[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
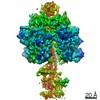
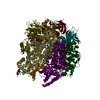
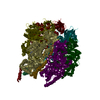
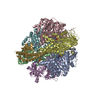
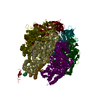
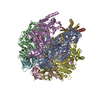
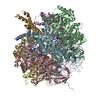
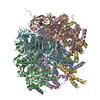
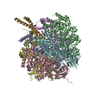
Yorodumi- PDB-7md3: The F1 region of apoptolidin-bound Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATP s... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7md3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The F1 region of apoptolidin-bound Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATP synthase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase subunit ...) x 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE/HYDROLASE INHIBITOR / F1-ATPase / inhibitor / anti-cancer / HYDROLASE / TRANSLOCASE / HYDROLASE-HYDROLASE INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / : / : / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism ...: / : / : / : / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guo, H. / Rubinstein, J.L. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, Canada,  United States, 8items United States, 8items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022Title: Apoptolidin family glycomacrolides target leukemia through inhibition of ATP synthase. Authors: Benjamin J Reisman / Hui Guo / Haley E Ramsey / Madison T Wright / Bradley I Reinfeld / P Brent Ferrell / Gary A Sulikowski / W Kimryn Rathmell / Michael R Savona / Lars Plate / John L ...Authors: Benjamin J Reisman / Hui Guo / Haley E Ramsey / Madison T Wright / Bradley I Reinfeld / P Brent Ferrell / Gary A Sulikowski / W Kimryn Rathmell / Michael R Savona / Lars Plate / John L Rubinstein / Brian O Bachmann /   Abstract: Cancer cells have long been recognized to exhibit unique bioenergetic requirements. The apoptolidin family of glycomacrolides are distinguished by their selective cytotoxicity towards oncogene- ...Cancer cells have long been recognized to exhibit unique bioenergetic requirements. The apoptolidin family of glycomacrolides are distinguished by their selective cytotoxicity towards oncogene-transformed cells, yet their molecular mechanism remains uncertain. We used photoaffinity analogs of the apoptolidins to identify the F subcomplex of mitochondrial ATP synthase as the target of apoptolidin A. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) of apoptolidin and ammocidin-ATP synthase complexes revealed a novel shared mode of inhibition that was confirmed by deep mutational scanning of the binding interface to reveal resistance mutations which were confirmed using CRISPR-Cas9. Ammocidin A was found to suppress leukemia progression in vivo at doses that were tolerated with minimal toxicity. The combination of cellular, structural, mutagenesis, and in vivo evidence defines the mechanism of action of apoptolidin family glycomacrolides and establishes a path to address oxidative phosphorylation-dependent cancers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7md3.cif.gz 7md3.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7md3.ent.gz pdb7md3.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7md3.json.gz 7md3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7md3_validation.pdf.gz 7md3_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7md3_full_validation.pdf.gz 7md3_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7md3_validation.xml.gz 7md3_validation.xml.gz | 88.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7md3_validation.cif.gz 7md3_validation.cif.gz | 137.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/md/7md3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/md/7md3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/md/7md3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/md/7md3 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 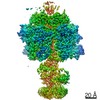 23764MC  7md2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 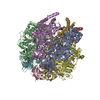
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 4 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55007.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 51181.082 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A6A5PX46, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 30657.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 6618.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 8 molecules 


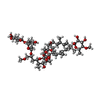



| #5: Chemical | | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ZH7 / ( | |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera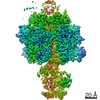
 PDBj
PDBj




