[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-27782: Structure of human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 proteins -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 proteins | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | dynein / motor protein / transport | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / corpus callosum morphogenesis / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / acrosome assembly / central region of growth cone ...microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity / ameboidal-type cell migration / establishment of planar polarity of embryonic epithelium / 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase complex / corpus callosum morphogenesis / maintenance of centrosome location / platelet activating factor metabolic process / radial glia-guided pyramidal neuron migration / acrosome assembly / central region of growth cone / cerebral cortex neuron differentiation / establishment of centrosome localization / microtubule sliding / positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of embryonic development / microtubule organizing center organization / interneuron migration / layer formation in cerebral cortex / auditory receptor cell development / astral microtubule / nuclear membrane disassembly / cortical microtubule organization / positive regulation of intracellular transport / positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / myeloid leukocyte migration / reelin-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of metaphase plate congression / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / osteoclast development / stereocilium / microtubule plus-end binding / brain morphogenesis / vesicle transport along microtubule / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / retrograde axonal transport / kinesin complex / P-body assembly / negative regulation of JNK cascade / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / microtubule associated complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / neuromuscular process controlling balance / stem cell division / nuclear migration / germ cell development / cell leading edge / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / transmission of nerve impulse / dynactin binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / protein secretion / cochlea development / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of axon extension / microtubule-based process / lipid catabolic process / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / phospholipase binding / cytoplasmic microtubule / JNK cascade / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Mitotic Prometaphase / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / stress granule assembly / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / mitotic spindle organization / adult locomotory behavior / filopodium / hippocampus development / phosphoprotein binding / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / neuron migration / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Reimer JM / DeSantis M / Reck-Peterson SL / Leschziner AE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2023 Journal: Elife / Year: 2023Title: Structures of human dynein in complex with the lissencephaly 1 protein, LIS1. Authors: Janice M Reimer / Morgan E DeSantis / Samara L Reck-Peterson / Andres E Leschziner /  Abstract: The lissencephaly 1 protein, LIS1, is mutated in type-1 lissencephaly and is a key regulator of cytoplasmic dynein-1. At a molecular level, current models propose that LIS1 activates dynein by ...The lissencephaly 1 protein, LIS1, is mutated in type-1 lissencephaly and is a key regulator of cytoplasmic dynein-1. At a molecular level, current models propose that LIS1 activates dynein by relieving its autoinhibited form. Previously we reported a 3.1 Å structure of yeast dynein bound to Pac1, the yeast homologue of LIS1, which revealed the details of their interactions (Gillies et al., 2022). Based on this structure, we made mutations that disrupted these interactions and showed that they were required for dynein's function in vivo in yeast. We also used our yeast dynein-Pac1 structure to design mutations in human dynein to probe the role of LIS1 in promoting the assembly of active dynein complexes. These mutations had relatively mild effects on dynein activation, suggesting that there may be differences in how dynein and Pac1/LIS1 interact between yeast and humans. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of human dynein-LIS1 complexes. Our new structures reveal the differences between the yeast and human systems, provide a blueprint to disrupt the human dynein-LIS1 interactions more accurately, and map type-1 lissencephaly disease mutations, as well as mutations in dynein linked to malformations of cortical development/intellectual disability, in the context of the dynein-LIS1 complex. #1:  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for cytoplasmic dynein-1 regulation by Lis1. Authors: Gillies JP / Reimer JM / Karasmanis EP / Lahiri I / Htet ZM / Leschziner AE / Reck-Peterson SL | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27782.map.gz emd_27782.map.gz | 157.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27782-v30.xml emd-27782-v30.xml emd-27782.xml emd-27782.xml | 22.6 KB 22.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27782_fsc.xml emd_27782_fsc.xml | 11.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
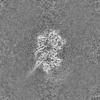
| Images |  emd_27782.png emd_27782.png | 53 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27782.cif.gz emd-27782.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27782_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27782_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27782_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27782_half_map_2.map.gz | 154.4 MB 154.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27782 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27782 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27782 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27782 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 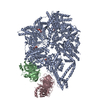 8dyuMC  8dyvC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27782.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27782.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
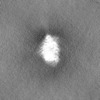
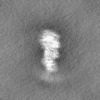
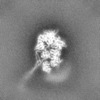
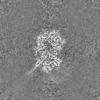
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.16 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27782_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
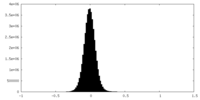
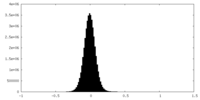
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27782_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
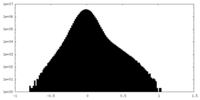
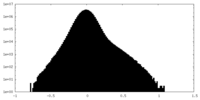
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 WD40 domains.
| Entire | Name: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 WD40 domains. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 WD40 domains.
| Supramolecule | Name: Human cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to two Lis1 WD40 domains. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 380.953594 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GQVALEELQD LKGVWSELSK VWEQIDQMKE QPWVSVQPRK LRQNLDALLN QLKSFPARLR QYASYEFVQR LLKGYMKINM LVIELKSEA LKDRHWKQLM KRLHVNWVVS ELTLGQIWDV DLQKNEAIVK DVLLVAQGEM ALEEFLKQIR EVWNTYELDL V NYQNKCRL ...String: GQVALEELQD LKGVWSELSK VWEQIDQMKE QPWVSVQPRK LRQNLDALLN QLKSFPARLR QYASYEFVQR LLKGYMKINM LVIELKSEA LKDRHWKQLM KRLHVNWVVS ELTLGQIWDV DLQKNEAIVK DVLLVAQGEM ALEEFLKQIR EVWNTYELDL V NYQNKCRL IRGWDDLFNK VKEHINSVSA MKLSPYYKVF EEDALSWEDK LNRIMALFDV WIDVQRRWVY LEGIFTGSAD IK HLLPVET QRFQSISTEF LALMKKVSKS PLVMDVLNIQ GVQRSLERLA DLLGKIQKAL GEYLERERSS FPRFYFVGDE DLL EIIGNS KNVAKLQKHF KKMFAGVSSI ILNEDNSVVL GISSREGEEV MFKTPVSITE HPKINEWLTL VEKEMRVTLA KLLA ESVTE VEIFGKATSI DPNTYITWID KYQAQLVVLS AQIAWSENVE TALSSMGGGG DAAPLHSVLS NVEVTLNVLA DSVLM EQPP LRRRKLEHLI TELVHQRDVT RSLIKSKIDN AKSFEWLSQM RFYFDPKQTD VLQQLSIQMA NAKFNYGFEY LGVQDK LVQ TPLTDRCYLT MTQALEARLG GSPFGPAGTG KTESVKALGH QLGRFVLVFN CDETFDFQAM GRIFVGLCQV GAWGCFD EF NRLEERMLSA VSQQVQCIQE ALREHSNPNY DKTSAPITCE LLNKQVKVSP DMAIFITMNP GYAGRSNLPD NLKKLFRS L AMTKPDRQLI AQVMLYSQGF RTAEVLANKI VPFFKLCDEQ LSSQSHYDFG LRALKSVLVS AGNVKRERIQ KIKREKEER GEAVDEGEIA ENLPEQEILI QSVCETMVPK LVAEDIPLLF SLLSDVFPGV QYHRGEMTAL REELKKVCQE MYLTYGDGEE VGGMWVEKV LQLYQITQIN HGLMMVGPSG SGKSMAWRVL LKALERLEGV EGVAHIIDPK AISKDHLYGT LDPNTREWTD G LFTHVLRK IIDSVRGELQ KRQWIVFDGD VDPEWVENLN SVLDDNKLLT LPNGERLSLP PNVRIMFEVQ DLKYATLATV SR CGMVWFS EDVLSTDMIF NNFLARLRSI PLDEGEDEAQ RRRKGKEDEG EEAASPMLQI QRDAATIMQP YFTSNGLVTK ALE HAFQLE HIMDLTRLRC LGSLFSMLHQ ACRNVAQYNA NHPDFPMQIE QLERYIQRYL VYAILWSLSG DSRLKMRAEL GEYI RRITT VPLPTAPNIP IIDYEVSISG EWSPWQAKVP QIEVETHKVA APDVVVPTLD TVRHEALLYT WLAEHKPLVL CGPPG SGKT MTLFSALRAL PDMEVVGLNF SSATTPELLL KTFDHYCEYR RTPNGVVLAP VQLGKWLVLF CDEINLPDMD KYGTQR VIS FIRQMVEHGG FYRTSDQTWV KLERIQFVGA CNPPTDPGRK PLSHRFLRHV PVVYVDYPGP ASLTQIYGTF NRAMLRL IP SLRTYAEPLT AAMVEFYTMS QERFTQDTQP HYIYSPREMT RWVRGIFEAL RPLETLPVEG LIRIWAHEAL RLFQDRLV E DEERRWTDEN IDTVALKHFP NIDREKAMSR PILYSNWLSK DYIPVDQEEL RDYVKARLKV FYEEELDVPL VLFNEVLDH VLRIDRIFRQ PQGHLLLIGV SGAGKTTLSR FVAWMNGLSV YQIKVHRKYT GEDFDEDLRT VLRRSGCKNE KIAFIMDESN VLDSGFLER MNTLLANGEV PGLFEGDEYA TLMTQCKEGA QKEGLMLDSH EELYKWFTSQ VIRNLHVVFT MNPSSEGLKD R AATSPALF NRCVLNWFGD WSTEALYQVG KEFTSKMDLE KPNYIVPDYM PVVYDKLPQP PSHREAIVNS CVFVHQTLHQ AN ARLAKRG GRTMAITPRH YLDFINHYAN LFHEKRSELE EQQMHLNVGL RKIKETVDQV EELRRDLRIK SQELEVKNAA AND KLKKMV KDQQEAEKKK VMSQEIQEQL HKQQEVIADK QMSVKEDLDK VEPAVIEAQN AVKSIKKQHL VEVRSMANPP AAVK LALES ICLLLGESTT DWKQIRSIIM RENFIPTIVN FSAEEISDAI REKMKKNYMS NPSYNYEIVN RASLACGPMV KWAIA QLNY ADMLKRVEPL RNELQKLEDD AKDNQQKANE VEQMIRDLEA SIARYKEEYA VLISEAQAIK ADLAAVEAKV NRSTAL LKS LSAERERWEK TSETFKNQMS TIAGDCLLSA AFIAYAGYFD QQMRQNLFTT WSHHLQQANI QFRTDIARTE YLSNADE RL RWQASSLPAD DLCTENAIML KRFNRYPLII DPSGQATEFI MNEYKDRKIT RTSFLDDAFR KNLESALRFG NPLLVQDV E SYDPVLNPVL NREVRRTGGR VLITLGDQDI DLSPSFVIFL STRDPTVEFP PDLCSRVTFV NFTVTRSSLQ SQCLNEVLK AERPDVDEKR SDLLKLQGEF QLRLRQLEKS LLQALNEVKG RILDDDTIIT TLENLKREAA EVTRKVEETD IVMQEVETVS QQYLPLSTA CSSIYFTMES LKQIHFLYQY SLQFFLDIYH NVLYENPNLK GVTDHTQRLS IITKDLFQVA FNRVARGMLH Q DHITFAML LARIKLKGTV GEPTYDAEFQ HFLRGNEIVL SAGSTPRIQG LTVEQAEAVV RLSCLPAFKD LIAKVQADEQ FG IWLDSSS PEQTVPYLWS EETPATPIGQ AIHRLLLIQA FRPDRLLAMA HMFVSTNLGE SFMSIMEQPL DLTHIVGTEV KPN TPVLMC SVPGYDASGH VEDLAAEQNT QITSIAIGSA EGFNQADKAI NTAVKSGRWV MLKNVHLAPG WLMQLEKKLH SLQP HACFR LFLTMEINPK VPVNLLRAGR IFVFEPPPGV KANMLRTFSS IPVSRICKSP NERARLYFLL AWFHAIIQER LRYAP LGWS KKYEFGESDL RSACDTVDTW LDDTAKGRQN ISPDKIPWSA LKTLMAQSIY GGRVDNEFDQ RLLNTFLERL FTTRSF DSE FKLACKVDGH KDIQMPDGIR REEFVQWVEL LPDTQTPSWL GLPNNAERVL LTTQGVDMIS KMLKMQMLED EDDLAYA ET EKKTRTDSTS DGRPAWMRTL HTTASNWLHL IPQTLSHLKR TVENIKDPLF RFFEREVKMG AKLLQDVRQD LADVVQVC E GKKKQTNYLR TLINELVKGI LPRSWSHYTV PAGMTVIQWV SDFSERIKQL QNISLAAASG GAKELKNIHV CLGGLFVPE AYITATRQYV AQANSWSLEE LCLEVNVTTS QGATLDACSF GVTGLKLQGA TCNNNKLSLS NAISTALPLT QLRWVKQTNT EKKASVVTL PVYLNFTRAD LIFTVDFEIA TKEDPRSFYE RGVAVLCTE UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.722918 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSVLSQRQRD ELNRAIADYL RSNGYEEAYS VFKKEAELDV NEELDKKYAG LLEKKWTSVI RLQKKVMELE SKLNEAKEEF TSGGPLGQK RDPKEWIPRP PEKYALSGHR SPVTRVIFHP VFSVMVSASE DATIKVWDYE TGDFERTLKG HTDSVQDISF D HSGKLLAS ...String: GSVLSQRQRD ELNRAIADYL RSNGYEEAYS VFKKEAELDV NEELDKKYAG LLEKKWTSVI RLQKKVMELE SKLNEAKEEF TSGGPLGQK RDPKEWIPRP PEKYALSGHR SPVTRVIFHP VFSVMVSASE DATIKVWDYE TGDFERTLKG HTDSVQDISF D HSGKLLAS CSADMTIKLW DFQGFECIRT MHGHDHNVSS VAIMPNGDHI VSASRDKTIK MWEVQTGYCV KTFTGHREWV RM VRPNQDG TLIASCSNDQ TVRVWVVATK ECKAELREHE HVVECISWAP ESSYSSISEA TGSETKKSGK PGPFLLSGSR DKT IKMWDV STGMCLMTLV GHDNWVRGVL FHSGGKFILS CADDKTLRVW DYKNKRCMKT LNAHEHFVTS LDFHKTAPYV VTGS VDQTV KVWECR UniProtKB: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)