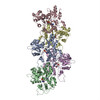
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j8a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
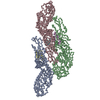
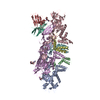
| Title | Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN/HYDROLASE / contractile filament / muscle / thin filament / cytoskeleton / structural protein-hydrolase complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / lamellipodium / cell body / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | von der Ecken, J. / Mueller, M. / Lehman, W. / Manstein, J.M. / Penczek, A.P. / Raunser, S. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex. Authors: Julian von der Ecken / Mirco Müller / William Lehman / Dietmar J Manstein / Pawel A Penczek / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead ...Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead to early-onset autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss, familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, and multiple variations of myopathies. In striated muscle fibres, the binding of myosin motors to actin filaments is mainly regulated by tropomyosin and troponin. Tropomyosin also binds to F-actin in smooth muscle and in non-muscle cells and stabilizes and regulates the filaments there in the absence of troponin. Although crystal structures for monomeric actin (G-actin) are available, a high-resolution structure of F-actin is still missing, hampering our understanding of how disease-causing mutations affect the function of thin muscle filaments and microfilaments. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of F-actin at a resolution of 3.7 Å in complex with tropomyosin at a resolution of 6.5 Å, determined by electron cryomicroscopy. The structure reveals that the D-loop is ordered and acts as a central region for hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions that stabilize the F-actin filament. We clearly identify map density corresponding to ADP and Mg(2+) and explain the possible effect of prominent disease-causing mutants. A comparison of F-actin with G-actin reveals the conformational changes during filament formation and identifies the D-loop as their key mediator. We also confirm that negatively charged tropomyosin interacts with a positively charged groove on F-actin. Comparison of the position of tropomyosin in F-actin-tropomyosin with its position in our previously determined F-actin-tropomyosin-myosin structure reveals a myosin-induced transition of tropomyosin. Our results allow us to understand the role of individual mutations in the genesis of actin- and tropomyosin-related diseases and will serve as a strong foundation for the targeted development of drugs. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 700 | SHEET DETERMINATION METHOD: AUTHOR DETERMINED |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j8a.cif.gz 3j8a.cif.gz | 391.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j8a.ent.gz pdb3j8a.ent.gz | 315.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j8a.json.gz 3j8a.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j8/3j8a https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j8/3j8a ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j8/3j8a ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j8/3j8a | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6124MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 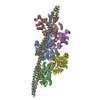
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 1 / Rise per n subunits: 27.5 Å / Rotation per n subunits: -166.4 °) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Component-ID: 1 / Ens-ID: 1 / Beg auth comp-ID: THR / Beg label comp-ID: THR / End auth comp-ID: HIS / End label comp-ID: HIS / Auth seq-ID: 5 - 371 / Label seq-ID: 5 - 371
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | The full filament can be generated using the provided helical parameters from a small repeating subunit comprising chain A and residues 145-184 of chains F and G. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 11507.176 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: SEE REMARK 999 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)    Keywords: SEE REMARK 999 Keywords: SEE REMARK 999#2: Protein | Mass: 41875.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / Has protein modification | Y | Sequence details | MOUSE TROPOMYSIN WAS USED (UNP P58771, RESIDUES 97-231). DUE TO THE LIMITED RESOLUTION OF THE CRYO- ...MOUSE TROPOMYSIN | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2 pH: 7.5 Details: 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: C-flats 2/1 copper 300 mesh, Protochips, glow-discharged | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Temp: 106 K / Humidity: 90 % Details: Sample was applied to grid, incubated for 10 seconds, and manually blotted for 3 seconds from the backside with filter paper before plunging into liquid ethane (GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3) Method: Sample was applied to grid, incubated for 10 seconds, and manually blotted for 3 seconds from the backside with filter paper. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Date: Oct 17, 2013 / Details: Cs-corrected microscope |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 0 mm / Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 14.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 1311 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: each micrograph | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 166.4 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.5 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 / Details: none | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: helicon, cter / Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Nominal pixel size: 1.14 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.12 Å Details: The tropomyosin map filtered to 6.5 Angstrom was merged with the final F-actin map (3.7 Angstrom) to obtain a map of the entire F-actin tropomyosin complex. Coordinates must be shifted by (0. ...Details: The tropomyosin map filtered to 6.5 Angstrom was merged with the final F-actin map (3.7 Angstrom) to obtain a map of the entire F-actin tropomyosin complex. Coordinates must be shifted by (0.123 -0.381 0.273) to match coordinates to fibre diffraction standards (filament axis = z axis passing through x=0 and y=0). Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Accession code: 4A7N / Initial refinement model-ID: 1 / PDB-ID: 4A7N / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 3.7→95.2 Å / SU ML: 0.2 / σ(F): 100 / Phase error: 26.02 / Stereochemistry target values: MLHL
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 129.39 Å2 / Biso mean: 50.7811 Å2 / Biso min: 0 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.7→95.2 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 3.7→95.2 Å / Total num. of bins used: 1
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj