[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8772: Core Factor local refinement from Pol I Initial Transcribing Comp... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8772 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
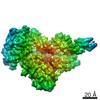
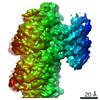
| Title | Core Factor local refinement from Pol I Initial Transcribing Complex at 4.2 angstrom | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Core Factor local refinement from Pol I Initial Transcribing Complex | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase I transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I core factor complex / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / RNA polymerase I core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / TBP-class protein binding / nucleolus ...RNA polymerase I transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I core factor complex / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / RNA polymerase I core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / TBP-class protein binding / nucleolus / zinc ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Han Y / He Y | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Structural mechanism of ATP-independent transcription initiation by RNA polymerase I. Authors: Yan Han / Chunli Yan / Thi Hoang Duong Nguyen / Ashleigh J Jackobel / Ivaylo Ivanov / Bruce A Knutson / Yuan He /  Abstract: Transcription initiation by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) depends on the Core Factor (CF) complex to recognize the upstream promoter and assemble into a Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC). Here, we solve a ...Transcription initiation by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) depends on the Core Factor (CF) complex to recognize the upstream promoter and assemble into a Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC). Here, we solve a structure of Pol I-CF-DNA to 3.8 Å resolution using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The structure reveals a bipartite architecture of Core Factor and its recognition of the promoter from -27 to -16. Core Factor's intrinsic mobility correlates well with different conformational states of the Pol I cleft, in addition to the stabilization of either Rrn7 N-terminal domain near Pol I wall or the tandem winged helix domain of A49 at a partially overlapping location. Comparison of the three states in this study with the Pol II system suggests that a ratchet motion of the Core Factor-DNA sub-complex at upstream facilitates promoter melting in an ATP-independent manner, distinct from a DNA translocase actively threading the downstream DNA in the Pol II PIC. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8772.map.gz emd_8772.map.gz | 1.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8772-v30.xml emd-8772-v30.xml emd-8772.xml emd-8772.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8772_fsc.xml emd_8772_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8772.png emd_8772.png | 214.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8772 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8772 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8772 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8772 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8771C  8773C  8774C  8775C  8776C 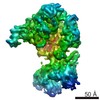 8777C  5w5yC  5w64C  5w65C  5w66C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8772.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8772.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Core Factor local refinement from Pol I Initial Transcribing Complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
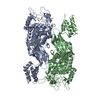
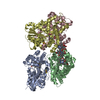
-Entire : Yeast Core Factor
| Entire | Name: Yeast Core Factor |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Yeast Core Factor
| Supramolecule | Name: Yeast Core Factor / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 250 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Rrn7
| Macromolecule | Name: Rrn7 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSTFIRGPIC GTDNCPSRLW RIIDGRRTCQ YGHVMEGDVE FNDDEDDLNG LGAGVITRRL NLTTNATGS FQSSQLTNSQ LLQQQQRQSH KKFKKLIGHE AKLLFLKSFQ FILKRQIRWL I TEMRFPKE FEHVAKIIWL KILKTINDQP QEELKLQLHM TSTISILYLA ...String: MSTFIRGPIC GTDNCPSRLW RIIDGRRTCQ YGHVMEGDVE FNDDEDDLNG LGAGVITRRL NLTTNATGS FQSSQLTNSQ LLQQQQRQSH KKFKKLIGHE AKLLFLKSFQ FILKRQIRWL I TEMRFPKE FEHVAKIIWL KILKTINDQP QEELKLQLHM TSTISILYLA STHLSLPVYT CD YIKWICT AKMPYFQASE ILPKSWRIQL PNYYVSILEG SISPFNGQLY NKIALTCGMI HFK EFFNSE ISCQGLLLKL VMQCALPPEF YFYTKQVIEF EETDIRNLTL WERTDERHTG RVSN HAELR VLSYFMLTIN WMLSFDRDRQ YPLKWILSLT ESLTQRTTTS ESIGRNIVKV VYPDK PTSS DYFQWSEEET LEFLKWMEKQ FLPTQTKSLH NENGSMEMTI DQKIARRKLY KIFPLD REA NHDGEFNDST HQLTFIEDLQ ERYAKQTPFF ESNKIRDSLN YQEANPPARK EAIGRLL TH IASQLLVDFA ISKEQLKDCI SRIKNACLHR MN |
-Macromolecule #2: Rrn11
| Macromolecule | Name: Rrn11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFEVPITLTN RKFAQRRKLK YQYINYISRR FDRISKKSTT TDSLPTPENS AAENNDEEEG QNSEAGTYR RSVLQQKKRR RERHWRSVVG EIYSTTESET DSQEEETEEG GEHDTGIDKE D SDEERKFW KKYEKPEKSF EIWRTVSSQN KQPINKQKMT YHNFKKIEKI ...String: MFEVPITLTN RKFAQRRKLK YQYINYISRR FDRISKKSTT TDSLPTPENS AAENNDEEEG QNSEAGTYR RSVLQQKKRR RERHWRSVVG EIYSTTESET DSQEEETEEG GEHDTGIDKE D SDEERKFW KKYEKPEKSF EIWRTVSSQN KQPINKQKMT YHNFKKIEKI PLRKMEIPLL HC TKENKLY FQSISRGLEP LKTSTSEVRN YRTRHIVTLT DLLHLNVSRH NWSLAYKIFA TLI RIPGVQ IKSLWGIGVE ILDNLSNSSS GLDFLQWMCQ IYSSKSRFVQ NINYRSIVPP FQTG SRTHT AKFAITYLWS SLINCQKSME PSSNIIDKPF DTENDLLQEL IDKISEWVLT PPFME DAEV WFIYASCHLL KADTLSRQFV NDNKNNDLIG LDRDIKINQV IKHIHYVRTF LKICLD KGG FAVPSRLIEN QLKSFESRLY GEAQDIQERD VANVYDSIDN SSVENSFGDV YETNAEF LD TQLMDLSPED NGLDEMHYSD EDSSE |
-Macromolecule #3: Rrn6
| Macromolecule | Name: Rrn6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSEGQIPSSD VLGSQLGVGV QGASLYCPQE NYTTKKQEKP QWLRPVDDTL AEDALDLHIV VKSLLCDTA IRYISDDKVL QESDADDDLI TSDIDEDTDN QGDTSIVVNP VIPVVPKDVH F FKKVDVGN DSMFGVNCDT PVSFQDYIPS DLLRNLDDTL QESTNSSRPM ...String: MSEGQIPSSD VLGSQLGVGV QGASLYCPQE NYTTKKQEKP QWLRPVDDTL AEDALDLHIV VKSLLCDTA IRYISDDKVL QESDADDDLI TSDIDEDTDN QGDTSIVVNP VIPVVPKDVH F FKKVDVGN DSMFGVNCDT PVSFQDYIPS DLLRNLDDTL QESTNSSRPM QDAFFWDPTV AN RLDSQYI QTASDLRNYR DGTEIIAYAS GKTGSVLNIA VLTRQNTLHL NRHNNVTSIE LHS PIKSIK IPGASESIGR RSNLVGIITE NSFQIFRIES VHSRSCDVMV SSSEPLYFVE IDDL QVVDF AFNPWDLQQF AIIDIKGNWS IGRIPKNFNN NNKRKLQLID NLHGTIFDPE ELSSW KRIE WFSHFQKILV FDRSKMIEID FMNNWQTEVV QAKAWSNIRD YKRIDDKNGI LLTSRE III VGASESNDPV RRISWKHDLD PDDTTLRITV QKVKKPDHIL LVAFVYSMRH KRIYMHV FS HRKANLFQSL GCSTVLEIPG GTPTGIETIL TLDHIDDESR REEDADENFE LVVDFLVK L RNSSEVYYYA LSNTQNSEPN KQETPIIVDH PEWASLFNNA DEREKESIGA LVSQIKLKE RERISRVQNL IEHENSHDED KYLQDLGYRL SIATNELLES WQKTKDESIL SGSLSHSKLK NLLENSDSF ASIPEFSSLL DQFFQYYQDQ DVTFIGFEKL LHLFLHEDVP GLDIFYNKLL Q CWVLVSPQ AELLTKEIVK DIIWSLARLE KPSLFEPIQN EISRSLSGPY QDIISSWDMD DI NEEDESN EFNFDSQFSA PFNGRPPFNL NSQSQIPTIK SSQSSGLARR KRILKTQSQK ATP LSQSTQ NLSVLPDSMT PAFTLMQPPS SQISFVNDSQ PRNSQKAKKK KKRIRGFG |
-Macromolecule #4: non-template strand DNA
| Macromolecule | Name: non-template strand DNA / type: dna / ID: 4 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: CAAGTGTGAG GAAAAGTAGT TGGGTTTTTT TTTTTTTTTT TGCAGTTGAA GACA |
-Macromolecule #5: template DNA
| Macromolecule | Name: template DNA / type: dna / ID: 5 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: TGTCTTCAAC TGCTTTCGCA TGAAGTACCT CCCAACTACT TTTCCTCACA CTTG |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil S7/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average exposure time: 12.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 56.8 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 4.5 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.5 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)