+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23057 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Full map from 3D refinement | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complex / Hemophilia / FVIII / VWF / BLOOD CLOTTING | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen ...Defective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen / Defective binding of VWF variant to GPIb:IX:V / Weibel-Palade body / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / hemostasis / platelet alpha granule / Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen / Cargo concentration in the ER / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / p130Cas linkage to MAPK signaling for integrins / Defective F8 cleavage by thrombin / Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) / cell-substrate adhesion / GRB2:SOS provides linkage to MAPK signaling for Integrins / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / immunoglobulin binding / Integrin cell surface interactions / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / collagen binding / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Integrin signaling / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / acute-phase response / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / platelet activation / : / response to wounding / Golgi lumen / integrin binding / extracellular matrix / blood coagulation / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Platelet degranulation / protein-folding chaperone binding / protease binding / oxidoreductase activity / cell adhesion / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / copper ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
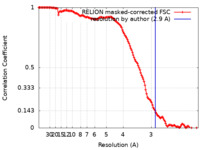
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fuller JR / Batchelor JD | |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: Elife / Year: 2016 Title: Automated structure refinement of macromolecular assemblies from cryo-EM maps using Rosetta. Authors: Ray Yu-Ruei Wang / Yifan Song / Benjamin A Barad / Yifan Cheng / James S Fraser / Frank DiMaio /  Abstract: Cryo-EM has revealed the structures of many challenging yet exciting macromolecular assemblies at near-atomic resolution (3-4.5Å), providing biological phenomena with molecular descriptions. ...Cryo-EM has revealed the structures of many challenging yet exciting macromolecular assemblies at near-atomic resolution (3-4.5Å), providing biological phenomena with molecular descriptions. However, at these resolutions, accurately positioning individual atoms remains challenging and error-prone. Manually refining thousands of amino acids - typical in a macromolecular assembly - is tedious and time-consuming. We present an automated method that can improve the atomic details in models that are manually built in near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM maps. Applying the method to three systems recently solved by cryo-EM, we are able to improve model geometry while maintaining the fit-to-density. Backbone placement errors are automatically detected and corrected, and the refinement shows a large radius of convergence. The results demonstrate that the method is amenable to structures with symmetry, of very large size, and containing RNA as well as covalently bound ligands. The method should streamline the cryo-EM structure determination process, providing accurate and unbiased atomic structure interpretation of such maps. #1:  Journal: Comput. Cryst. Newsl. / Year: 2013 Journal: Comput. Cryst. Newsl. / Year: 2013Title: New tool: phenix.real_space_refine Authors: Afonine PV / Headd JJ / Terwilliger TC / Adams PD | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23057.map.gz emd_23057.map.gz | 170.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23057-v30.xml emd-23057-v30.xml emd-23057.xml emd-23057.xml | 34.5 KB 34.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_23057_fsc.xml emd_23057_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_23057.png emd_23057.png | 112.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_23057_msk_1.map emd_23057_msk_1.map | 216 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23057.cif.gz emd-23057.cif.gz | 9.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_23057_additional_1.map.gz emd_23057_additional_1.map.gz emd_23057_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23057_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23057_half_map_2.map.gz emd_23057_half_map_2.map.gz | 125.7 MB 171.4 MB 171.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23057 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23057 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23057 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7kwoMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23057.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23057.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Full map from 3D refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
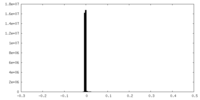
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_23057_msk_1.map emd_23057_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
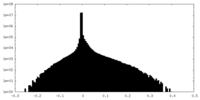
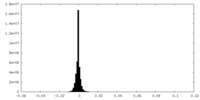
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Map sharpened by an automatically-fit B-factor (-69.3204) then...
| File | emd_23057_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map sharpened by an automatically-fit B-factor (-69.3204) then filtered to local resolution. Used for model building and refinement. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
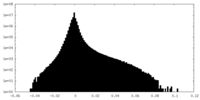
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 2
| File | emd_23057_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 1
| File | emd_23057_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001)
| Entire | Name: rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001)
| Supramolecule | Name: rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: An engineered therapeutic complex between coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor D'D3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 311.64974 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Coagulation factor FVIII-Fc-XTEN
| Macromolecule | Name: Coagulation factor FVIII-Fc-XTEN / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 218.874969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MQIELSTCFF LCLLRFCFSA TRRYYLGAVE LSWDYMQSDL GELPVDARFP PRVPKSFPFN TSVVYKKTLF VEFTDHLFNI AKPRPPWMG LLGPTIQAEV YDTVVITLKN MASHPVSLHA VGVSYWKASE GAEYDDQTSQ REKEDDKVFP GGSHTYVWQV L KENGPMAS ...String: MQIELSTCFF LCLLRFCFSA TRRYYLGAVE LSWDYMQSDL GELPVDARFP PRVPKSFPFN TSVVYKKTLF VEFTDHLFNI AKPRPPWMG LLGPTIQAEV YDTVVITLKN MASHPVSLHA VGVSYWKASE GAEYDDQTSQ REKEDDKVFP GGSHTYVWQV L KENGPMAS DPLCLTYSYL SHVDLVKDLN SGLIGALLVC REGSLAKEKT QTLHKFILLF AVFDEGKSWH SETKNSLMQD RD AASARAW PKMHTVNGYV NRSLPGLIGC HRKSVYWHVI GMGTTPEVHS IFLEGHTFLV RNHRQASLEI SPITFLTAQT LLM DLGQFL LFCHISSHQH DGMEAYVKVD SCPEEPQLRM KNNEEAEDYD DDLTDSEMDV VRFDDDNSPS FIQIRSVAKK HPKT WVHYI AAEEEDWDYA PLVLAPDDRS YKSQYLNNGP QRIGRKYKKV RFMAYTDETF KTREAIQHES GILGPLLYGE VGDTL LIIF KNQASRPYNI YPHGITDVRP LYSRRLPKGV KHLKDFPILP GEIFKYKWTV TVEDGPTKSD PRCLTRYYSS FVNMER DLA SGLIGPLLIC YKESVDQRGN QIMSDKRNVI LFSVFDENRS WYLTENIQRF LPNPAGVQLE DPEFQASNIM HSINGYV FD SLQLSVCLHE VAYWYILSIG AQTDFLSVFF SGYTFKHKMV YEDTLTLFPF SGETVFMSME NPGLWILGCH NSDFRNRG M TALLKVSSCD KNTGDYYEDS YEDISAYLLS KNNAIEPRSF SQNGTSESAT PESGPGSEPA TSGSETPGTS ESATPESGP GSEPATSGSE TPGTSESATP ESGPGTSTEP SEGSAPGSPA GSPTSTEEGT SESATPESGP GSEPATSGSE TPGTSESATP ESGPGSPAG SPTSTEEGSP AGSPTSTEEG TSTEPSEGSA PGTSESATPE SGPGTSESAT PESGPGTSES ATPESGPGSE P ATSGSETP GSEPATSGSE TPGSPAGSPT STEEGTSTEP SEGSAPGTST EPSEGSAPGS EPATSGSETP GTSESATPES GP GTSTEPS EGSAPASSEI TRTTLQSDQE EIDYDDTISV EMKKEDFDI(TYS) DEDENQSPRS FQKKTRHYFI AAVERLWDY GMSSSPHVLR NRAQSGSVPQ FKKVVFQEFT DGSFTQPLYR GELNEHLGLL GPYIRAEVED NIMVTFRNQA SRPYSFYSSL ISYEEDQRQ GAEPRKNFVK PNETKTYFWK VQHHMAPTKD EFDCKAWAYF SDVDLEKDVH SGLIGPLLVC HTNTLNPAHG R QVTVQEFA LFFTIFDETK SWYFTENMER NCRAPCNIQM EDPTFKENYR FHAINGYIMD TLPGLVMAQD QRIRWYLLSM GS NENIHSI HFSGHVFTVR KKEEYKMALY NLYPGVFETV EMLPSKAGIW RVECLIGEHL HAGMSTLFLV YSNKCQTPLG MAS GHIRDF QITASGQYGQ WAPKLARLHY SGSINAWSTK EPFSWIKVDL LAPMIIHGIK TQGARQKFSS LYISQFIIMY SLDG KKWQT YRGNSTGTLM VFFGNVDSSG IKHNIFNPPI IARYIRLHPT HYSIRSTLRM ELMGCDLNSC SMPLGMESKA ISDAQ ITAS SYFTNMFATW SPSKARLHLQ GRSNAWRPQV NNPKEWLQVD FQKTMKVTGV TTQGVKSLLT SMYVKEFLIS SSQDGH QWT LFFQNGKVKV FQGNQDSFTP VVNSLDPPLL TRYLRIHPQS WVHQIALRME VLGCEAQDLY DKTHTCPPCP APELLGG PS VFLFPPKPKD TLMISRTPEV TCVVVDVSHE DPEVKFNWYV DGVEVHNAKT KPREEQYNST YRVVSVLTVL HQDWLNGK E YKCKVSNKAL PAPIEKTISK AKGQPREPQV YTLPPSRDEL TKNQVSLTCL VKGFYPSDIA VEWESNGQPE NNYKTTPPV LDSDGSFFLY SKLTVDKSRW QQGNVFSCSV MHEALHNHYT QKSLSLSPG |
-Macromolecule #2: von Willebrand factor-XTEN-Fc
| Macromolecule | Name: von Willebrand factor-XTEN-Fc / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 179.048953 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MIPARFAGVL LALALILPGT LCAEGTRGRS STARCSLFGS DFVNTFDGSM YSFAGYCSYL LAGGCQKRSF SIIGDFQNGK RVSLSVYLG EFFDIHLFVN GTVTQGDQRV SMPYASKGLY LETEAGYYKL SGEAYGFVAR IDGSGNFQVL LSDRYFNKTC G LCGNFNIF ...String: MIPARFAGVL LALALILPGT LCAEGTRGRS STARCSLFGS DFVNTFDGSM YSFAGYCSYL LAGGCQKRSF SIIGDFQNGK RVSLSVYLG EFFDIHLFVN GTVTQGDQRV SMPYASKGLY LETEAGYYKL SGEAYGFVAR IDGSGNFQVL LSDRYFNKTC G LCGNFNIF AEDDFMTQEG TLTSDPYDFA NSWALSSGEQ WCERASPPSS SCNISSGEMQ KGLWEQCQLL KSTSVFARCH PL VDPEPFV ALCEKTLCEC AGGLECACPA LLEYARTCAQ EGMVLYGWTD HSACSPVCPA GMEYRQCVSP CARTCQSLHI NEM CQERCV DGCSCPEGQL LDEGLCVEST ECPCVHSGKR YPPGTSLSRD CNTCICRNSQ WICSNEECPG ECLVTGQSHF KSFD NRYFT FSGICQYLLA RDCQDHSFSI VIETVQCADD RDAVCTRSVT VRLPGLHNSL VKLKHGAGVA MDGQDIQLPL LKGDL RIQH TVTASVRLSY GEDLQMDWDG RGRLLVKLSP VYAGKTCGLC GNYNGNQGDD FLTPSGLAEP RVEDFGNAWK LHGDCQ DLQ KQHSDPCALN PRMTRFSEEA CAVLTSPTFE ACHRAVSPLP YLRNCRYDVC SCSDGRECLC GALASYAAAC AGRGVRV AW REPGRCELNC PKGQVYLQCG TPCNLTCRSL SYPDEECNEA CLEGCFCPPG LYMDERGDCV PKAQCPCYYD GEIFQPED I FSDHHTMCYC EDGFMHCTMS GVPGSLLPDA VLSSPLSHRS KRSLSCRPPM VKLVCPADNL RAEGLECTKT CQNYDLECM SMGCVSGCLC PPGMVRHENR CVALERCPCF HQGKEYAPGE TVKIGCNTCV CRDRKWNCTD HVCDATCSTI GMAHYLTFDG LKYLFPGEC QYVLVQDYCG SNPGTFRILV GNKGCSHPSV KCKKRVTILV EGGEIELFDG EVNVKRPMKD ETHFEVVESG R YIILLLGK ALSVVWDRHL SISVVLKQTY QEKVCGLCGN FDGIQNNDLT SSNLQVEEDP VDFGNSWKVS SQCADTRKVP LD SSPATCH NNIMKQTMVD SSCRILTSDV FQDCNKLVDP EPYLDVCIYD TCSCESIGDC AAFCDTIAAY AHVCAQHGKV VTW RTATLC PQSCEERNLR ENGYEAEWRY NSCAPACQVT CQHPEPLACP VQCVEGCHAH CPPGKILDEL LQTCVDPEDC PVCE VAGRR FASGKKVTLN PSDPEHCQIC HCDVVNLTCE ACQEPGTSES ATPESGPGSE PATSGSETPG TSESATPESG PGSEP ATSG SETPGTSESA TPESGPGTST EPSEGSAPGS PAGSPTSTEE GTSESATPES GPGSEPATSG SETPGTSESA TPESGP GSP AGSPTSTEEG SPAGSPTSTE EGASSDKNTG DYYEDSYEDI SAYLLSKNNA IEPRSFSDKT HTCPPCPAPE LLGGPSV FL FPPKPKDTLM ISRTPEVTCV VVDVSHEDPE VKFNWYVDGV EVHNAKTKPR EEQYNSTYRV VSVLTVLHQD WLNGKEYK C KVSNKALPAP IEKTISKAKG QPREPQVYTL PPSRDELTKN QVSLTCLVKG FYPSDIAVEW ESNGQPENNY KTTPPVLDS DGSFFLYSKL TVDKSRWQQG NVFSCSVMHE ALHNHYTQKS LSLSPG |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #5: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: COPPER (II) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: COPPER (II) ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.546 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CU: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation #1
Sample preparation #1
| Preparation ID | 1 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 0.75 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer | pH: 7.3 Component:
Details: NP-40s detergent was added to samples immediately prior to vitrification, to a final concentration of 0.0038 % (weight/volume). | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Film type ID: 1 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 75 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||
| Details | Prepared by gel filtration chromatography immediately prior to vitrification. |
- Sample preparation #2
Sample preparation #2
| Preparation ID | 2 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 0.75 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer | pH: 7.3 Component:
Details: NP-40s detergent was added to samples immediately prior to vitrification, to a final concentration of 0.0038 % (weight/volume). | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Film type ID: 1 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 75 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||
| Details | Prepared by gel filtration chromatography immediately prior to vitrification. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 11520 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 8184 pixel / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




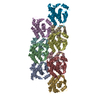

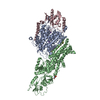

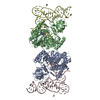


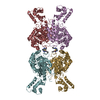


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)