-Å-wide and ~750-Å-tall assembly of ~1000 proteins, collectively termed nucleoporins. Because of the NPC's eightfold rotational symmetry along the nucleocytoplasmic axis, each of the ~34 different nucleoporins occurs in multiples of eight. Architecturally, the NPC's symmetric core is composed of an inner ring encircling the central transport channel and two outer rings anchored on both sides of the nuclear envelope. Because of its central role in the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, the NPC is commonly targeted in viral infections and its nucleoporin constituents are associated with a plethora of diseases. RATIONALE Although the arrangement of most scaffold nucleoporins in the NPC's symmetric core was determined by quantitative docking of crystal structures into cryo-electron tomographic (cryo-ET) maps of intact NPCs, the topology and molecular details of their cohesion by multivalent linker nucleoporins have remained elusive. Recently, in situ cryo-ET reconstructions of NPCs from various species have indicated that the NPC's inner ring is capable of reversible constriction and dilation in response to variations in nuclear envelope membrane tension, thereby modulating the diameter of the central transport channel by ~200 Å. We combined biochemical reconstitution, high-resolution crystal and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure determination, docking into cryo-ET maps, and physiological validation to elucidate the molecular architecture of the linker-scaffold interaction network that not only is essential for the NPC's integrity but also confers the plasticity and robustness necessary to allow and withstand such large-scale conformational changes. RESULTS By biochemically mapping scaffold-binding regions of all fungal and human linker nucleoporins and determining crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of linker-scaffold complexes, we completed the characterization of the biochemically tractable linker-scaffold network and established its evolutionary conservation, despite considerable sequence divergence. We determined a series of crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of the intact Nup188 and Nup192 scaffold hubs bound to their Nic96, Nup145N, and Nup53 linker nucleoporin binding regions, revealing that both proteins form distinct question mark-shaped keystones of two evolutionarily conserved hetero‑octameric inner ring complexes. Linkers bind to scaffold surface pockets through short defined motifs, with flanking regions commonly forming additional disperse interactions that reinforce the binding. Using a structure‑guided functional analysis in , we confirmed the robustness of linker‑scaffold interactions and established the physiological relevance of our biochemical and structural findings. The near-atomic composite structures resulting from quantitative docking of experimental structures into human and cryo-ET maps of constricted and dilated NPCs structurally disambiguated the positioning of the Nup188 and Nup192 hubs in the intact fungal and human NPC and revealed the topology of the linker-scaffold network. The linker-scaffold gives rise to eight relatively rigid inner ring spokes that are flexibly interconnected to allow for the formation of lateral channels. Unexpectedly, we uncovered that linker‑scaffold interactions play an opposing role in the outer rings by forming tight cross-link staples between the eight nuclear and cytoplasmic outer ring spokes, thereby limiting the dilatory movements to the inner ring. CONCLUSION We have substantially advanced the structural and biochemical characterization of the symmetric core of the and human NPCs and determined near-atomic composite structures. The composite structures uncover the molecular mechanism by which the evolutionarily conserved linker‑scaffold establishes the NPC's integrity while simultaneously allowing for the observed plasticity of the central transport channel. The composite structures are roadmaps for the mechanistic dissection of NPC assembly and disassembly, the etiology of NPC‑associated diseases, the role of NPC dilation in nucleocytoplasmic transport of soluble and integral membrane protein cargos, and the anchoring of asymmetric nucleoporins. [Figure: see text]. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24059.map.gz emd_24059.map.gz | 32.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24059-v30.xml emd-24059-v30.xml emd-24059.xml emd-24059.xml | 25.3 KB 25.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24059_fsc.xml emd_24059_fsc.xml | 11.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
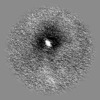
| Images |  emd_24059.png emd_24059.png | 57.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_24059_msk_1.map emd_24059_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24059.cif.gz emd-24059.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24059_additional_1.map.gz emd_24059_additional_1.map.gz emd_24059_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24059_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24059_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24059_half_map_2.map.gz | 1.7 MB 4.4 MB 4.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24059 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24059 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24059 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24059 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24059_validation.pdf.gz emd_24059_validation.pdf.gz | 596.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24059_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24059_full_validation.pdf.gz | 596.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24059_validation.xml.gz emd_24059_validation.xml.gz | 15.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24059_validation.cif.gz emd_24059_validation.cif.gz | 20.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24059 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24059 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24059 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24059 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mvzMC  7mvtC  7mvuC  7mvvC  7mvwC  7mvxC  7mvyC 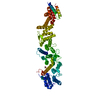 7mw0C  7mw1C  7tbiC  7tbjC  7tbkC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24059.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24059.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map generated with cryoSPARC NU refine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.296 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_24059_msk_1.map emd_24059_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
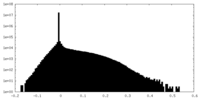
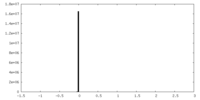
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: LocScale locally sharpened map (model B-factor based scaling)
| File | emd_24059_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | LocScale locally sharpened map (model B-factor based scaling) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
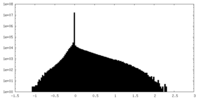
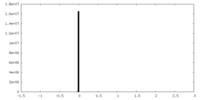
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC
| File | emd_24059_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC
| File | emd_24059_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-dataset map generated with cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Nup188-Nic96-Nup145N heterotrimer
| Entire | Name: Nup188-Nic96-Nup145N heterotrimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Nup188-Nic96-Nup145N heterotrimer
| Supramolecule | Name: Nup188-Nic96-Nup145N heterotrimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum var. thermophilum DSM 1495 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220.9 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Nucleoporin NUP188
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleoporin NUP188 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus)Strain: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 204.429719 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GPHNMATLTD RTYLPPLEDC LTGRTVILSW RLVASALEDA DLARLTSPAL STFLRDGFVH ELLKHPARVF EPKDLKQEFE TKTSSIQTV APGVDTIKKD ALWLADAVAI NQVAALRIVL IEYQTRAHSH LVLPLSTQDV ANIQEAAGVG DAHASSILSL L NPASAVDA ...String: GPHNMATLTD RTYLPPLEDC LTGRTVILSW RLVASALEDA DLARLTSPAL STFLRDGFVH ELLKHPARVF EPKDLKQEFE TKTSSIQTV APGVDTIKKD ALWLADAVAI NQVAALRIVL IEYQTRAHSH LVLPLSTQDV ANIQEAAGVG DAHASSILSL L NPASAVDA ETMWCDFETE ARRRERILAT YLSERRSFTA AVDALVTFLL HSAPGQHKDL DSLRRALLKD AFAFDEDLDV PD RSKLLTM APTYMNLVED CIARAQALPA KLGESFKTEA FELDWLRTAI TEAVHSLSIA FQALDLDTPY FAPHELLSEW FEL MNSSLF LESILGFEVV ADLAMPARSL VSAICLKMLN IDRTIQFLHD FDYPDGEEPY LLSSQTLNKI HTAVTNAVNS GVAA SLPVA FAWSLIVHQM HLGYQERAER RDLLVNQRAQ AGFELEFQPS ASTPNRRRRN SAGSIVSLEA SPYDDFLREQ RLDND IAPV EQIAMLATSR GQVYQVMSEM ALCLGTTHEA AFRPAVGARA RLVFQDLLKR SAYLIPYQDE PVFSLLAILA TGRQYW DVT DALSASSLNQ VYTDMLDDET LFTQFTMQAI NRFPYEFNPF SVLCRVLAAA LITNKDKADV VTGWLWRTPT LTVDWNP AW DRSYELCFED ENTNSFRLTR DVDLFGSASP ARPRHLAAEE RFIIPEGTLG RFVTDVGRTA RLEFEHSALA LLGKRLEV K AAEEICDSGM APLDVDEQAE AVAMLATVLR AESLKSTAKG GDPEAPLKFL KEASRLLPHN KDILTVISDT IDGLVEKEL LELDGPQIAV LASCLQFLHA ALAVCPGRVW AYMSRCALIA GDARPGRLSR ITGSLDMYAE RFDLLSSAVK LFAALIDSAA CSAVQRRAG STALVSVRSA VENPWLGTSE KILSRVALAI AQAALDVYES TTTWRFRSEL DRSILVRDVV GLMHKLVVHA H TLSSHLTS TLSPAAAHII SSFLTPPPSA SSLRFQPLLG TLLVALITPR ATLYPGQSRI LAERVTSVLA FCTSLLRAAD FL GQTHIPL QTHLFQSACL LARLPAANAV YRAPVLELLR ALVEVAGRAA NGSGEPPSLL GYLGSHAARS FISLVEGIDK PFG RVEHAV VTWRFFAAVI RNRQQWMAGC LLTGRTPREA LKGGGEQKIE RKVGEGSVLA AAMERLREVK SLDVQEAVAV MDFV VSAQN YWPWTIFAVR KEKEVVDALR GYVRGLKAPG MVMKTDGAAA AAFQARIAAY VAETFAMQLY HMRQMRQAEK FAGEL VADL DYFLREGVMV WGYNASLHGN FARNFAKRFP GVEVDDFKRT MWLPRELGKG YYYALEVAEQ MLGFDAGWGG VKQSGF RKE METANLNLSL VEAQVSLFHA WEYLLLELTL SLLPKKENAA FARQVLQVVE QCLEANQRSQ PPENIFVVLG HARAGLA LT LLQRLADANQ LPRDVTHLLA LVSSAIHAVE NPFGANDLPY FRTLLKILFV VLRAAKQGTA KPGESNVAIT QQVLTILD R VVARCFRALA ALVHEQQQNA TDGTTTAPED LALITAILQA CLSVPGIEQC QVQVLNIMAA HDVFQVAVAL FSWADRLLP ANPSPASSST STSATNPASG DPVYGELALL FLLELSALPA LAEHLACDGL LGHLAAARLA GYMRRTNVGP FAENAGAARC YAIWAKCLL PLLLNILAAL GSTVAPEVAW VLNQFPNLLQ SSVERIEPPG FSRPTLSLAS TPPRQKFISL LEISEIHSLA L LTRVLAAC RAQNARDVPE VTWDGAKVLE CVEYWLRGRK VLRERLVPLG PREVEWRGMV ATGGVVGVAG DGGEGCENRL EE KAVGLLV GVREVLEGGL EGEGE UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NUP188 |
-Macromolecule #2: Nucleoporin NIC96
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleoporin NIC96 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus)Strain: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.173938 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SGTGLGEVDV DTYLSNLQTK TTLSMIADGL ERSARDFDAF LEENVTLEWE AQRKRIYQHF GIK UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NIC96 |
-Macromolecule #3: Nucleoporin NUP145N
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleoporin NUP145N / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus) Chaetomium thermophilum (strain DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719) (fungus)Strain: DSM 1495 / CBS 144.50 / IMI 039719 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.690699 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SNASRLVTTP QKRAYGFSFS AYGSPTSPSS SASSTPGAFG QSILSSSINR GLNKSISASN LRRSLNVEDS ILQPGAFSAN SSMRLLGGP GSHKK UniProtKB: Nucleoporin NUP145 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 10740 / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 103.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7mvz: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7mvz: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)