+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-11694 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
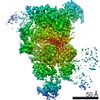
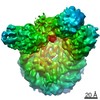
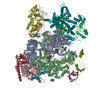
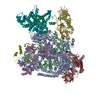
| Title | Human pre-Bact-1 spliceosome core structure | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened/masked map for pre-Bact-1 core structure. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complex / spliceosome / catalytic activation / splicing | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrofibril / regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / U2-type catalytic step 1 spliceosome / RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions / positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / transcription elongation factor activity / Notch binding / host-mediated activation of viral transcription ...microfibril / regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / U2-type catalytic step 1 spliceosome / RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions / positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / transcription elongation factor activity / Notch binding / host-mediated activation of viral transcription / mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / U2-type precatalytic spliceosome / positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / nuclear vitamin D receptor binding / RNA polymerase binding / U2-type spliceosomal complex / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / positive regulation of neurogenesis / : / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / nuclear androgen receptor binding / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / WW domain binding / precatalytic spliceosome / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / SMAD binding / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / spliceosomal tri-snRNP complex assembly / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Prp19 complex / U5 snRNA binding / U5 snRNP / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / U2 snRNA binding / U6 snRNA binding / pre-mRNA intronic binding / protein localization to nucleus / U1 snRNA binding / Cajal body / retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / U4/U6 x U5 tri-snRNP complex / cellular response to retinoic acid / catalytic step 2 spliceosome / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / RNA splicing / nuclear receptor binding / transcription coregulator activity / response to cocaine / spliceosomal complex / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Downregulation of SMAD2/3:SMAD4 transcriptional activity / mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / protein modification process / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / nuclear matrix / fibrillar center / protein tag activity / mRNA processing / rRNA processing / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / transcription corepressor activity / single-stranded DNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / nuclear membrane / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / transcription coactivator activity / nuclear speck / nuclear body / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / GTPase activity / centrosome / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / GTP binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Townsend C / Kastner B | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Mechanism of protein-guided folding of the active site U2/U6 RNA during spliceosome activation. Authors: Cole Townsend / Majety N Leelaram / Dmitry E Agafonov / Olexandr Dybkov / Cindy L Will / Karl Bertram / Henning Urlaub / Berthold Kastner / Holger Stark / Reinhard Lührmann /  Abstract: Spliceosome activation involves extensive protein and RNA rearrangements that lead to formation of a catalytically active U2/U6 RNA structure. At present, little is known about the assembly pathway ...Spliceosome activation involves extensive protein and RNA rearrangements that lead to formation of a catalytically active U2/U6 RNA structure. At present, little is known about the assembly pathway of the latter and the mechanism whereby proteins aid its proper folding. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of two human, activated spliceosome precursors (that is, pre-B complexes) at core resolutions of 3.9 and 4.2 angstroms. These structures elucidate the order of the numerous protein exchanges that occur during activation, the mutually exclusive interactions that ensure the correct order of ribonucleoprotein rearrangements needed to form the U2/U6 catalytic RNA, and the stepwise folding pathway of the latter. Structural comparisons with mature B complexes reveal the molecular mechanism whereby a conformational change in the scaffold protein PRP8 facilitates final three-dimensional folding of the U2/U6 catalytic RNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_11694.map.gz emd_11694.map.gz | 14.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-11694-v30.xml emd-11694-v30.xml emd-11694.xml emd-11694.xml | 36.3 KB 36.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_11694.png emd_11694.png | 33.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11694.cif.gz emd-11694.cif.gz | 12.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11694 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11694 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11694 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11694 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7abfMC  7aavC  7abgC  7abhC  7abiC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10616 (Title: Cryo-EM dataset of human pre-Bact spliceosome / Data size: 584.5 EMPIAR-10616 (Title: Cryo-EM dataset of human pre-Bact spliceosome / Data size: 584.5 Data #1: Motion-corrected micrographs (without dose-weighting) of human pre-Bact spliceosome [micrographs - single frame] Data #2: Motion-corrected micrographs (with dose-weighting) of human pre-Bact spliceosome [micrographs - single frame]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_11694.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_11694.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened/masked map for pre-Bact-1 core structure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.16 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : pre-Bact-1 spliceosomal complex
+Supramolecule #1: pre-Bact-1 spliceosomal complex
+Supramolecule #2: pre-Bact-1 spliceosomal complex
+Supramolecule #3: MINX M3 RNA
+Macromolecule #1: Protein BUD31 homolog
+Macromolecule #2: Pre-mRNA-splicing factor 38A
+Macromolecule #3: Pre-mRNA-processing-splicing factor 8
+Macromolecule #4: 116 kDa U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein component
+Macromolecule #5: Zinc finger matrin-type protein 2
+Macromolecule #6: Ubiquitin-like protein 5
+Macromolecule #7: Spliceosome-associated protein CWC15 homolog
+Macromolecule #10: WW domain-binding protein 11
+Macromolecule #11: SNW domain-containing protein 1
+Macromolecule #12: Pleiotropic regulator 1
+Macromolecule #14: Microfibrillar-associated protein 1
+Macromolecule #15: Transcription elongation regulator 1
+Macromolecule #8: U5 small nuclear RNA
+Macromolecule #9: U6 small nuclear RNA
+Macromolecule #13: MINX M3 RNA
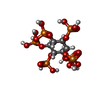
+Macromolecule #16: INOSITOL HEXAKISPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #17: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #18: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R3.5/1 / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.25 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7abf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)