[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
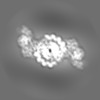
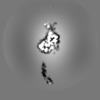
Yorodumi- EMDB-8164: Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at ne... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8164 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
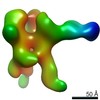
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution (tropomyosin filtered to 7 Angstrom) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | None | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CONTRACTILE FILAMENT / MUSCLE / THIN FILAMENT / CYTOSKELETON / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / HYDROLASE COMPLEX / F-actin / tropomyosin / filament / myosin / protein polymers / cryo EM / Contractile protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / : / : / contractile vacuole / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Platelet degranulation / basal body patch / myosin II filament / sorocarp development / Neutrophil degranulation ...RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / : / : / contractile vacuole / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Platelet degranulation / basal body patch / myosin II filament / sorocarp development / Neutrophil degranulation / tight junction assembly / macropinocytic cup / actin crosslink formation / profilin binding / actin filament-based movement / vocalization behavior / protein localization to bicellular tight junction / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / actomyosin / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / Gap junction degradation / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / myosin filament / dense body / regulation of stress fiber assembly / RHO GTPases Activate ROCKs / RHO GTPases activate CIT / actomyosin structure organization / Sema4D induced cell migration and growth-cone collapse / Adherens junctions interactions / myosin II complex / hyperosmotic response / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / sarcomere organization / regulation of focal adhesion assembly / EPHA-mediated growth cone collapse / apical junction complex / positive regulation of wound healing / microfilament motor activity / cortical actin cytoskeleton / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / filamentous actin / myofibril / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / pseudopodium / cell leading edge / Recycling pathway of L1 / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / brush border / mitotic cytokinesis / actin filament bundle assembly / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / skeletal muscle contraction / phagocytosis / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / neuronal action potential / skeletal muscle tissue development / RHO GTPases activate PKNs / stress fiber / phagocytic vesicle / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / extracellular matrix / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / cellular response to starvation / cell projection / actin filament / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / mitochondrion organization / cell motility / sensory perception of sound / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / cellular response to type II interferon / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / platelet aggregation / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / cell-cell junction / actin filament binding / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / regulation of cell shape / actin cytoskeleton / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | von der Ecken J / Heissler SM / Pathan-Chhatbar S / Manstein DJ / Raunser S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution. Abstract: The interaction of myosin with actin filaments is the central feature of muscle contraction and cargo movement along actin filaments of the cytoskeleton. The energy for these movements is generated ...The interaction of myosin with actin filaments is the central feature of muscle contraction and cargo movement along actin filaments of the cytoskeleton. The energy for these movements is generated during a complex mechanochemical reaction cycle. Crystal structures of myosin in different states have provided important structural insights into the myosin motor cycle when myosin is detached from F-actin. The difficulty of obtaining diffracting crystals, however, has prevented structure determination by crystallography of actomyosin complexes. Thus, although structural models exist of F-actin in complex with various myosins, a high-resolution structure of the F-actin–myosin complex is missing. Here, using electron cryomicroscopy, we present the structure of a human rigor actomyosin complex at an average resolution of 3.9 Å. The structure reveals details of the actomyosin interface, which is mainly stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. The negatively charged amino (N) terminus of actin interacts with a conserved basic motif in loop 2 of myosin, promoting cleft closure in myosin. Surprisingly, the overall structure of myosin is similar to rigor-like myosin structures in the absence of F-actin, indicating that F-actin binding induces only minimal conformational changes in myosin. A comparison with pre-powerstroke and intermediate (Pi-release) states of myosin allows us to discuss the general mechanism of myosin binding to F-actin. Our results serve as a strong foundation for the molecular understanding of cytoskeletal diseases, such as autosomal dominant hearing loss and diseases affecting skeletal and cardiac muscles, in particular nemaline myopathy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8164.map.gz emd_8164.map.gz | 48.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8164-v30.xml emd-8164-v30.xml emd-8164.xml emd-8164.xml | 24.2 KB 24.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8164.png emd_8164.png | 156.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8164.cif.gz emd-8164.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8164 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8164 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8164 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8164 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
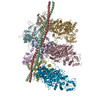
| Related structure data | 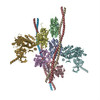 5jlhMC 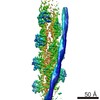 8162C  8163C 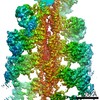 8165C  5jlfC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8164.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8164.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : F-actin-myosin-tropomyosin complex
| Entire | Name: F-actin-myosin-tropomyosin complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: F-actin-myosin-tropomyosin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: F-actin-myosin-tropomyosin complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 / Details: Filament |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 440 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: actin, myosin
| Supramolecule | Name: actin, myosin / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: tropomyosin
| Supramolecule | Name: tropomyosin / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, cytoplasmic 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.70757 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EEEIAALVID NGSGMCKAGF AGDDAPRAVF PSIVGRPRHQ GVMVGMGQKD SYVGDEAQSK RGILTLKYPI EHGIVTNWDD MEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT H TVPIYEGY ...String: EEEIAALVID NGSGMCKAGF AGDDAPRAVF PSIVGRPRHQ GVMVGMGQKD SYVGDEAQSK RGILTLKYPI EHGIVTNWDD MEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT H TVPIYEGY ALPHAILRLD LAGRDLTDYL MKILTERGYS FTTTAEREIV RDIKEKLCYV ALDFEQEMAT AASSSSLEKS YE LPDGQVI TIGNERFRCP EALFQPSFLG MESCGIHETT FNSIMKCDVD IRKDLYANTV LSGGTTMYPG IADRMQKEIT ALA PSTMKI KIIAPPERKY SVWIGGSILA SLSTFQQMWI SKQEYDESGP SIVHRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Myosin-14,Alpha-actinin A
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin-14,Alpha-actinin A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: NON MUSCLE MYOSIN 2C HEAVY CHAIN, MOTOR DOMAIN RESIDUES 1-799 LINKED TO ALPHA-ACTININ 3, REPEATS 1 AND 2 RESIDUES 800-1039 FRAGMENT: UNP Q7Z406-1 RESIDUES 1-799, UNP P05095 RESIDUES 265-502 Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 117.570633 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAAVTMSVPG RKAPPRPGPV PEAAQPFLFT PRGPSAGGGP GSGTSPQVEW TARRLVWVPS ELHGFEAAAL RDEGEEEAEV ELAESGRRL RLPRDQIQRM NPPKFSKAED MAELTCLNEA SVLHNLRERY YSGLIYTYSG LFCVVINPYK QLPIYTEAIV E MYRGKKRH ...String: MAAVTMSVPG RKAPPRPGPV PEAAQPFLFT PRGPSAGGGP GSGTSPQVEW TARRLVWVPS ELHGFEAAAL RDEGEEEAEV ELAESGRRL RLPRDQIQRM NPPKFSKAED MAELTCLNEA SVLHNLRERY YSGLIYTYSG LFCVVINPYK QLPIYTEAIV E MYRGKKRH EVPPHVYAVT EGAYRSMLQD REDQSILCTG ESGAGKTENT KKVIQYLAHV ASSPKGRKEP GVPGELERQL LQ ANPILEA FGNAKTVKND NSSRFGKFIR INFDVAGYIV GANIETYLLE KSRAIRQAKD ECSFHIFYQL LGGAGEQLKA DLL LEPCSH YRFLTNGPSS SPGQERELFQ ETLESLRVLG FSHEEIISML RMVSAVLQFG NIALKRERNT DQATMPDNTA AQKL CRLLG LGVTDFSRAL LTPRIKVGRD YVQKAQTKEQ ADFALEALAK ATYERLFRWL VLRLNRALDR SPRQGASFLG ILDIA GFEI FQLNSFEQLC INYTNEKLQQ LFNHTMFVLE QEEYQREGIP WTFLDFGLDL QPCIDLIERP ANPPGLLALL DEECWF PKA TDKSFVEKVA QEQGGHPKFQ RPRHLRDQAD FSVLHYAGKV DYKANEWLMK NMDPLNDNVA ALLHQSTDRL TAEIWKD VE GIVGLEQVSS LGDGPPGGRP RRGMFRTVGQ LYKESLSRLM ATLSNTNPSF VRCIVPNHEK RAGKLEPRLV LDQLRCNG V LEGIRICRQG FPNRILFQEF RQRYEILTPN AIPKGFMDGK QACEKMIQAL ELDPNLYRVG QSKIFFRAGV LAQLEEERA SEQTKSDYLK RANELVQWIN DKQASLESRD FGDSIESVQS FMNAHKEYKK TEKPPKGQEV SELEAIYNSL QTKLRLIKRE PFVAPAGLT PNEIDSTWSA LEKAEQEHAE ALRIELKRQK KIAVLLQKYN RILKKLENWA TTKSVYLGSN ETGDSITAVQ A KLKNLEAF DGECQSLEGQ SNSDLLSILA QLTELNYNGV PELTERKDTF FAQQWTGVKS SAETYKNTLL AELERLQKIE D UniProtKB: Myosin-14, Alpha-actinin A |
-Macromolecule #3: Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: Human TROPOMYSIN WAS USED (UNP P06753-2,TPM3_HUMAN, RESIDUES 62-196). DUE TO THE LIMITED RESOLUTION OF THE CRYO-EM DENSITY IN THE REGION OF TROPOMYOSIN, TROPOMYOSIN HAS BEEN REPRESENTED AS POLY(UNK). Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.507176 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 5 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM KCl, and 2 mM MgCl2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar embedding | Material: I | ||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | ||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 Details: Sample (2 uL of F-actin-tropomyosin solution) was applied to a glow-discharged holey carbon grid, incubated for 20 s and manually blotted from the backside for less than a second with filter ...Details: Sample (2 uL of F-actin-tropomyosin solution) was applied to a glow-discharged holey carbon grid, incubated for 20 s and manually blotted from the backside for less than a second with filter paper. Afterwards 1.5 uL of myosin solution (3 uM without nucleotide) were added directly on the grid, incubated for 10 s and then manually blotted for 5 s from the backside with filter paper.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Details | Cs corrected microscope |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 2-8 / Number real images: 6300 / Average exposure time: 0.475 sec. / Average electron dose: 16.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm / Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE / Overall B value: 180 | ||||||||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-5jlh: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | tropomyosin fitting | ||||||
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | ||||||
| Output model |  PDB-5jlh: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






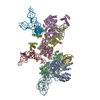























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)