+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
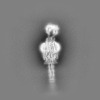
| Title | Zorya anti-bacteriophage defense system ZorAB | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nuclease / ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology | : / :  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.67 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu H / Taylor NMI | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 3 items Denmark, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Structure and mechanism of the Zorya anti-phage defence system. Authors: Haidai Hu / Philipp F Popp / Thomas C D Hughes / Aritz Roa-Eguiara / Nicole R Rutbeek / Freddie J O Martin / Ivo Alexander Hendriks / Leighton J Payne / Yumeng Yan / Dorentina Humolli / ...Authors: Haidai Hu / Philipp F Popp / Thomas C D Hughes / Aritz Roa-Eguiara / Nicole R Rutbeek / Freddie J O Martin / Ivo Alexander Hendriks / Leighton J Payne / Yumeng Yan / Dorentina Humolli / Victor Klein-Sousa / Inga Songailiene / Yong Wang / Michael Lund Nielsen / Richard M Berry / Alexander Harms / Marc Erhardt / Simon A Jackson / Nicholas M I Taylor /       Abstract: Zorya is a recently identified and widely distributed bacterial immune system that protects bacteria from viral (phage) infections. Three Zorya subtypes have been identified, each containing ...Zorya is a recently identified and widely distributed bacterial immune system that protects bacteria from viral (phage) infections. Three Zorya subtypes have been identified, each containing predicted membrane-embedded ZorA-ZorB (ZorAB) complexes paired with soluble subunits that differ among Zorya subtypes, notably ZorC and ZorD in type I Zorya systems. Here we investigate the molecular basis of Zorya defence using cryo-electron microscopy, mutagenesis, fluorescence microscopy, proteomics and functional studies. We present cryo-electron microscopy structures of ZorAB and show that it shares stoichiometry and features of other 5:2 inner membrane ion-driven rotary motors. The ZorAB complex contains a dimeric ZorB peptidoglycan-binding domain and a pentameric α-helical coiled-coil tail made of ZorA that projects approximately 70 nm into the cytoplasm. We also characterize the structure and function of the soluble Zorya components ZorC and ZorD, finding that they have DNA-binding and nuclease activity, respectively. Comprehensive functional and mutational analyses demonstrate that all Zorya components work in concert to protect bacterial cells against invading phages. We provide evidence that ZorAB operates as a proton-driven motor that becomes activated after sensing of phage invasion. Subsequently, ZorAB transfers the phage invasion signal through the ZorA cytoplasmic tail to recruit and activate the soluble ZorC and ZorD effectors, which facilitate the degradation of the phage DNA. In summary, our study elucidates the foundational mechanisms of Zorya function as an anti-phage defence system. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18751.map.gz emd_18751.map.gz | 450.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18751-v30.xml emd-18751-v30.xml emd-18751.xml emd-18751.xml | 21.2 KB 21.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18751_fsc.xml emd_18751_fsc.xml | 16.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18751.png emd_18751.png | 40.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18751.cif.gz emd-18751.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18751_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18751_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18751_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18751_half_map_2.map.gz | 443.2 MB 443.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18751 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18751 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18751 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18751 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8qydMC  8qy7C  8qycC  8qyhC  8qykC  8qyyC 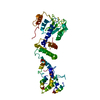 8r68C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18751.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18751.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_18751_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_18751_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Zorya anti-bacteriophage defense system ZorAB
| Entire | Name: Zorya anti-bacteriophage defense system ZorAB |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Zorya anti-bacteriophage defense system ZorAB
| Supramolecule | Name: Zorya anti-bacteriophage defense system ZorAB / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Anti-phage defense ZorAB system ZorA
| Macromolecule | Name: Anti-phage defense ZorAB system ZorA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80.339195 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSWLNSILVT LTSVEPYKVP VTVIVTVTFA FVCFIFFYLL RSIRIIYGLK KYTRSINSIE KSAPEVQLEH LKSLFQRSEL KHAWNEFEE SLHSQYELEN GEEKIVRIRA TAPSASFFSE QQLVDIPLNT EFFKHLPGIL TGMGIIGTFY GLMIGLNHFD P STPEQVSS ...String: MSWLNSILVT LTSVEPYKVP VTVIVTVTFA FVCFIFFYLL RSIRIIYGLK KYTRSINSIE KSAPEVQLEH LKSLFQRSEL KHAWNEFEE SLHSQYELEN GEEKIVRIRA TAPSASFFSE QQLVDIPLNT EFFKHLPGIL TGMGIIGTFY GLMIGLNHFD P STPEQVSS SVNNLLRDVL YAFLGSAFAI FASILVTWLE KLSIAKSYKY LEKFTAALDS LYDSGVGEEY LASLVKSSNE SA TQARHLK ESLVTDLRDM LLHLAESQKI ENERLANTLS ATYRESGSQF ADQVSGAIEN SLKSPLDKIA GAVQTASGDQ SGM VQNMLQ NVLTAFMAKL DTTFGQQFTN LNEMMGQTVG AIQTMQTGFS ALLQDMRQVS DDSRQGSAQL IEQLLSEMKS GQQA LQAGM NDMLTSLQVS VAKIGAEGEG AGERIARQLE KMFADSEARE KAQAEHMAAF VEAIQNSVQQ GQSATMEKMA ASVGA LGEQ LGSLFGQIDK GQQQISATQQ ANQQSLHEQT QRVMSEVDDQ IKQLVETVAS QHQGTTETLR LLAEQTNRQI QDMQAG ADK MRLAAERFEH AGERVSEANH LTADVLNKAQ SAGSSLSLAT SELTSVVADY RNNREAVSKS IAMLELLAAN TQSEQTT RN QFIADLKQHG ERLQSYNREA QVFMENVSDV LGKGFEDFSE GVSRSLDKTL GKLDVEMAKA SNLLAGSVEQ LGESVSEL D DVLSRVRT UniProtKB: UNIPROTKB: A0A0V7WZR2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Membrane protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Membrane protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.103229 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFGNAFGVKK RRSDEAEKPF WISYADLMTA MMVLFLVVMV ASLSSVTQRI QRAEQGEKAR GQDISRLCER LELHARNVNK NIVVDCHDN RISFGEAGRF AHNQFFLNAE GQKALQDVVP LVLEASNSEE GKKWFKQIVI EGFTDTDGSY LYNLHLSLQR S EWVMCSLL ...String: MFGNAFGVKK RRSDEAEKPF WISYADLMTA MMVLFLVVMV ASLSSVTQRI QRAEQGEKAR GQDISRLCER LELHARNVNK NIVVDCHDN RISFGEAGRF AHNQFFLNAE GQKALQDVVP LVLEASNSEE GKKWFKQIVI EGFTDTDGSY LYNLHLSLQR S EWVMCSLL DSRSPLQKNI SAEQQLQIRK LFLAGGVSFN NAKESKEASR RVELRMQFFG LKDKRDKADE VDFPPVVNKE VC QLVMPL UniProtKB: UNIPROTKB: A0A0V7WZP0 |
-Macromolecule #3: CARDIOLIPIN
| Macromolecule | Name: CARDIOLIPIN / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: CDL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.464043 KDa |
| Chemical component information | 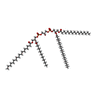 ChemComp-CDL: |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: PEE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 744.034 Da |
| Chemical component information | 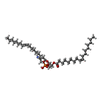 ChemComp-PEE: |
-Macromolecule #6: PALMITIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PLM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.424 Da |
| Chemical component information | 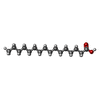 ChemComp-PLM: |
-Macromolecule #7: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 313 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





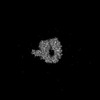




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)