[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10422: Human kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state bound to microtubules -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10422 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
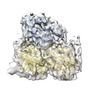
| Title | Human kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state bound to microtubules | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
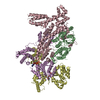
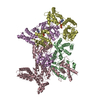
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | kinesin / microtubule / mitosis / inhibition / motor / CELL CYCLE | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III ...spindle elongation / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Hedgehog 'off' state / Cilium Assembly / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / RHOH GTPase cycle / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / PKR-mediated signaling / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Aggrephagy / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Kinesins / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / mitotic centrosome separation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule motor activity / kinesin complex / spindle organization / microtubule-based movement / mitotic spindle assembly / MHC class II antigen presentation / mitotic spindle organization / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / spindle microtubule / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / mitotic spindle / spindle pole / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / microtubule cytoskeleton / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule binding / microtubule / cell division / GTPase activity / GTP binding / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / membrane / nucleus / metal ion binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
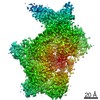
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pena AP / Sweeney A | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4 items United Kingdom, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2020 Journal: Structure / Year: 2020Title: Structure of Microtubule-Trapped Human Kinesin-5 and Its Mechanism of Inhibition Revealed Using Cryoelectron Microscopy. Authors: Alejandro Peña / Aaron Sweeney / Alexander D Cook / Julia Locke / Maya Topf / Carolyn A Moores /  Abstract: Kinesin-5 motors are vital mitotic spindle components, and disruption of their function perturbs cell division. We investigated the molecular mechanism of the human kinesin-5 inhibitor GSK-1, which ...Kinesin-5 motors are vital mitotic spindle components, and disruption of their function perturbs cell division. We investigated the molecular mechanism of the human kinesin-5 inhibitor GSK-1, which allosterically promotes tight microtubule binding. GSK-1 inhibits monomeric human kinesin-5 ATPase and microtubule gliding activities, and promotes the motor's microtubule stabilization activity. Using cryoelectron microscopy, we determined the 3D structure of the microtubule-bound motor-GSK-1 at 3.8 Å overall resolution. The structure reveals that GSK-1 stabilizes the microtubule binding surface of the motor in an ATP-like conformation, while destabilizing regions of the motor around the empty nucleotide binding pocket. Density corresponding to GSK-1 is located between helix-α4 and helix-α6 in the motor domain at its interface with the microtubule. Using a combination of difference mapping and protein-ligand docking, we characterized the kinesin-5-GSK-1 interaction and further validated this binding site using mutagenesis. This work opens up new avenues of investigation of kinesin inhibition and spindle perturbation. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10422.map.gz emd_10422.map.gz | 460.2 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10422-v30.xml emd-10422-v30.xml emd-10422.xml emd-10422.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10422_fsc.xml emd_10422_fsc.xml | 13.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10422.png emd_10422.png | 159.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10422.cif.gz emd-10422.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10422 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10422 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_10422_validation.pdf.gz emd_10422_validation.pdf.gz | 429.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_10422_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_10422_full_validation.pdf.gz | 429.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_10422_validation.xml.gz emd_10422_validation.xml.gz | 11.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_10422_validation.cif.gz emd_10422_validation.cif.gz | 15.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10422 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10422 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ta4MC  6ta3C  6tiwC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Sample components
Sample components


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera