[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-16889: Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 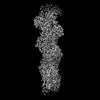 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Actin filament / cytoskeletal protein / ATPase / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex ...positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / regulation of double-strand break repair / Adherens junctions interactions / RHOF GTPase cycle / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / apical junction complex / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / Recycling pathway of L1 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / kinesin binding / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / actin filament / adherens junction / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / cell motility / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / kinetochore / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / platelet aggregation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / tau protein binding / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / nuclear matrix / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / cell-cell junction / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / UCH proteinases / nucleosome Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert W / Blanc FEC / Roy A / Belyy A / Hofnagel O / Hummer G / Bieling P / Raunser S | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3 items Germany, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Molecular mechanisms of inorganic-phosphate release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Florian E C Blanc / Ankit Roy / Alexander Belyy / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Oliver Hofnagel / Gerhard Hummer / Peter Bieling / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release ...The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments remain unclear. Here, using human and bovine actin isoforms, we combine cryo-EM with molecular-dynamics simulations and in vitro reconstitution to demonstrate how actin releases P through a 'molecular backdoor'. While constantly open at the barbed end, the backdoor is predominantly closed in filament-core subunits and opens only transiently through concerted amino acid rearrangements. This explains why P escapes rapidly from the filament end but slowly from internal subunits. In a nemaline-myopathy-associated actin variant, the backdoor is predominantly open in filament-core subunits, resulting in accelerated P release and filaments with drastically shortened ADP-P caps. Our results provide the molecular basis for P release from actin and exemplify how a disease-linked mutation distorts the nucleotide-state distribution and atomic structure of the filament. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16889.map.gz emd_16889.map.gz | 129.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16889-v30.xml emd-16889-v30.xml emd-16889.xml emd-16889.xml | 25.6 KB 25.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16889_fsc.xml emd_16889_fsc.xml | 13.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16889.png emd_16889.png | 89.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_16889_msk_1.map emd_16889_msk_1.map | 216 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16889.cif.gz emd-16889.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16889_additional_1.map.gz emd_16889_additional_1.map.gz emd_16889_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16889_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16889_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16889_half_map_2.map.gz | 168.6 MB 170.5 MB 170.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16889 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16889 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16889 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16889 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8oidMC  8oi6C  8oi8C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16889.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16889.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
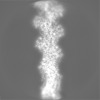
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.695 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
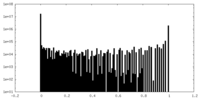
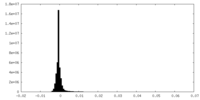
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_16889_msk_1.map emd_16889_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: 3D refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of filamentous...
| File | emd_16889_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1 of the refinement of filamentous...
| File | emd_16889_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1 of the refinement of filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2 of the refinement of filamentous...
| File | emd_16889_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2 of the refinement of filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Actin filament harboring the N111S mutation.
| Entire | Name: Actin filament harboring the N111S mutation. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Actin filament harboring the N111S mutation.
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament harboring the N111S mutation. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: Beta-actin was expressed as fusion protein, with thymosin beta4 and a deca-His-tag fused to the actin C-terminus. During the purification, thymosin beta-4 and the deca-His-tag were removed. ...Details: Beta-actin was expressed as fusion protein, with thymosin beta4 and a deca-His-tag fused to the actin C-terminus. During the purification, thymosin beta-4 and the deca-His-tag were removed. Actin was purified as monomer from insect cells. It was then polymerized into a filament in vitro. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.73659 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GIV TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LSPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSG DG VTHTVPIYEG ...String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GIV TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPVLLTEAP LSPKANREKM TQIMFETFNT PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVMDSG DG VTHTVPIYEG YALPHAILRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFTTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFEQEMA TAASSSSL E KSYELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PEALFQPSFL GMESAGIHET TFNSIMKCDV DIRKDLYANT VLSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKE ITALAPSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ISKQEYDESG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 616 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.1 Component:
Details: 1x KMEH (10 mM HEPES pH 7.1, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA) supplemented with 0.02% Tween20 (v/v) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 90 sec. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | Actin filaments were reconstituted by adding salt to monomeric actin. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 15 eV |
| Details | Titan Krios G3 microscope was aligned using Sherpa (FEI). Data collected in superresolution mode. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 9516 / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model |
|---|---|
| Details | chain C of pdb 8A2T (including all water molecules) was fit in the central actin subunit of the density map. After substitution of all alpha-actin specific amino-acids to the corresponding beta-actin residues, introducing the N111S mutation, and further manual model building in Coot, the resulting model was fitted in four more actin subunits (chains A, B, D, E) in the density map. The filament was modeled as a pentamer to capture the full interaction interface of the central subunit with its four neighboring subunits. All water molecules were first manually built, inspected and adjusted in the central subunit, and were then copied to the other chains with non-crystallographic symmetry (NCS). Because the local resolution was worse at the periphery of the reconstruction, we removed water molecules that displayed poor corresponding cryo-EM density in the non-central actin chains. The model was refined in Phenix real-space refine with NCS restraints but without Ramachandran and rotamer restraints. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
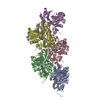
| Output model |  PDB-8oid: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)