[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0728: Structure of human cardiac thin filament in the calcium free state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0728 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
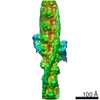
| Title | Structure of human cardiac thin filament in the calcium free state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
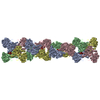
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Troponin / Tropomyosin / Actin / Thin filement / Muscle / CONTRACTILE PROTEIN-ACTIN BINDING PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by ischemic conditions / troponin C binding / regulation of muscle filament sliding speed / troponin T binding / diaphragm contraction / regulation of ATP-dependent activity / cardiac myofibril / cardiac Troponin complex ...positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by ischemic conditions / troponin C binding / regulation of muscle filament sliding speed / troponin T binding / diaphragm contraction / regulation of ATP-dependent activity / cardiac myofibril / cardiac Troponin complex / troponin complex / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of smooth muscle contraction / regulation of muscle contraction / muscle filament sliding / bleb / transition between fast and slow fiber / negative regulation of ATP-dependent activity / ruffle organization / positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity / Striated Muscle Contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling / response to metal ion / structural constituent of muscle / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / sarcomere organization / regulation of heart contraction / tropomyosin binding / heart contraction / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle contraction / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / Smooth Muscle Contraction / vasculogenesis / calcium channel inhibitor activity / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / skeletal muscle fiber development / Ion homeostasis / titin binding / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeleton organization / cytoskeletal protein binding / actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of cell adhesion / sarcomere / negative regulation of cell migration / filopodium / actin filament organization / actin filament / wound healing / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / actin cytoskeleton / lamellipodium / heart development / regulation of cell shape / actin binding / cell body / cytoskeleton / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / protein domain specific binding / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / protein kinase binding / magnesium ion binding / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fujii T / Yamada Y | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Cardiac muscle thin filament structures reveal calcium regulatory mechanism. Authors: Yurika Yamada / Keiichi Namba / Takashi Fujii /  Abstract: Contraction of striated muscles is driven by cyclic interactions of myosin head projecting from the thick filament with actin filament and is regulated by Ca released from sarcoplasmic reticulum. ...Contraction of striated muscles is driven by cyclic interactions of myosin head projecting from the thick filament with actin filament and is regulated by Ca released from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Muscle thin filament consists of actin, tropomyosin and troponin, and Ca binding to troponin triggers conformational changes of troponin and tropomyosin to allow actin-myosin interactions. However, the structural changes involved in this regulatory mechanism remain unknown. Here we report the structures of human cardiac muscle thin filament in the absence and presence of Ca by electron cryomicroscopy. Molecular models in the two states built based on available crystal structures reveal the structures of a C-terminal region of troponin I and an N-terminal region of troponin T in complex with the head-to-tail junction of tropomyosin together with the troponin core on actin filament. Structural changes of the thin filament upon Ca binding now reveal the mechanism of Ca regulation of muscle contraction. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0728.map.gz emd_0728.map.gz | 28 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0728-v30.xml emd-0728-v30.xml emd-0728.xml emd-0728.xml | 16.2 KB 16.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_0728_fsc.xml emd_0728_fsc.xml | 7.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_0728.png emd_0728.png | 49.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0728.cif.gz emd-0728.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0728 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0728 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0728 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0728 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_0728_validation.pdf.gz emd_0728_validation.pdf.gz | 531 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_0728_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_0728_full_validation.pdf.gz | 530.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_0728_validation.xml.gz emd_0728_validation.xml.gz | 9.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_0728_validation.cif.gz emd_0728_validation.cif.gz | 12.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0728 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0728 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0728 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0728 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6kn7MC  7utlM 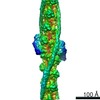 0729C  6kn8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0728.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0728.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.22 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
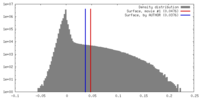
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cardiac muscle thin filament in the calcium free state
+Supramolecule #1: Cardiac muscle thin filament in the calcium free state
+Supramolecule #2: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
+Supramolecule #3: Tropomyosin, Troponin
+Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
+Macromolecule #2: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain
+Macromolecule #3: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain
+Macromolecule #4: Troponin T, cardiac muscle
+Macromolecule #5: Troponin I, cardiac muscle
+Macromolecule #6: Troponin C, slow skeletal and cardiac muscles
+Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.05 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 200 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 65.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



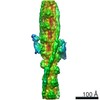
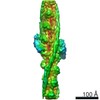
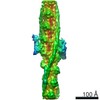









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)