+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9837 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of RyR2 (F/A/C/H-Ca2+/Ca2+CaM dataset) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cryo-EM / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers ...: / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / CaM pathway / response to redox state / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / negative regulation of heart rate / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / 'de novo' protein folding / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / FK506 binding / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / smooth muscle contraction / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / T cell proliferation / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of cytokinesis / protein maturation / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / peptidylprolyl isomerase / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gong DS / Chi XM | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Modulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 by calmodulin. Authors: Deshun Gong / Ximin Chi / Jinhong Wei / Gewei Zhou / Gaoxingyu Huang / Lin Zhang / Ruiwu Wang / Jianlin Lei / S R Wayne Chen / Nieng Yan /    Abstract: The high-conductance intracellular calcium (Ca) channel RyR2 is essential for the coupling of excitation and contraction in cardiac muscle. Among various modulators, calmodulin (CaM) regulates RyR2 ...The high-conductance intracellular calcium (Ca) channel RyR2 is essential for the coupling of excitation and contraction in cardiac muscle. Among various modulators, calmodulin (CaM) regulates RyR2 in a Ca-dependent manner. Here we reveal the regulatory mechanism by which porcine RyR2 is modulated by human CaM through the structural determination of RyR2 under eight conditions. Apo-CaM and Ca-CaM bind to distinct but overlapping sites in an elongated cleft formed by the handle, helical and central domains. The shift in CaM-binding sites on RyR2 is controlled by Ca binding to CaM, rather than to RyR2. Ca-CaM induces rotations and intradomain shifts of individual central domains, resulting in pore closure of the PCB95 and Ca-activated channel. By contrast, the pore of the ATP, caffeine and Ca-activated channel remains open in the presence of Ca-CaM, which suggests that Ca-CaM is one of the many competing modulators of RyR2 gating. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9837.map.gz emd_9837.map.gz | 226.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9837-v30.xml emd-9837-v30.xml emd-9837.xml emd-9837.xml | 17.5 KB 17.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_9837_fsc.xml emd_9837_fsc.xml | 13.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_9837.png emd_9837.png | 209.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9837.cif.gz emd-9837.cif.gz | 9.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9837 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9837 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6jiyMC 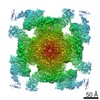 9831C 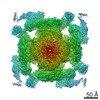 9833C  9834C 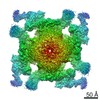 9836C  9879C  9880C  9889C  6ji0C  6ji8C  6jiiC  6jiuC  6jrrC  6jrsC  6jv2C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9837.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9837.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.091 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RyR2 in complex with FKBP12.6 and Ca2+-loaded Calmodulin at high ...
| Entire | Name: RyR2 in complex with FKBP12.6 and Ca2+-loaded Calmodulin at high Ca2+ concentrations |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RyR2 in complex with FKBP12.6 and Ca2+-loaded Calmodulin at high ...
| Supramolecule | Name: RyR2 in complex with FKBP12.6 and Ca2+-loaded Calmodulin at high Ca2+ concentrations type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: RyR2
| Macromolecule | Name: RyR2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 564.905625 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MADGGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ ...String: MADGGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ RSEGEKVRVG DDLILVSVSS ERYLHLSYGN VSLHVDAAFQ QTLWSVAPIS SGSEAAQGYL IGGDVLRLLH GH MDECLTV PSGEHGEEQR RTVHYEGGAV SVHARSLWRL ETLRVAWSGS HIRWGQPFRL RHVTTGKYLS LMEDKSLLLM DKE KADVKS TAFTFRSSKE KLDVGVRKEV DGMGTSEIKY GDSVCFIQHI GTGLWLTYQS VDVKSVRMGS IQRKAIMHHE GHMD DGLNL SRSQHEESRT ARVIRSTVFL FNRFIRGLDA LSKKAKASTV DLPIESVSLS LQDLIGYFHP PDEHLEHEDK QNRLR ALKN RQNLFQEEGM INLVLECIDR LHVYSSAAHF ADVAGREAGE SWKSILNSLY ELLAALIRGN RKNCAQFSGS LDWLIS RLE RLEASSGILE VLHCVLVESP EALNIIKEGH IKSIISLLDK HGRNHKVLDV LCSLCVCHGV AVRSNQHLIC DNLLPGR DL LLQTRLVNHV SSMRPNIFLG VSEGSAQYKK WYYELMVDHT EPFVTAEATH LRVGWASTEG YSPYPGGGEE WGGNGVGD D LFSYGFDGLH LWSGCIARTV SSPNQHLLRT DDVISCCLDL SAPSISFRIN GQPVQGMFEN FNIDGLFFPV VSFSAGIKV RFLLGGRHGE FKFLPPPGYA PCYEAVLPKE KLKVEHSREY KQERTYTRDL LGPTVSLTQA AFTPIPVDTS QIVLPPHLER IREKLAENI HELWVMNKIE LGWQYGPVRD DNKRQHPCLV EFSKLPEQER NYNLQMSLET LKTLLALGCH VGISDEHAEE K VKKMKLPK NYQLTSGYKP APMDLSFIKL TPSQEAMVDK LAENAHNVWA RDRIRQGWTY GIQQDVKNRR NPRLVPYALL DD RTKKSNK DSLREAVRTL LGYGYNLEAP DQDHAARAEV CSGTGERFRI FRAEKTYAVK AGRWYFEFEA VTAGDMRVGW SRP GCQPDQ ELGSDERAFA FDGFKAQRWH QGNEHYGRSW QAGDVVGCMV DMTEHTMMFT LNGEILLDDS GSELAFKDFD VGDG FIPVC SLGVAQVGRM NFGKDVSTLK YFTICGLQEG YEPFAVNTNR DITMWLSKRL PQFLQVPSSH EHIEVTRIDG TIDSS PCLK VTQKSFGSQN SSTDIMFYRL SMPIECAEVF SKTSAGGIPG ASLFGPKNDL EDYDADSDFE VLMKTAHGHL VPDRVD KDK EATKPEFNNH KDYAQEKPSR LKQRFLLRRT KPDYSTSHSA RLTEDVLADD RDDYDYLMQT STYYYSVRIF PGQEPAN VW VGWITSDFHQ YDTAFDLDRV RTVTVTLGDE KGKVHESIKR SNCYMVCAGE SMSPGQGRNN NGLEIGCVVD AASGLLTF T ANGKDLSTYY QVEPSTKLFP AVFAQATSPN VFQFELGRIK NVMPLSAGLF KSEHKNPVPQ CPPRLHVQFL SHVLWSRMP NQFLKVDVSR ISERQGWLVQ CLEPLQFMSL HIPEENRSVD ILELTEQEEL LKFHYHTLRL YSAVCALGNH RVAHALCSHV DEPQLLYAI ENKYMPGLLR AGYYDLLIDI HLSSYATARL MMNNEFIVPM TEETKSITLF PDENKKHGLP GIGLSTSLRP R MQFSSPSF VSINNECYQY SPEFPLDILK AKTIQMLTEA VQEGSLHARD PVGGTTEFLF VPLIKLFYTL LIMGIFHNED LK HILQLIE PSVFKEAAGP EEESDTLEKE PCASEDSRLE GPAEEESKGG KRPKEGLLQM KLPEPVKLQM CLLLQYLCDC QVR HRIEAI VAFSDDFVAK LQDNQRFRYN EVMQALNMSA ALTARKTKEF RSPPQEQINM LLNFKDDKSE CPCPEEIRDQ LLDF HEDLM THCGIELDED GSLDGNSDLT IRGRLLSLVE KVTYLKKKQA EKLVESDSKK SSTLQQLISE TMVRWAQESV IEDPE LVRA MFVLLHRQYD GIGGLVRALP KTYTINGVSV EDTINLLASL GQIRSLLSVR MGKEEEKLMI RGLGDIMNNK VFYQHP NLM RALGMHETVM EVMVNVLGGG ESKEITFPKM VANCCRFLCY FCRISRQNQK AMFDHLSYLL ENSSVGLASP AMRGSTP LD VAAASVMDNN ELALALREPD LEKVVRYLAG CGLQSCQMLV SKGYPDIGWN PVEGERYLDF LRFAVFCNGE SVEENANV V VRLLIRRPEC FGPALRGEGG NGLLAAMEEA IKIAEDPSRD GPSPTSGSSK MPDTEGEEDD TIHMGNAIMT FYAALIDLL GRCAPEMHLI HAAKGEAIRI RSILRSLIPL GDLVGVISIA FQMPTIAKDG NVVEPDMSAG FCPDHKAAMV LFLDRVYGIE VQDFLLHLL EVGFLPDLRA AASLDTAALS ATDMALALNR YLCTAVLPLL TRCAPLFAGT EHHASLIDSL LHTVYRLSKG C SLTKAQRD SIEVCLLSIC GQLRPSMMQH LLRRLVFDVP LLNEHAKMPL KLLTNHYERC WKYYCLPGGW GNFGAASEEE LH LSRKLFW GIFDALSQKK YEQELFKLAL PCLSAVAGAL PPDYMESNYV SMMEKQSSMD SEGNFNPQPV DTSNITIPEK LEY FINKYA EHSHDKWSMD KLANGWIYGE IYSDSSKVQP LMKPYKLLSE KEKEIYRWPI KESLKTMLAW GWRIERTREG DSMA LYNRT RRISQTSQVS VDAAHGYSPR AIDMSNVTLS RDLHAMAEMM AENYHNIWAK KKKLELESKG GGNHPLLVPY DTLTA KEKA KDREKAQDIL KFLQINGYAV SRGFKDLELD TPSIEKRFAY SFLQQLIRYV DEAHQYILEF DGGSRSKGEH FPYEQE IKF FAKVVLPLID QYFKNHRLYF LSAASRPLCS GGHASNKEKE MVTSLFCKLG VLVRHRISLF GNDATSIVNC LHILGQT LD ARTVMKTGLE SVKSALRAFL DNAAEDLEKT MENLKQGQFT HTRNQPKGVT QIINYTTVAL LPMLSSLFEH IGQHQFGE D LILEDVQVSC YRILTSLYAL GTSKSIYVER QRSALGECLA AFAGAFPVAF LETHLDKHNI YSIYNTKSSR ERAALNLPT NVEDVCPNIP SLEKLMEEIV DLAESGIRYT QMPHVMEVVL PMLCSYMSRW WEHGPENNPG RAEMCCTALN SEHMNTLLGN ILKIIYNNL GIDEGAWMKR LAVFSQPIIN KVKPQLLKTH FLPLMEKLKK KAAMVVSEED HLKSEVRGDM SEAELLILDE F TTLARDLY AFYPLLIRFV DYNRAKWLKE PNPEAEDLFR MVAEVFIYWS KSHNFKREEQ NFVVQNEINN MSFLITDTKS KM SKAAVSD QERKKMKRKG DRYSMQTSLI VAALKRLLPI GLNICAPGDQ ELIALAKNRF SLKDTEDEVR DIIRSNIHLQ GKL EDPAIR WQMALYKDLP NRTEDTSDPE KTVERVLDIA NVLFHLEQKS TCMRRRYYSL VEHPQRSKKA VWHKLLSKQR KRAV VACFR MAPLYNLPRH RAVNLFLQGY EKSWIETEEH YFEDKLIEDL AKPGAVPPEE DEGTKRVDPL HQLILLFSRT ALTEK CKLE EDFLYMAYAD IMAKSCHDEE DDDGEEEVKS FEEKEMEKQK LLYQQARLHD RGAAEMVLQT ISASKGETGP MVAATL KLG IAILNGGNST VQQKMLEYLK EKKDVGFFQS LAGLMQSCSV LDLNAFERQN KAEGLGMVTE EGSGEKVLQD DEFTCDL FR FLQLLCEGHN SDFQNYLRTQ TGNNTTVNII ISTVDYLLRV QESISDFYWY YSGKDVIDEQ GQRNFSKAIQ VAKQVFNT L TEYIQGPCTG NQQSLAHSRL WDAVVGFLHV FAHMQMKLSQ DSSQIELLKE LMDLQKDMVV MLLSMLEGNV VNGTIGKQM VDMLVESSNN VEMILKFFDM FLKLKDLTSS DTFKEYDPDG KGVISKRDFH KAMESHKHYT QSETEFLLSC AETDENETLD YEEFVKRFH EPAKDIGFNV AVLLTNLSEH MPNDTRLQTF LELAESVLNY FQPFLGRIEI MGSAKRIERV YFEISESSRT Q WEKPQVKE SKRQFIFDVV NEGGEKEKME LFVNFCEDTI FEMQLAAQIS ESDLNERSAN KEESEKEKPE EQGPRMGFFS LV TVRSALL ALRYNVLTLM RMLSLKSLKK QMKKVKKMTV RDMVTAFFTS YWSVFMTLLH FAASVSRGFS RIIGGLLLGG SLV EGAKKI KVAELLANMP DPTQDEVRGD GDEGERKVLE GTLPSEDLTD LKELTEESDL LSDIFGLDLK REGGQYKLIP HNPN AGLSD LMSSPAPIPE VQEKFQEQKA KEEEKEEKEE NKSEPEKAEG EDGEKEEKAK EDKGKQKLRQ LHTHRYGEPE VPESA FWKK IIAYQQKLLN YFARNFYNMR MLALFVAFAI NFILLFYKVS TSSVVEGKEL PTRSSSENAN FGSLDSSSPR IIAVHY VLE ESSGYMEPTL RILAILHTVI SFFCIIGYYC LKVPLVIFKR EKEVARKLEF DGLYITEQPS EDDIKGQWDR LVINTQS FP NNYWDKFVKR KVMDKYGEFY GRDRISELLG MDKAALDFSD AREKKKPKKD SSLSAVLNSI DVKYQMWKLG VVFTDNSF L YLAWYMTMSV LGHYNNFFFA AHLLDIAMGF KTLRTILSSV THNGKQLVLT VGLLAVVVYL YTVVAFNFFR KFYNKSEDG DTPDMKCDDM LTCYMFHMYV GVRAGGGIGD EIEDPAGDEY EIYRIIFDIT FFFFVIVILL AIIQGLIIDA FGELRDQQEQ VKEDMETKC FICGIGNDYF DTVPHGFETH TLQEHNLANY LFFLMYLINK DETEHTGQES YVWKMYQERC WEFFPAGDCF R KQYEDQLN |
-Macromolecule #2: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.798501 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGVEIETISP GDGRTFPKKG QTCVVHYTGM LQNGKKFDSS RDRNKPFKFR IGKQEVIKGF EEGAAQMSLG QRAKLTCTPD VAYGATGHP GVIPPNATLI FDVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 20 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #7: CAFFEINE
| Macromolecule | Name: CAFFEINE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CFF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 194.191 Da |
| Chemical component information | 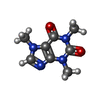 ChemComp-CFF: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















