+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-11217 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
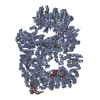
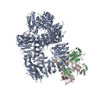
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of DNA-PK monomer | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | Kinase / DNA-PKcs / NHEJ / DNA-repair / DNA-PK / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Ku70/80 | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報positive regulation of platelet formation / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / DNA end binding / pro-B cell differentiation / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex ...positive regulation of platelet formation / Ku70:Ku80 complex / negative regulation of t-circle formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / DNA end binding / pro-B cell differentiation / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / nonhomologous end joining complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / immature B cell differentiation / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / cellular response to X-ray / nuclear telomere cap complex / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / telomere capping / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / positive regulation of neurogenesis / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / regulation of telomere maintenance / recombinational repair / U3 snoRNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / T cell lineage commitment / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / 2-LTR circle formation / telomeric DNA binding / B cell lineage commitment / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / site of DNA damage / 付加脱離酵素(リアーゼ); 炭素-酸素リアーゼ類; その他の炭素-酸素リアーゼ / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / telomere maintenance via telomerase / somitogenesis / neurogenesis / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance / activation of innate immune response / DNA helicase activity / cyclin binding / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of translation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / response to gamma radiation / small-subunit processome / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / enzyme activator activity / cellular response to gamma radiation / regulation of circadian rhythm / protein destabilization / protein-DNA complex / brain development / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / protein modification process / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / 加水分解酵素; 酸無水物に作用; 酸無水物に作用・細胞または細胞小器官の運動に関与 / cellular response to insulin stimulus / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / rhythmic process / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / double-strand break repair / T cell differentiation in thymus / heart development / double-stranded DNA binding / scaffold protein binding / secretory granule lumen / DNA recombination / transcription regulator complex / damaged DNA binding / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / chromosome, telomeric region / protein phosphorylation / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / protein kinase activity / positive regulation of apoptotic process / ribonucleoprotein complex / protein domain specific binding / innate immune response / protein serine kinase activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
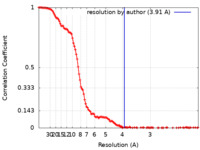
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.91 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Chaplin AK / Hardwick SW | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  英国, 1件 英国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2021 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2021タイトル: Dimers of DNA-PK create a stage for DNA double-strand break repair. 著者: Amanda K Chaplin / Steven W Hardwick / Shikang Liang / Antonia Kefala Stavridi / Ales Hnizda / Lee R Cooper / Taiana Maia De Oliveira / Dimitri Y Chirgadze / Tom L Blundell /  要旨: DNA double-strand breaks are the most dangerous type of DNA damage and, if not repaired correctly, can lead to cancer. In humans, Ku70/80 recognizes DNA broken ends and recruits the DNA-dependent ...DNA double-strand breaks are the most dangerous type of DNA damage and, if not repaired correctly, can lead to cancer. In humans, Ku70/80 recognizes DNA broken ends and recruits the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form DNA-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme (DNA-PK) in the process of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). We present a 2.8-Å-resolution cryo-EM structure of DNA-PKcs, allowing precise amino acid sequence registration in regions uninterpreted in previous 4.3-Å X-ray maps. We also report a cryo-EM structure of DNA-PK at 3.5-Å resolution and reveal a dimer mediated by the Ku80 C terminus. Central to dimer formation is a domain swap of the conserved C-terminal helix of Ku80. Our results suggest a new mechanism for NHEJ utilizing a DNA-PK dimer to bring broken DNA ends together. Furthermore, drug inhibition of NHEJ in combination with chemo- and radiotherapy has proved successful, making these models central to structure-based drug targeting efforts. #1:  ジャーナル: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / 年: 2020 ジャーナル: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / 年: 2020タイトル: Dimers of DNA-PK create a stage for DNA-double strand break repair 著者: Chaplin AK / Hardwick SW / Liang S / Stavridi AK / Hnizda A / Cooper LR / De Oliveira TM / Chirgadze DY / Blundell TL | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_11217.map.gz emd_11217.map.gz | 141.6 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-11217-v30.xml emd-11217-v30.xml emd-11217.xml emd-11217.xml | 27.8 KB 27.8 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_11217_fsc.xml emd_11217_fsc.xml | 15.7 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_11217.png emd_11217.png | 46.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-11217.cif.gz emd-11217.cif.gz | 9.7 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_11217_additional_1.map.gz emd_11217_additional_1.map.gz emd_11217_half_map_1.map.gz emd_11217_half_map_1.map.gz emd_11217_half_map_2.map.gz emd_11217_half_map_2.map.gz | 21.9 MB 139.3 MB 139.3 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11217 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11217 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11217 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-11217 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_11217_validation.pdf.gz emd_11217_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_11217_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_11217_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_11217_validation.xml.gz emd_11217_validation.xml.gz | 19.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_11217_validation.cif.gz emd_11217_validation.cif.gz | 25.4 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-11217 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-11217 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-11217 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-11217 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_11217.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 149.9 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_11217.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 149.9 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
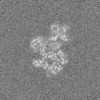
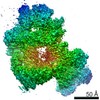
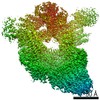
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
-追加マップ: Resolve cryoEM density modified map at 3.51 angstrom resolution
| ファイル | emd_11217_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Resolve cryoEM density modified map at 3.51 angstrom resolution | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
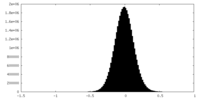
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_11217_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
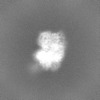
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
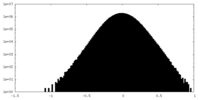
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_11217_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : DNA-PK monomer
| 全体 | 名称: DNA-PK monomer |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: DNA-PK monomer
| 超分子 | 名称: DNA-PK monomer / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 640 KDa |
-超分子 #2: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
| 超分子 | 名称: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit / タイプ: complex / ID: 2 / 親要素: 1 / 含まれる分子: #1 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-超分子 #3: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5+6
| 超分子 | 名称: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5+6 / タイプ: complex / ID: 3 / 親要素: 1 / 含まれる分子: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-超分子 #4: DNA
| 超分子 | 名称: DNA / タイプ: complex / ID: 4 / 親要素: 1 / 含まれる分子: #4-#5 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-分子 #1: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-dependent prot...
| 分子 | 名称: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-PKcs タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 472.056281 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: MAGSGAGVRC SLLRLQETLS AADRCGAALA GHQLIRGLGQ ECVLSSSPAV LALQTSLVFS RDFGLLVFVR KSLNSIEFRE CREEILKFL CIFLEKMGQK IAPYSVEIKN TCTSVYTKDR AAKCKIPALD LLIKLLQTFR SSRLMDEFKI GELFSKFYGE L ALKKKIPD ...文字列: MAGSGAGVRC SLLRLQETLS AADRCGAALA GHQLIRGLGQ ECVLSSSPAV LALQTSLVFS RDFGLLVFVR KSLNSIEFRE CREEILKFL CIFLEKMGQK IAPYSVEIKN TCTSVYTKDR AAKCKIPALD LLIKLLQTFR SSRLMDEFKI GELFSKFYGE L ALKKKIPD TVLEKVYELL GLLGEVHPSE MINNAENLFR AFLGELKTQM TSAVREPKLP VLAGCLKGLS SLLCNFTKSM EE DPQTSRE IFNFVLKAIR PQIDLKRYAV PSAGLRLFAL HASQFSTCLL DNYVSLFEVL LKWCAHTNVE LKKAALSALE SFL KQVSNM VAKNAEMHKN KLQYFMEQFY GIIRNVDSNN KELSIAIRGY GLFAGPCKVI NAKDVDFMYV ELIQRCKQMF LTQT DTGDD RVYQMPSFLQ SVASVLLYLD TVPEVYTPVL EHLVVMQIDS FPQYSPKMQL VCCRAIVKVF LALAAKGPVL RNCIS TVVH QGLIRICSKP VVLPKGPESE SEDHRASGEV RTGKWKVPTY KDYVDLFRHL LSSDQMMDSI LADEAFFSVN SSSESL NHL LYDEFVKSVL KIVEKLDLTL EIQTVGEQEN GDEAPGVWMI PTSDPAANLH PAKPKDFSAF INLVEFCREI LPEKQAE FF EPWVYSFSYE LILQSTRLPL ISGFYKLLSI TVRNAKKIKY FEGVSPKSLK HSPEDPEKYS CFALFVKFGK EVAVKMKQ Y KDELLASCLT FLLSLPHNII ELDVRAYVPA LQMAFKLGLS YTPLAEVGLN ALEEWSIYID RHVMQPYYKD ILPCLDGYL KTSALSDETK NNWEVSALSR AAQKGFNKVV LKHLKKTKNL SSNEAISLEE IRIRVVQMLG SLGGQINKNL LTVTSSDEMM KSYVAWDRE KRLSFAVPFR EMKPVIFLDV FLPRVTELAL TASDRQTKVA ACELLHSMVM FMLGKATQMP EGGQGAPPMY Q LYKRTFPV LLRLACDVDQ VTRQLYEPLV MQLIHWFTNN KKFESQDTVA LLEAILDGIV DPVDSTLRDF CGRCIREFLK WS IKQITPQ QQEKSPVNTK SLFKRLYSLA LHPNAFKRLG ASLAFNNIYR EFREEESLVE QFVFEALVIY MESLALAHAD EKS LGTIQQ CCDAIDHLCR IIEKKHVSLN KAKKRRLPRG FPPSASLCLL DLVKWLLAHC GRPQTECRHK SIELFYKFVP LLPG NRSPN LWLKDVLKEE GVSFLINTFE GGGCGQPSGI LAQPTLLYLR GPFSLQATLC WLDLLLAALE CYNTFIGERT VGALQ VLGT EAQSSLLKAV AFFLESIAMH DIIAAEKCFG TGAAGNRTSP QEGERYNYSK CTVVVRIMEF TTTLLNTSPE GWKLLK KDL CNTHLMRVLV QTLCEPASIG FNIGDVQVMA HLPDVCVNLM KALKMSPYKD ILETHLREKI TAQSIEELCA VNLYGPD AQ VDRSRLAAVV SACKQLHRAG LLHNILPSQS TDLHHSVGTE LLSLVYKGIA PGDERQCLPS LDLSCKQLAS GLLELAFA F GGLCERLVSL LLNPAVLSTA SLGSSQGSVI HFSHGEYFYS LFSETINTEL LKNLDLAVLE LMQSSVDNTK MVSAVLNGM LDQSFRERAN QKHQGLKLAT TILQHWKKCD SWWAKDSPLE TKMAVLALLA KILQIDSSVS FNTSHGSFPE VFTTYISLLA DTKLDLHLK GQAVTLLPFF TSLTGGSLEE LRRVLEQLIV AHFPMQSREF PPGTPRFNNY VDCMKKFLDA LELSQSPMLL E LMTEVLCR EQQHVMEELF QSSFRRIARR GSCVTQVGLL ESVYEMFRKD DPRLSFTRQS FVDRSLLTLL WHCSLDALRE FF STIVVDA IDVLKSRFTK LNESTFDTQI TKKMGYYKIL DVMYSRLPKD DVHAKESKIN QVFHGSCITE GNELTKTLIK LCY DAFTEN MAGENQLLER RRLYHCAAYN CAISVICCVF NELKFYQGFL FSEKPEKNLL IFENLIDLKR RYNFPVEVEV PMER KKKYI EIRKEAREAA NGDSDGPSYM SSLSYLADST LSEEMSQFDF STGVQSYSYS SQDPRPATGR FRRREQRDPT VHDDV LELE MDELNRHECM APLTALVKHM HRSLGPPQGE EDSVPRDLPS WMKFLHGKLG NPIVPLNIRL FLAKLVINTE EVFRPY AKH WLSPLLQLAA SENNGGEGIH YMVVEIVATI LSWTGLATPT GVPKDEVLAN RLLNFLMKHV FHPKRAVFRH NLEIIKT LV ECWKDCLSIP YRLIFEKFSG KDPNSKDNSV GIQLLGIVMA NDLPPYDPQC GIQSSEYFQA LVNNMSFVRY KEVYAAAA E VLGLILRYVM ERKNILEESL CELVAKQLKQ HQNTMEDKFI VCLNKVTKSF PPLADRFMNA VFFLLPKFHG VLKTLCLEV VLCRVEGMTE LYFQLKSKDF VQVMRHRDDE RQKVCLDIIY KMMPKLKPVE LRELLNPVVE FVSHPSTTCR EQMYNILMWI HDNYRDPES ETDNDSQEIF KLAKDVLIQG LIDENPGLQL IIRNFWSHET RLPSNTLDRL LALNSLYSPK IEVHFLSLAT N FLLEMTSM SPDYPNPMFE HPLSECEFQE YTIDSDWRFR STVLTPMFVE TQASQGTLQT RTQEGSLSAR WPVAGQIRAT QQ QHDFTLT QTADGRSSFD WLTGSSTDPL VDHTSPSSDS LLFAHKRSER LQRAPLKSVG PDFGKKRLGL PGDEVDNKVK GAA GRTDLL RLRRRFMRDQ EKLSLMYARK GVAEQKREKE IKSELKMKQD AQVVLYRSYR HGDLPDIQIK HSSLITPLQA VAQR DPIIA KQLFSSLFSG ILKEMDKFKT LSEKNNITQK LLQDFNRFLN TTFSFFPPFV SCIQDISCQH AALLSLDPAA VSAGC LASL QQPVGIRLLE EALLRLLPAE LPAKRVRGKA RLPPDVLRWV ELAKLYRSIG EYDVLRGIFT SEIGTKQITQ SALLAE ARS DYSEAAKQYD EALNKQDWVD GEPTEAEKDF WELASLDCYN HLAEWKSLEY CSTASIDSEN PPDLNKIWSE PFYQETY LP YMIRSKLKLL LQGEADQSLL TFIDKAMHGE LQKAILELHY SQELSLLYLL QDDVDRAKYY IQNGIQSFMQ NYSSIDVL L HQSRLTKLQS VQALTEIQEF ISFISKQGNL SSQVPLKRLL NTWTNRYPDA KMDPMNIWDD IITNRCFFLS KIEEKLTPL PEDNSMNVDQ DGDPSDRMEV QEQEEDISSL IRSCKFSMKM KMIDSARKQN NFSLAMKLLK ELHKESKTRD DWLVSWVQSY CRLSHCRSR SQGCSEQVLT VLKTVSLLDE NNVSSYLSKN ILAFRDQNIL LGTTYRIIAN ALSSEPACLA EIEEDKARRI L ELSGSSSE DSEKVIAGLY QRAFQHLSEA VQAAEEEAQP PSWSCGPAAG VIDAYMTLAD FCDQQLRKEE ENASVIDSAE LQ AYPALVV EKMLKALKLN SNEARLKFPR LLQIIERYPE ETLSLMTKEI SSVPCWQFIS WISHMVALLD KDQAVAVQHS VEE ITDNYP QAIVYPFIIS SESYSFKDTS TGHKNKEFVA RIKSKLDQGG VIQDFINALD QLSNPELLFK DWSNDVRAEL AKTP VNKKN IEKMYERMYA ALGDPKAPGL GAFRRKFIQT FGKEFDKHFG KGGSKLLRMK LSDFNDITNM LLLKMNKDSK PPGNL KECS PWMSDFKVEF LRNELEIPGQ YDGRGKPLPE YHVRIAGFDE RVTVMASLRR PKRIIIRGHD EREHPFLVKG GEDLRQ DQR VEQLFQVMNG ILAQDSACSQ RALQLRTYSV VPMTSRLGLI EWLENTVTLK DLLLNTMSQE EKAAYLSDPR APPCEYK DW LTKMSGKHDV GAYMLMYKGA NRTETVTSFR KRESKVPADL LKRAFVRMST SPEAFLALRS HFASSHALIC ISHWILGI G DRHLNNFMVA METGGVIGID FGHAFGSATQ FLPVPELMPF RLTRQFINLM LPMKETGLMY SIMVHALRAF RSDPGLLTN TMDVFVKEPS FDWKNFEQKM LKKGGSWIQE INVAEKNWYP RQKICYAKRK LAGANPAVIT CDELLLGHEK APAFRDYVAV ARGSKDHNI RAQEPESGLS EETQVKCLMD QATDPNILGR TWEGWEPWM(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) UniProtKB: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit |
-分子 #2: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6
| 分子 | 名称: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO EC番号: 加水分解酵素; 酸無水物に作用; 酸無水物に作用・細胞または細胞小器官の運動に関与 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 69.945039 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (その他) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MSGWESYYKT EGDEEAEEEQ EENLEASGDY KYSGRDSLIF LVDASKAMFE SQSEDELTPF DMSIQCIQSV YISKIISSDR DLLAVVFYG TEKDKNSVNF KNIYVLQELD NPGAKRILEL DQFKGQQGQK RFQDMMGHGS DYSLSEVLWV CANLFSDVQF K MSHKRIML ...文字列: MSGWESYYKT EGDEEAEEEQ EENLEASGDY KYSGRDSLIF LVDASKAMFE SQSEDELTPF DMSIQCIQSV YISKIISSDR DLLAVVFYG TEKDKNSVNF KNIYVLQELD NPGAKRILEL DQFKGQQGQK RFQDMMGHGS DYSLSEVLWV CANLFSDVQF K MSHKRIML FTNEDNPHGN DSAKASRART KAGDLRDTGI FLDLMHLKKP GGFDISLFYR DIISIAEDED LRVHFEESSK LE DLLRKVR AKETRKRALS RLKLKLNKDI VISVGIYNLV QKALKPPPIK LYRETNEPVK TKTRTFNTST GGLLLPSDTK RSQ IYGSRQ IILEKEETEE LKRFDDPGLM LMGFKPLVLL KKHHYLRPSL FVYPEESLVI GSSTLFSALL IKCLEKEVAA LCRY TPRRN IPPYFVALVP QEEELDDQKI QVTPPGFQLV FLPFADDKRK MPFTEKIMAT PEQVGKMKAI VEKLRFTYRS DSFEN PVLQ QHFRNLEALA LDLMEPEQAV DLTLPKVEAM NKRLGSLVDE FKELVYPPDY NPEGKVTKRK HDNEGSGSKR PKVEYS EEE LKTHISKGTL GKFTVPMLKE ACRAYGLKSG LKKQELLEAL TKHFQD UniProtKB: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6 |
-分子 #3: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5
| 分子 | 名称: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5 / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO EC番号: 加水分解酵素; 酸無水物に作用; 酸無水物に作用・細胞または細胞小器官の運動に関与 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 82.812438 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (その他) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MVRSGNKAAV VLCMDVGFTM SNSIPGIESP FEQAKKVITM FVQRQVFAEN KDEIALVLFG TDGTDNPLSG GDQYQNITVH RHLMLPDFD LLEDIESKIQ PGSQQADFLD ALIVSMDVIQ HETIGKKFEK RHIEIFTDLS SRFSKSQLDI IIHSLKKCDI S LQFFLPFS ...文字列: MVRSGNKAAV VLCMDVGFTM SNSIPGIESP FEQAKKVITM FVQRQVFAEN KDEIALVLFG TDGTDNPLSG GDQYQNITVH RHLMLPDFD LLEDIESKIQ PGSQQADFLD ALIVSMDVIQ HETIGKKFEK RHIEIFTDLS SRFSKSQLDI IIHSLKKCDI S LQFFLPFS LGKEDGSGDR GDGPFRLGGH GPSFPLKGIT EQQKEGLEIV KMVMISLEGE DGLDEIYSFS ESLRKLCVFK KI ERHSIHW PCRLTIGSNL SIRIAAYKSI LQERVKKTWT VVDAKTLKKE DIQKETVYCL NDDDETEVLK EDIIQGFRYG SDI VPFSKV DEEQMKYKSE GKCFSVLGFC KSSQVQRRFF MGNQVLKVFA ARDDEAAAVA LSSLIHALDD LDMVAIVRYA YDKR ANPQV GVAFPHIKHN YECLVYVQLP FMEDLRQYMF SSLKNSKKYA PTEAQLNAVD ALIDSMSLAK KDEKTDTLED LFPTT KIPN PRFQRLFQCL LHRALHPREP LPPIQQHIWN MLNPPAEVTT KSQIPLSKIK TLFPLIEAKK KDQVTAQEIF QDNHED GPT AKKLKTEQGG AHFSVSSLAE GSVTSVGSVN PAENFRVLVK QKKASFEEAS NQLINHIEQF LDTNETPYFM KSIDCIR AF REEAIKFSEE QRFNNFLKAL QEKVEIKQLN HFWEIVVQDG ITLITKEEAS GSSVTAEEAK KFLAPKDKPS GDTAAVFE E GGDVDDLLDM I UniProtKB: X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5 |
-分子 #4: DNA
| 分子 | 名称: DNA / タイプ: dna / ID: 4 / コピー数: 1 / 分類: DNA |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 7.672036 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DG) |
-分子 #5: DNA
| 分子 | 名称: DNA / タイプ: dna / ID: 5 / コピー数: 1 / 分類: DNA |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 7.402821 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: (DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DG) |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 検出モード: COUNTING / 平均電子線量: 52.97 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー





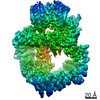
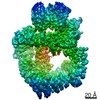
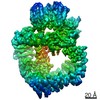
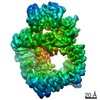











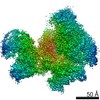
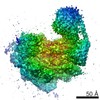










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)